Contextual advertising strategy with sales funnel in SaaS case: template and instructions
There are times when you talk to the potential client, recommending him contextual advertising, but he says: “I have already tried contextual ad, but it doesn’t work”. PPC specialists will for sure have doubts about the reliability of such conclusions, because in the majority of similar cases it turns out that web analytics wasn’t set up correctly or not all contextual advertising tools have been implemented.

In short, each context is unique.
We have already talked about setting up web analytics, so now I want to move to get maximum from contextual advertising. Getting maximum is not missing a thing and being sure that you have done everything you could.

In 90% of cases there is no opportunity and necessity to try out all instruments due to a limited budget: in this case, specialists will do everything to make a Pareto principle work because according to it 20% of efforts lead to 80% of result. If we are lucky enough to be able to “do it all” on the project, then, based personal experience, I recommend you to use an approach I called “contextual advertising strategy with sales funnel”.
Although there is a word “SaaS” in the headline, this post can be applied for any type of websites. What’s the point? The current method allows to systematize and launch ad campaigns and to sort out all nuances there are in the heads of specialist and client.

What is strategy and why do you need it
Strategy — plan, composed for achieving the initial goal. It is necessary to understand that strategy does not guarantee achieving the goal, but it helps to respond to the question “how to achieve the desired goal in given circumstances” and move in right direction.
In general, contextual advertising strategy helps to:
- Plan the development of a project with the help of contextual advertising;
- Achieve the goals (increase sales, improve brand awareness, grow traffic to the site).
Advertising strategy with sales funnel: what is it and what are the benefits
The main idea of a strategy is to understand and foresee each step that user makes towards purchase and guide him from the first stage of the funnel (broad audience) till the last one (narrow audience).
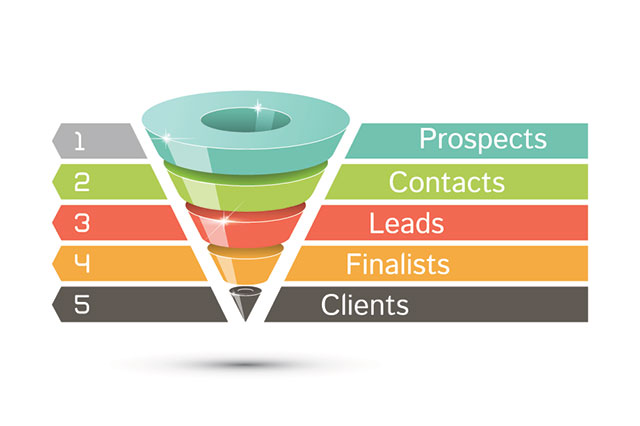
Classic funnel sample:
There are many users that can be interested in your proposal, but with each step down target audience gets smaller because people that don’t want to purchase your product “drop out”. At the last stage are your new and loyal clients that have made a purchase.
It’s hardly surprising that while moving up the funnel, a certain amount of customers drops out. To minimize this percentage, it is necessary to use different approaches to all audiences and take into account emerging necessities and interests.

Keep the aforementioned statement in mind as the principal one.
What do you have to understand before developing context strategy with sales funnel
First, you have to think through the client’s business. Most commonly, the client with “getting maximum from contextual advertising” query knows his funnel himself and can name all its stages. If not, you should delve deeper into the business together with client’s marketing specialist —it is not that hard. Client is interested in explaining the whole scheme of business’s work and even more—to make sure you understood everything because this is what contextual advertising strategy and therefore business development strategy will be grounding on.
What is necessary to underline in the contextual advertising strategy
When you have completely coped with the way your client’s business is constructed, you may switch to preparing the contextual advertising strategy with the funnel.
When you start working in a project, where it is necessary to do “everything, you:
- Construct a framework for the strategy with sales funnel
- Analyse sales funnel for your project.
- Fill in all tables of the pattern
- Start working with planned advertising campaigns and mark your results in the table.
Now, let’s review in details the main points this strategy consists of.
1. Vortex stage
Each stage is a separate block with the definition of each category of users, its needs and interests, as well as the main ad goals and tools for their achievement. If you can proceed user from the first step to the last one, then you have successfully dealt with your work.
2. Users category
Briefly describe the users category that refers to the chosen stage. This stap is required to understand which instruments and campaigns can be used for reaching the initial target.
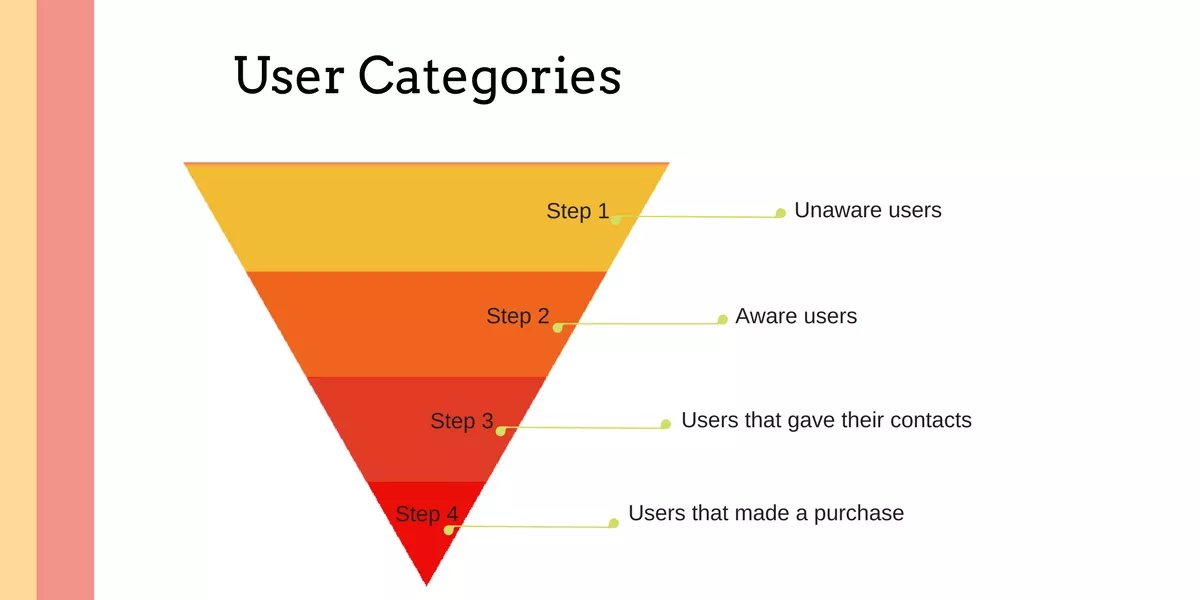
Target audience of any project can be divided into these categories:
Step 1. Uninformed users – have not visited the site, know nothing about the campaign and products, but they have the necessity in the services provided.
Step 2. Informed users – have already visited the site, are present in remarketing lists or in the client base, or they type the brand queries in search engines.
Step 3. Left their contacts – all users that have filled the application form on the site, where the email is required (registration, newsletter subscription (without registering), requesting the price for the product, requesting the demo version, downloading the product with trial version, contact form).
Step 4. Users that made a purchase.
3. Users description
Describe the users category in details, specify their interests and needs.
This will help to understand:
3.1. What you have to present and propose to users on this stage: if a person knows nothing about the company, but at the same time seeks for the product – you have to create more generalized ad texts.
3.2. What page you have to use as a target page. For example, it is better to guide potential clients at the final stage of the funnel to landing, where they can see available tariffs, comparison to competitors or information on the beneficial promo campaigns. If users are still unfamiliar with your campaign – guide them to the page with more detailed information about the products and conditions for the purchase.
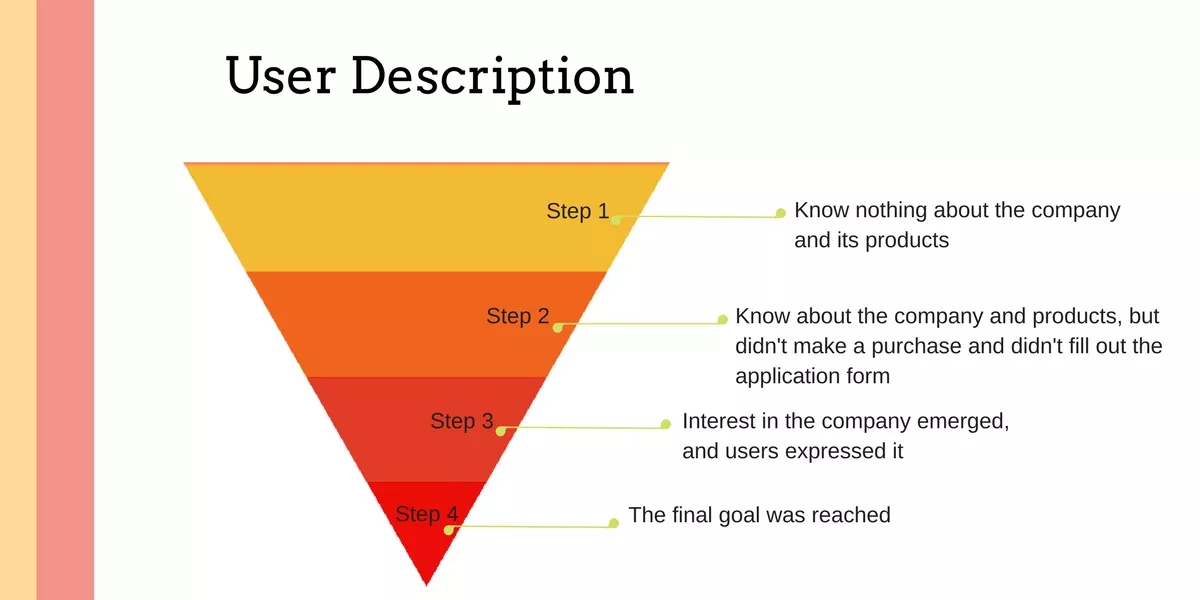
Thus, users on each stage can be characterized as:
Step 1. Are unaware about the campaign and its products.
Step 2. Are aware about the campaign, but haven’t purchased it and haven’t sent a purchase request.
Step 3. Users have interest in product and they have expressed it.
Step 4. The main goal has been achieved.
4. Pushing (Push to)
Pushing – something you want to sway users to on the current stage. You have to predict how the audience’s needs will change: if you offer “hot” users to purchase the product, then during the first step you would better not encourage them to pay for a product or service. First, propose them to go to the site and get acquainted with the offer.
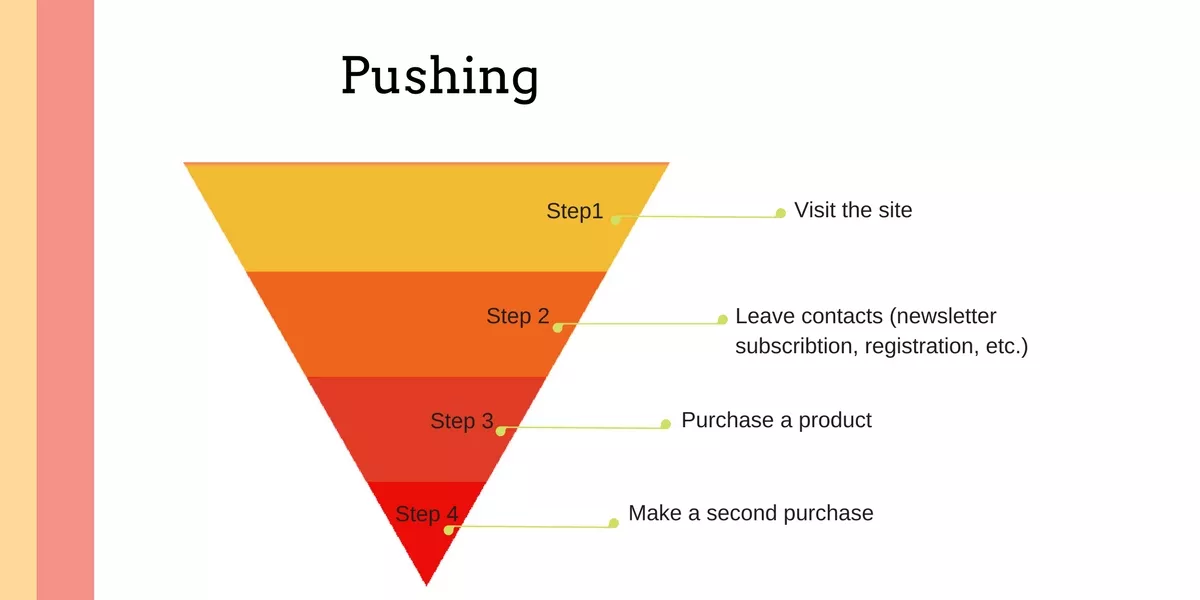
Example:
Step 1. Visit the site.
Step 2. Leave contact information (newsletter subscription, registration, etc.)
Step 3. Purchase a product.
Step 4. Make a second purchase.
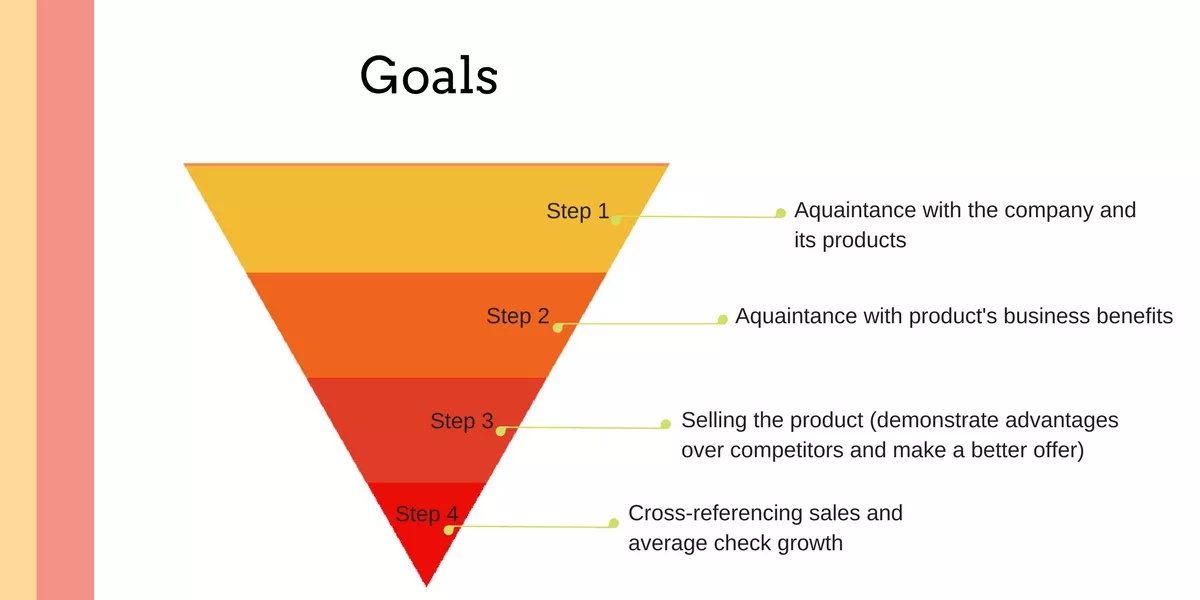
5. Main Goal
In the “Main goal” paragraph you have to define the goal for each stage of the funnel – this will help you to create a list of tools, target pages, and ad texts.
Step 1. Getting acquainted with company and products.
Step 2. Getting acquainted with business and products benefits.
Step 3. Selling the product (demonstrate competitive advantages and make a better offer).
Step 4. Cross-referencing sales and enlarging the average check.
6. Ideas
On this stage of planning you have to fix the real campaigns ideas, the realization of which will lead to reaching the goal.
Example of ideas for the first stage of the funnel:
6.1. Ad activity oriented towards users interested in the company’s products.
6.2. Displaying ad on the sites that are visited by the audience we are interested in.
6.3. Searching for the additional audience similar to the site target audience in behavioral indicators.
6.4. Attracting audience that is interested in competitors or is signed to their pages.

7. Campaign type
Which tools and campaign types will help you achieve the defined goals?
There are many tools in Google AdWords and it is necessary to be able to compartmentalize everything. In template I have described Google AdWords promotion tools, but based on project peculiarity you can add other tools as well.
8. Implementation status
To understand on which stage of works the campaigns ar, I have added “Implementation status” column in the strategy.
- Not started – implementation has not started yet, this parameter/ indicator is assigned to all sections by default;
- In Progress – is in the process of implementation, this status shows that campaigns are already punt into work;
- Need Clarification – for campaigns, creation and launching of which are blocked by some outside factors (for examples, you want to launch a campaign in Gmail with information about the promotion campaign, but at the moment there is no suitable promo);
- Done – is assigned to launched campaigns;
- Ball on the client’s side – you cannot launch the campaign because you are waiting for some actions or information;
- STOP – stopped campaigns that have demonstrated their ineffectiveness.
9. Strategy realization percentage
Thanks to this percentage, it is possible to track which part of the strategy have already been realized. In such a way I can immediately see what I am already able to do, and where I am still waiting for the data from client (for example, banners for media advertising or email database for Customer Match campaigns launching).
Calculations are held basing on three parameters:
9.1. Strategy realization percentage – general indicator that shows a part with realized points.
9.2. Strategy realization percentage, unrealizable due to pending answer/ data from client – customer can see the strategy percentage can be realized if it will help you. I have added this indicator because responsibility for the result of contextual advertising rests with both the implementor (internet-marketer) and client (customer).
Information, promptly provided by the client, and coordinated work is a way to successful ad campaign.
9.3. Campaign percentage that we decided not to launch yet (excluding points, where client’s actions are required) – displays segment with campaigns that we chose temporarily not to work with. For example, campaign aimed to increase coverage, but at the moment we are optimizing cost for attracting clients and therefore we have to postpone our work with coverage.
Advice on filling the strategy template
1.Vertically fill in the template
Focus on one particular indicator. Do not start filling template horizontally and do not hurry to think through all ideas and campaign types for each step – in such a way you might get confused or prioritize incorrectly.
2. Do not reduce funnel to two or three steps
Briefness is a key to unsuccessful strategy. Don’t simplify the way to purchase. The more detailed overview you make and visualizable your target audience and its necessities, the higher the probability that your offer will provoke users’ interest.

3. Do not try to add a document to all campaigns
Select campaign in accordance with the stage of the funnel. Do not write everything you know or have ever heard about. Clearly differentiate all campaign types and their possibilities.

4. Write in details
Coming back to strategy template within several days, you can remind yourself of what was meant by the paragraph “Remarketing campaign targeted on loyal users”. Write down which campaign type you will use (search or contextual media ad), who are your loyal users, and what audience you are going to exclude.
In case you don’t do that, you risk wasting your time on reconstructing information in your memory.

5. Activate strategy
I won’t recommend you to keep all your manipulations in your head. Mark campaigns status and then using strategy template you will be able to answer in a few seconds what is already working and what is only planned.
6. Supplement strategy
Don’t delude yourself: it is not enough to simply create a strategy template. Supplement it with new ideas and tools. In the future, when you reach the planned KPI rates, you will be able to share you experience with colleagues.
What are the benefits of this approach to contextual advertising strategy management with sales funnel?
The proposed approach allows to:
Structure up your strategy and make it easy to read.
Compartmentalize needs of the audience in accordance with the step it is currently going through and therefore propose your audience just war it needs at this step.
Analyze what campaign types that have been created, what are still launching, and which have not yet been taken into work.
Visualize the percentage of strategy fulfillment both for yourself and for any other projects: portals, corporate sites or ecommerce. The most important part here is to define step of the funnel and find individual approach to the audience at each stage.
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses