Search engine crawlers, while checking a page, first of all look at the HTTP status code and then proceed to check the content of the page. For example, non-existent pages should always return a 404 status code. Why? Google claims that pages with a HTTP status code different from 404 and 410 will be scanned and indexed. So, if you don't know what codes your pages respond with and how to check them, you are jeopardizing the future of your whole project.
Read about what do HTTP status codes mean in the new post of The Beginner’s SEO guide
What is a HTTP status code?
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) status code is a three-digit number that a server sends back to a user’s request, which corrects the further processing of the requested page. The number is always followed by a brief explanation of the code in English, separated by a space, which is the primary instruction for the client when accessing the page or document on the site.
Response code is checked by both browsers and search engine bots when accessing the page.
Why the response codes are important for SEO
HTTP status codes play an important role in SEO. If the response code is set up correctly and in time, the search engine bot will be able to quickly scan the page and make necessary actions.
On the other hand, response codes help us to control any changes on the website. For example, you change the page address, move to a secure connection protocol, or even change the CMS. In all these cases, by changing the HTTP status code we can inform the crawlers about what happens to the pages of our site, so they can correctly react to these actions.
What are the types of HTTP status codes?
These are groups of codes united by certain characteristics. A status type is indicated by the first number in the code.
There are five types of HTTP status codes :
- 1xx – Informational Responses. They are responsible for the process of data transmission. These are temporary codes, they inform that the request is accepted and processing will continue;
- 2xx – Success. A request has been received and processed successfully by the server;
- 3xx – Redirection. These response codes mean that further action needs to be taken to complete the request. For example, make a request to a different address;
- 4xx – Client Errors. This means that the request cannot be completed through the user's error;
- 5xx – Server errors. These response codes are caused by errors on the server side. In this case, the user did everything correctly, but the server cannot complete the request. For codes of this type the server obviously shows a message that it cannot process the request and for what reason.
What are the most important HTTP status codes
200 OK
The most popular and important response code. Indicates that the request has been completed successfully according to user expectations – the requested data or page exists and is available for viewing. All pages that we want to see in the search engine index should return the 200 OK HTTP status code.
301 Moved Permanently
This response code means that the document or page has been permanently moved to another address. If a page that was already in the search engine index has changed address, it is recommended to set up a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one to save traffic and link juice. Search engines will eventually "glue" these addresses together.
302 Found
Document has been temporarily moved to a different URL. This HTTP status code is a signal that the page should not be removed from the index. According to Gary Illyes of Google, the link juice is transferred in this case.
304 Not Modified
This is an important response code in terms of server load and amount of data transferred. The server returns a 304 code if the Last-Modified date in the HTTP header is older than the If-Modified-Since request. That is, if the document hasn't been modified since that date, the server returns a 304 Not Modified response code. In this case, search engine crawlers do not need to retrieve the document: it has not changed since their last visit. In fact, they only retrieve the HTTP headers and move on.
307 Temporary Redirect / Internal Redirect
This status code was created to clarify the 302 Temporary Redirect. It belongs to the HTTP 1.1 standard but is not as common as 302 code.
A 307 response code means that the requested page is now available at a different URL, but will then return to the previous URL anyway. Just like with the 302 redirect, the page is not cached and search engines bots will most probably not add the new URL to the index.
This response code is similar to 302, but it does not allow you to change the request method from POST to GET.
308 Permanent Redirect
This response code is the HTTP 1.1 analog of the 301 redirect. It does not allow changing the request method from POST to GET.
At the moment there is no clear information about how much page authority the 308 redirect passes, so we recommend using the 301 redirect instead to indicate that content has moved permanently.
401 Unauthorized
This HTTP status code is an error and means that HTTP Authentication failed. The requested page requires either a username and password combination, and/or isn't allowed access based on its IP address.
403 Forbidden
Access denied. This response code is returned if the user is denied access to this document. In this case it is not about HTTP authentication (for such cases 401 and 407 codes are used). A 403 code is shown for example if a user is logged in from a banned IP address or if an attempt to view the .htaccess system file is made.
404 Not Found
This HTTP status code is likely to be encountered by every user. It indicates that nothing was found at the given URL – the page does not exist. This code should be thrown when trying to reach a document which doesn't exist. If a page at the requested URL existed, but was removed and you want to report it, use 410 response code.
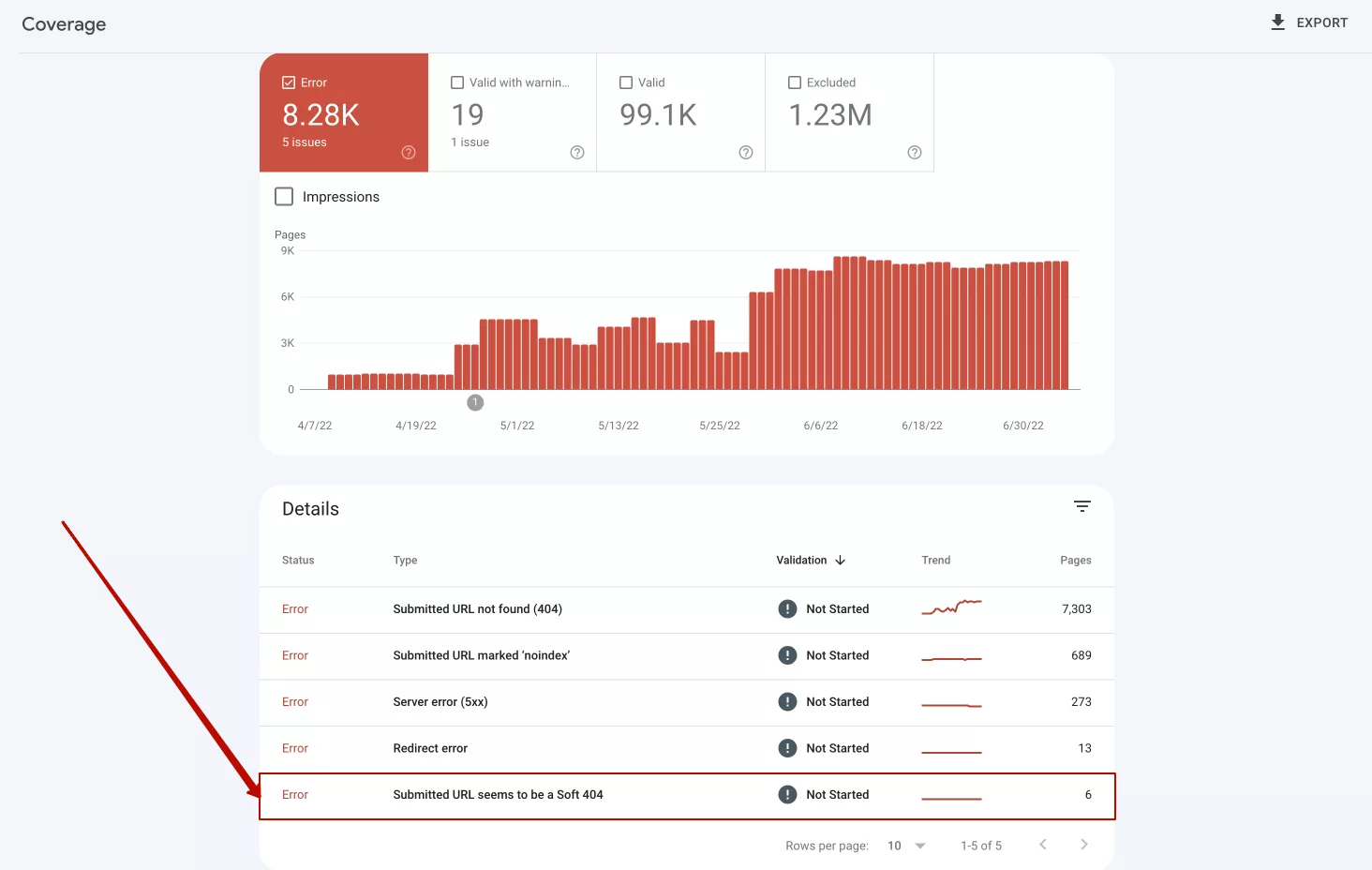
“Soft 404 pages”
A page with a 404 File Not Found message does not always return a 404 status code. Many webmasters do not pay attention to this, which can negatively affect the ranking of the entire site as a result. These are so-called "Soft 404" pages. They occur if a non-existent page gives a response code different from 404 and 410. “Soft 404" may include pages that should give a code of 200, but they have no content (blank page). The solution is to find such pages and be sure to configure a 404 code for them.
You can check the soft 404 pages on the Coverage panel in Google Search Console.
Example of “Soft 404 pages” in Google Search Console
Many webmasters have excelled in the art of 404 page design. Get distracted and check it out: you shouldn’t be here
407 Proxy Authentication Required
The 407 HTTP status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it does not have valid authentication credentials for the proxy server that is between the browser and the server that can access the requested resource.
410 Gone
This HTTP status code indicates that the document has been permanently deleted and is no longer available. Although 404 and 410 codes indicate the page is inaccessible in the same way, there are differences in how they are handled. When a crawler accesses a 404 page, it will not mark it as deleted and will access it again after a while to refine the information. The same cannot be said for the 410 code. In this case, the search engine bot will mark the page or document as permanently deleted from the server. Trusting the webmaster, the crawler will not check this page again.
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
This code has become increasingly common lately. It means that access to the server is denied because of a state ban or a court decision in a case of copyright infringement. Error 451 is a specific type of 403 status code.
500 Internal Server Error
This is any internal server error that isn't covered by other errors of this class. It occurs if the server encounters a problem which prevents the request from being completed. For example, this error can occur due to settings errors in the configuration file.
503 Service Unavailable
The server is temporarily unable to process requests due to technical issues. If the server is receiving too many requests and cannot handle them, we see this particular response.
504 Gateway Timeout
Gateway is not responding. This status code appears if the server was acting as a proxy and did not wait for a response from the upstream server to complete the request.
To prevent pages from appearing in the search engine index it is recommended to use the robots meta tag on the page with a “noindex” attribute:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">.
If you want to remove your document from search results, you can configure a 404 or 410 code. If the “noindex” meta tag is used the page will be re-scanned regularly, while the 410 response code will tell the robots that the page no longer exists and that there is no need to crawl the page.
How to check the HTTP status code
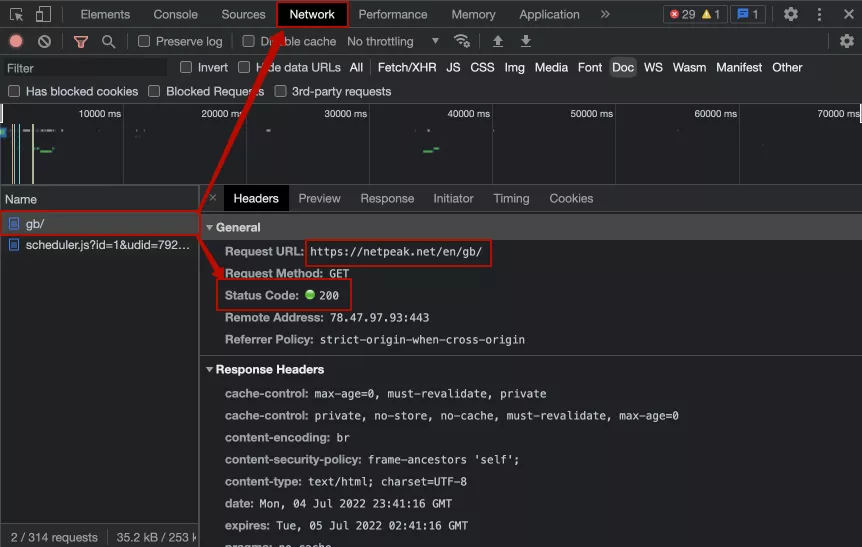
If you're using Google Chrome, you can use the Network tab on the Developer's toolbar to view the code. Once the panel is open, refresh the page.
Another way to check the HTTP status code is using a popular browser plug-in Redirect Path.
These methods are useful for a singular page. It is quite difficult to use them if you need to check the response codes on multiple pages.
Checking the HTTP status codes in Google Search Console
The “URL Inspection” feature in Google Search Console allows you to check HTTP response code for a certain page.
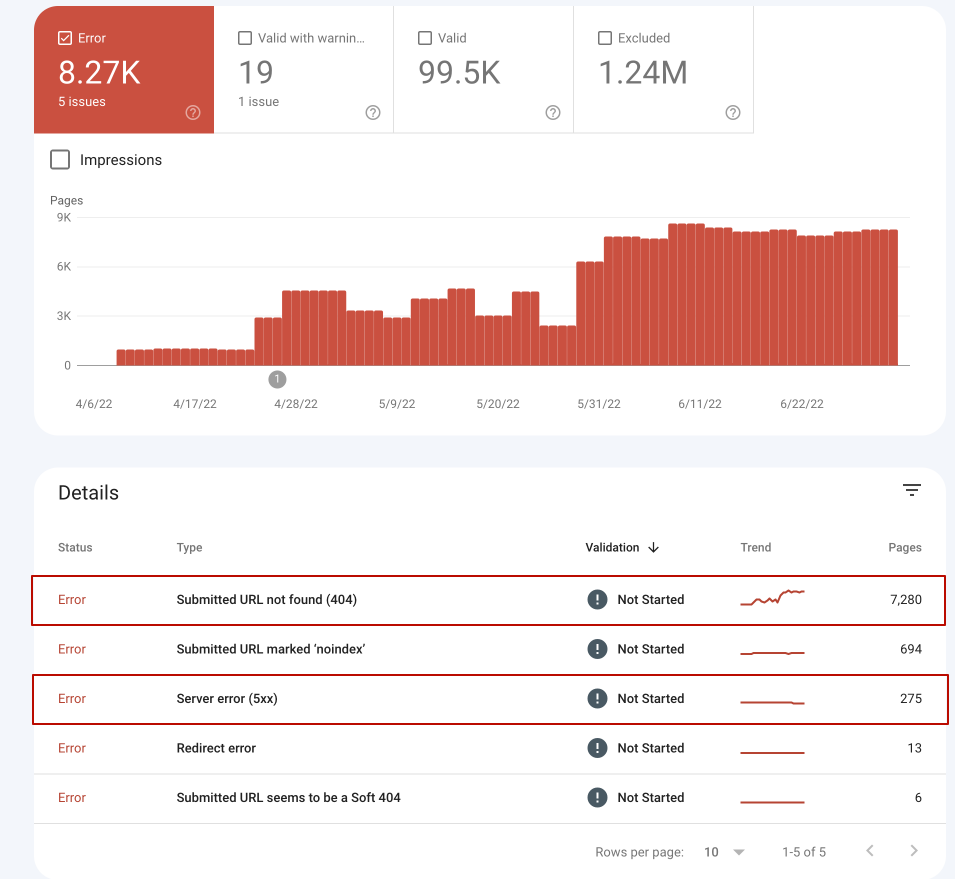
The panel “Coverage” shows the most important information and errors of HTTP status codes for all pages of the website.
In the example below we can see that there are pages with 404 status code and pages with 5xx errors:
How to check the HTTP status codes using Netpeak Spider and Netpeak Checker
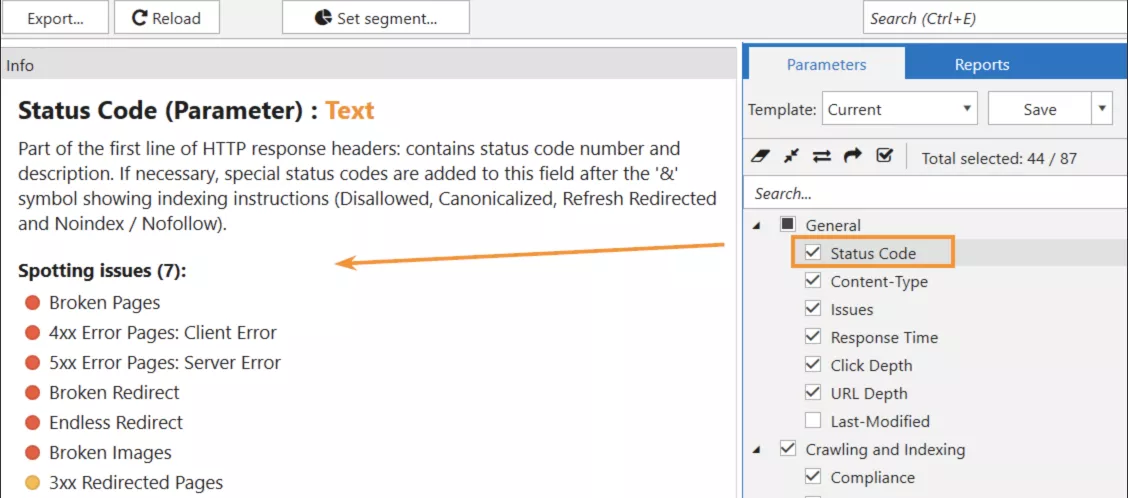
Netpeak Spider and Netpeak Checker both are used for crawling and conducting the technical audit of the website using a huge number of technical parameters. And the response code is one of them. You can check the responses from the all website pages, the URLs from sitemap.xml or just load a list of URLs that you need to check.
Example of checking the HTTP status codes in Netpeak Spider
Example of checking the HTTP status codes in Netpeak Checker
How to monitor the HTTP status codes
It is important to constantly monitor the response codes to be able to react to the errors that may occur on the website.
For monitoring the HTTP status codes it is convenient to use Google Search Console, which can send email alerts in case the page response code differs from 200 OK.
You should also regularly conduct a full audit of all website’s pages. It is useful to do this with software such as Netpeak Spider.
Key highlights
- There are five classes of HTTP status codes, which are classes of response indicating different stages of the submission process, from successful processing to a server error.
- All pages that we want to see in the search engine index need to return an 200 OK status code.
- If a page that was already in the search engine index has changed address, it is necessary to configure a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one.
- If a non-existent page returns a response code different from 404 and 410, a "Soft 404" page error occurs. This may include pages that should be giving status code 200, but have no content on them.
- Proper distribution of server responses allows search engines to save resources on handling the site. Search engine crawlers will only get the information they need - this is very important for SEO.
- Checking the HTTP status codes regularly helps to react quickly to any changes on the website.
As a final general erudition question, why was the number 451 chosen for the Unavailable For Legal Reasons server response?
FAQ
1. Q: What are HTTP status codes?
A: Status code is a three-digit number that a server sends back to a user’s request, which corrects the further processing of the requested page. The number is always followed by a brief explanation of the code in English, separated by a space, which is the primary instruction for the client when accessing the page or document on the site.
2. Q: What is a 404 status code?
A: The 404 status code means that nothing was found at the given URL – the page does not exist. This code should be thrown when trying to reach a document which doesn't exist.
3. Q: What are the “Soft 404 pages”?
A: “Soft 404 pages” occur if a non-existent page gives a response code different from 404 and 410. “Soft 404" may include pages that should give a code of 200, but they have no content (blank page). The solution is to find such pages and be sure to configure a 404 code for them.
4. Q: What is a status code 500?
A: This is any internal server error that isn't covered by other errors of this class. It occurs if the server encounters a problem which prevents the request from being completed. For example, this error can occur due to settings errors in the configuration file.
Related Articles
How to Set Up Consent Mode in GA4 on Your Website with Google Tag Manager
Let's explore how to properly integrate consent mode in GA4, configure it for effective data collection, and at the same time comply with GDPR and other legal regulations
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers