Google Analytics 4, also known as GA4, is the latest version of Google's popular web analytics platform. It gives businesses a strong and adaptable approach to monitoring user activity on the web and mobile app. The ability of GA4 to process and manage enormous amounts of data in real time is one of it is primary advantages. This is achieved through the use of data streams.
What are Data Streams in GA4?
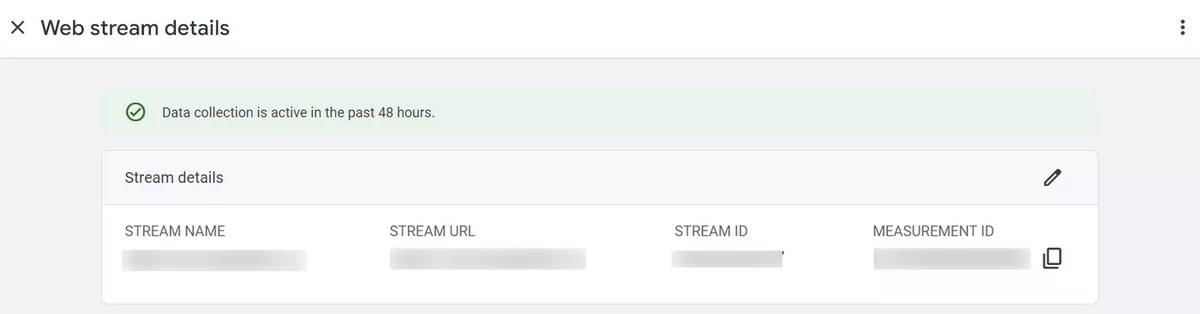
In GA4, a data stream is a collection of data from a single source, such as a website or mobile app. The reporting view, measurement ID, and data source type are just a few of the attributes that are unique to each data stream. You can organize your data, provide access to each data stream separately, and control that the data is used for the correct reporting purposes by creating data streams in GA4.
In this beginner's guide, we'll go over the fundamentals of managing data streams in GA4, including how to create, manage, update, and delete data streams. We will also give examples of how data streams may be used to enhance the performance of your web or app and comprehend user behavior better.
Web analytics underpins conversion optimization. What will CRO get you? Find out with Netpeak's calculator.
Creating data streams
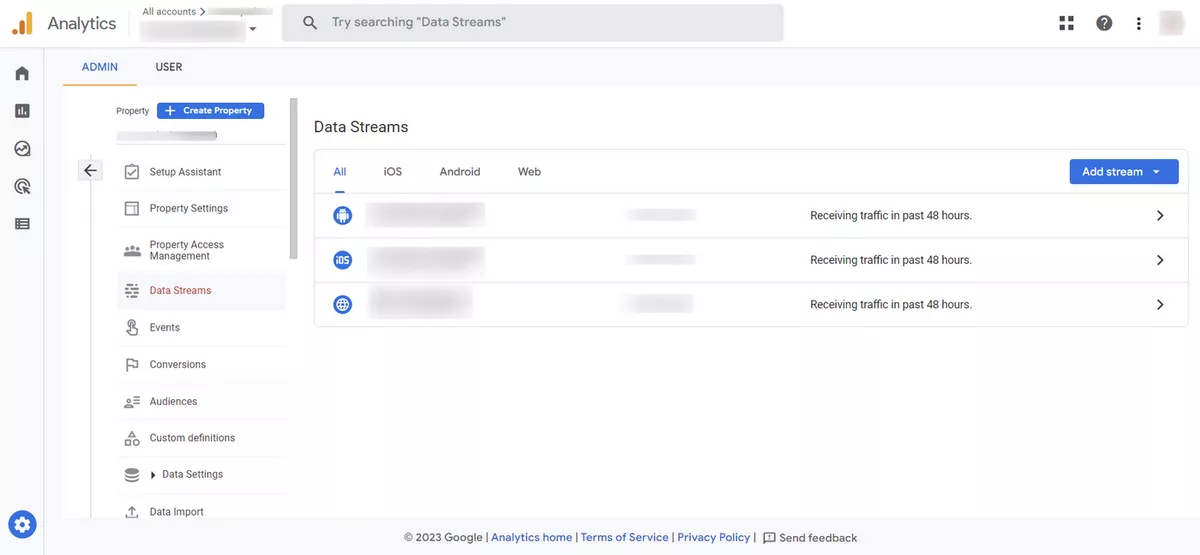
To create a data stream in GA4, you first need to have a GA4 property. If you do not have a GA4 property yet, you can create one by following the steps outlined in the GA4 setup guide. If you have just created a new property GA4, you can create the first data stream on the home page immediately.
Once you have access to a GA4 property and the data stream already is there, you can create a new data stream by following these steps:
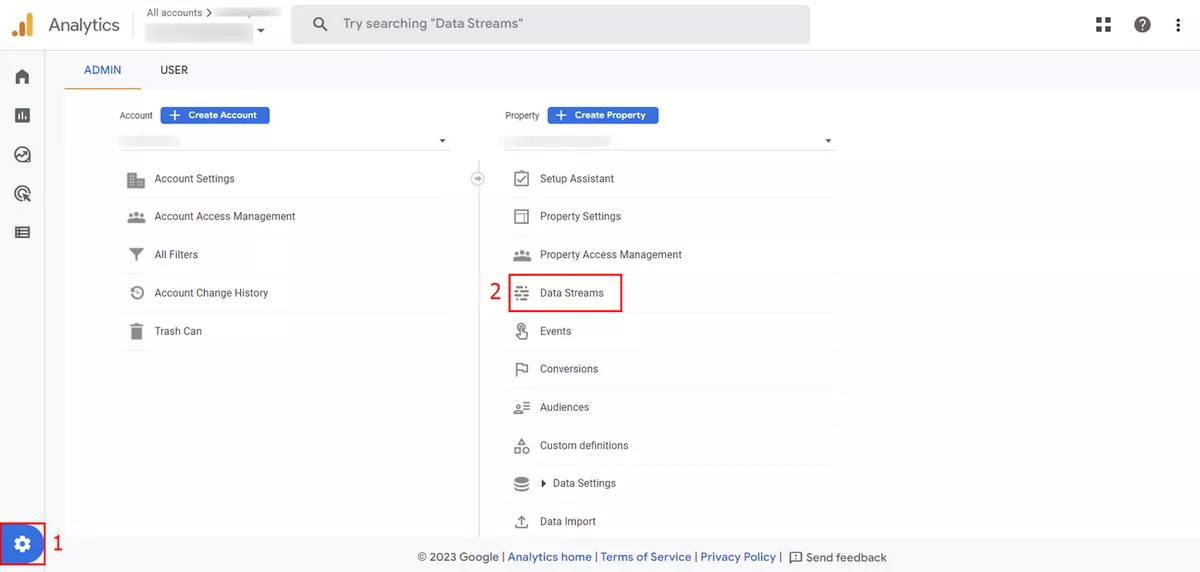
- Click on the "Admin" and choose the "Data Streams" tab in the navigation menu.
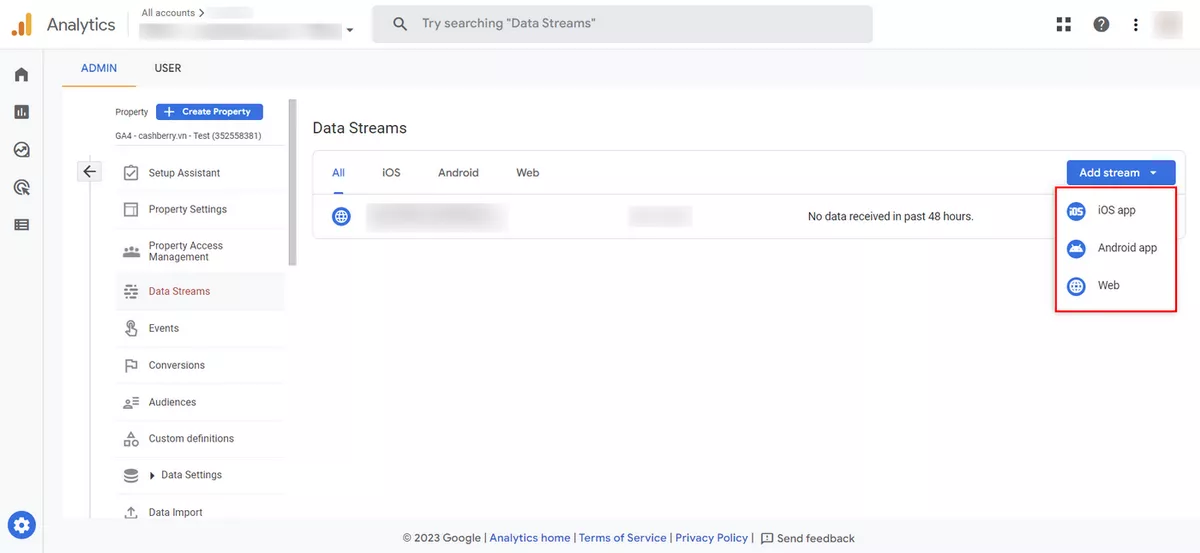
- Click the "Add Stream" button.
- Select the type of data stream you want to set up, such as a web stream, iOS app stream, or Android app stream.
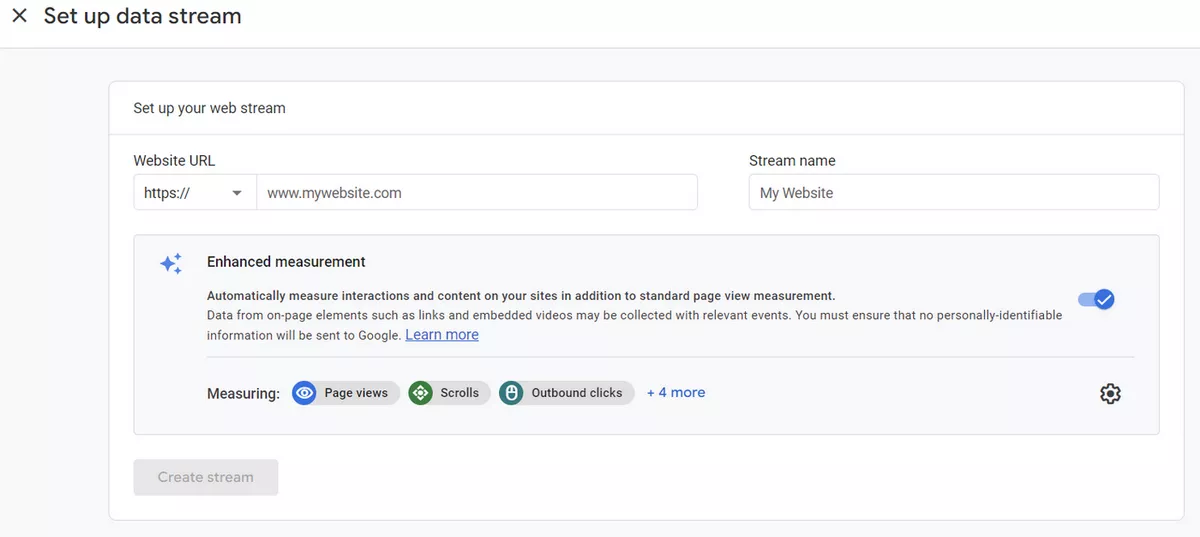
- Follow the on-screen instructions to set up the data stream.
Web data stream setup
App data stream setup
- If you have correctly placed the tracking code on your website, you will see a message that "Data stream is collecting data successfully". Afterward, you can easily analyze the data using the GA4 reporting interface. Below we will describe the basic configuration settings in the web data streams.
Configuration of Data Streams
A variety of parameters in GA4 can be modified to control the data collection and reporting processes for data streams. So let's look up the important settings of web and app data streams.
Web data stream
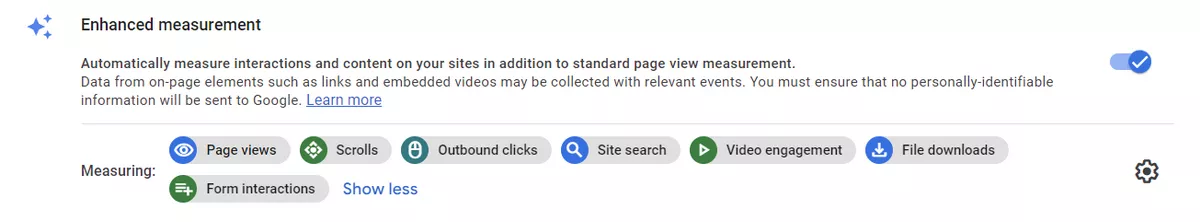
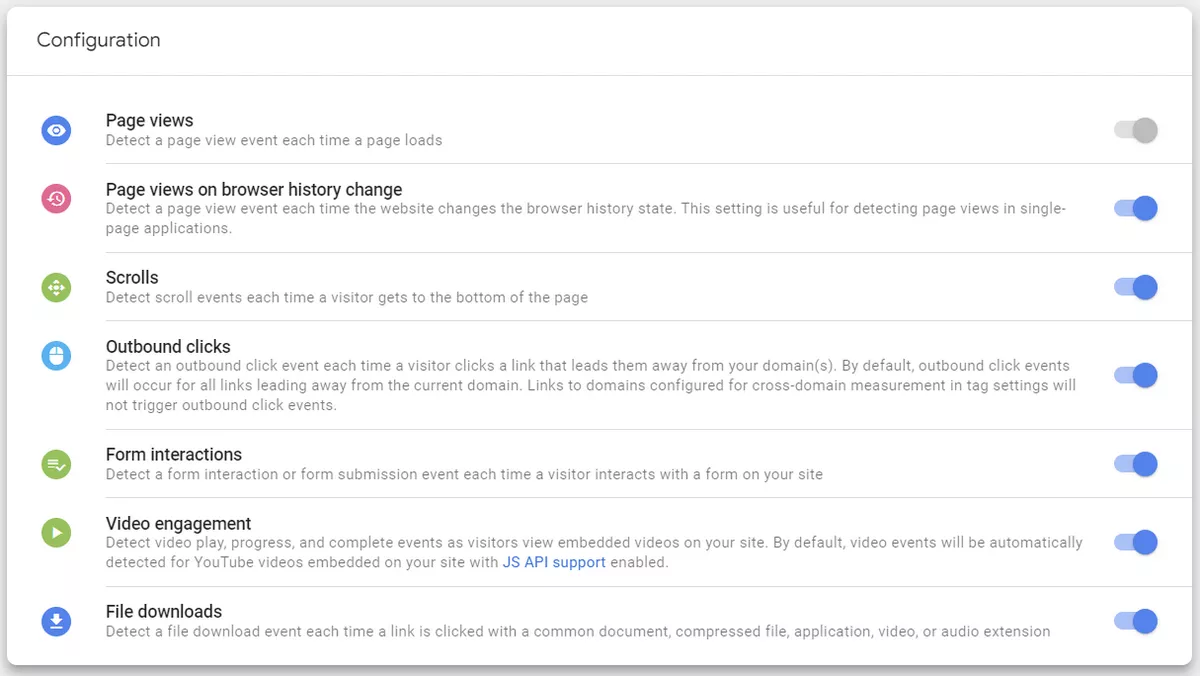
Enhanced measurement
Page views. The tracking of page views on your website by GA4 is decided by this option. This option is enabled by default, and GA4 will automatically track page views.
This setting enables additional data collection features, such as scroll tracking, outbound link clicks, form interactions, video engagement, and file downloads. By default, this setting is enabled, but you can disable it if you don't want to collect this additional data.
Site search. This setting enables GA4 to track searches performed on your website's internal search engine. By default, this setting has query parameters: q, s, search, query, keyword. If you have another parameter, you can add it in "Hide advanced settings".
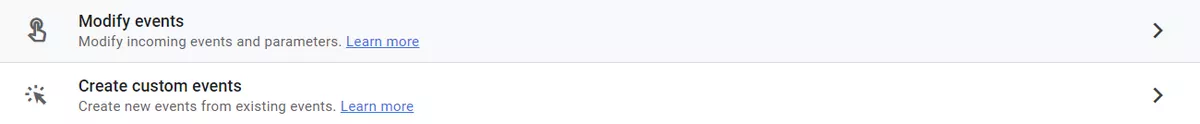
Modify and create events
You can modify current events and create new events based on existing ones within GA4 without the need to update the code in your website or app.
Events can help you track user interactions that aren't automatically measured by GA4, such as clicking a particular button or filling out a specific form. By modifying or creating events here, you can make data more accurate, actionable, and useful for business decisions without updating the code.
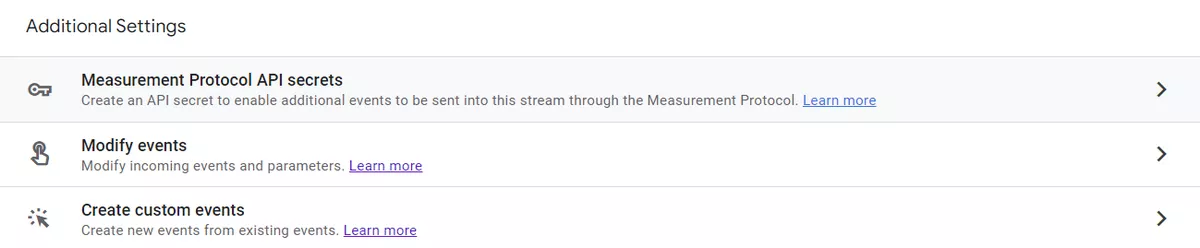
Measurement Protocol API secrets
The Measurement Protocol API in Google Analytics 4 allows you to send data to your property from other sources. To use the Measurement Protocol API, you need to send requests to the GA4 server using an HTTP POST request and include the measurement protocol parameters in the request.
Once you have generated an API secret for your data stream, you can use it to authorize your Measurement Protocol API requests. You'll need to include the API secret in the HTTP request as a query parameter named "api_secret". For example, here's how you would include the API secret in a Measurement Protocol API request:
In the example above, replace "TAG_ID" with your GA4 measurement ID, and replace "YOUR_API_SECRET" with the API secret you generated for the data stream.
Remember to keep your API secret secure and only share it with authorized users who need to use the Measurement Protocol API for your GA4 property.
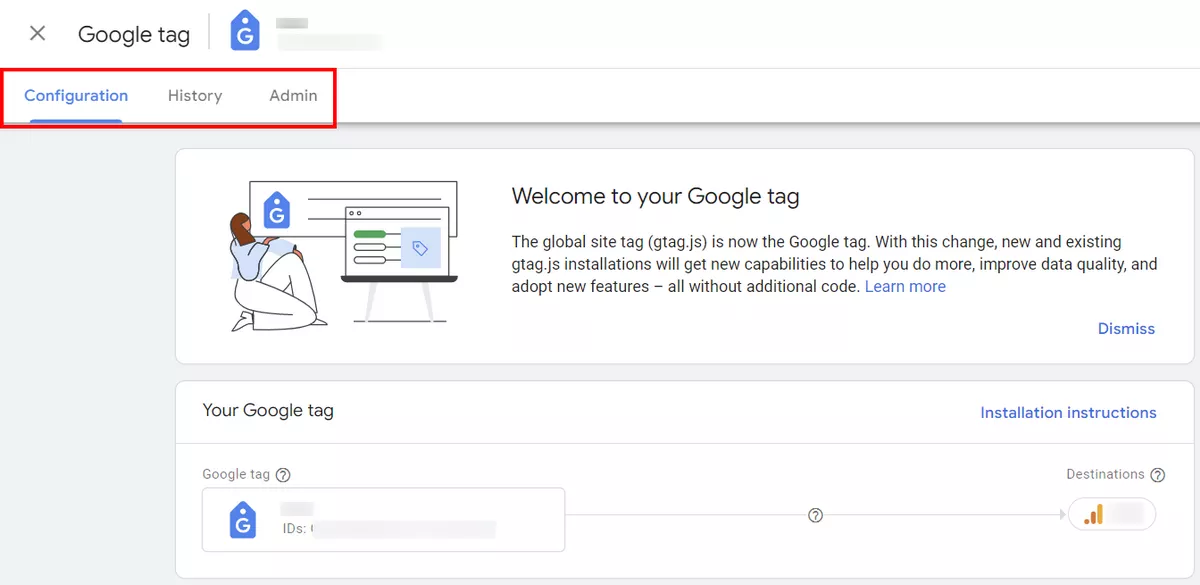
Configure tag settings
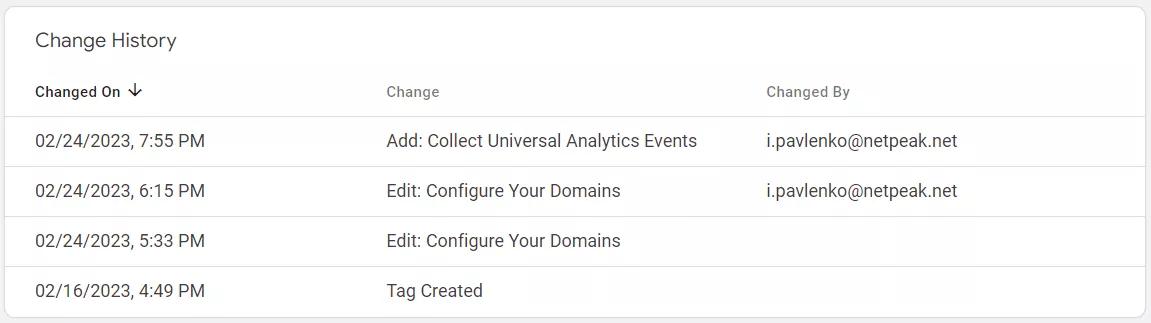
There are 3 tabs here: Configuration, History, and Admin.
In the History tab you will find the all history of data stream changes.
In the Admin tab you can manage your Google tag: edit name, edit destinations, combine and change administrators or editors.
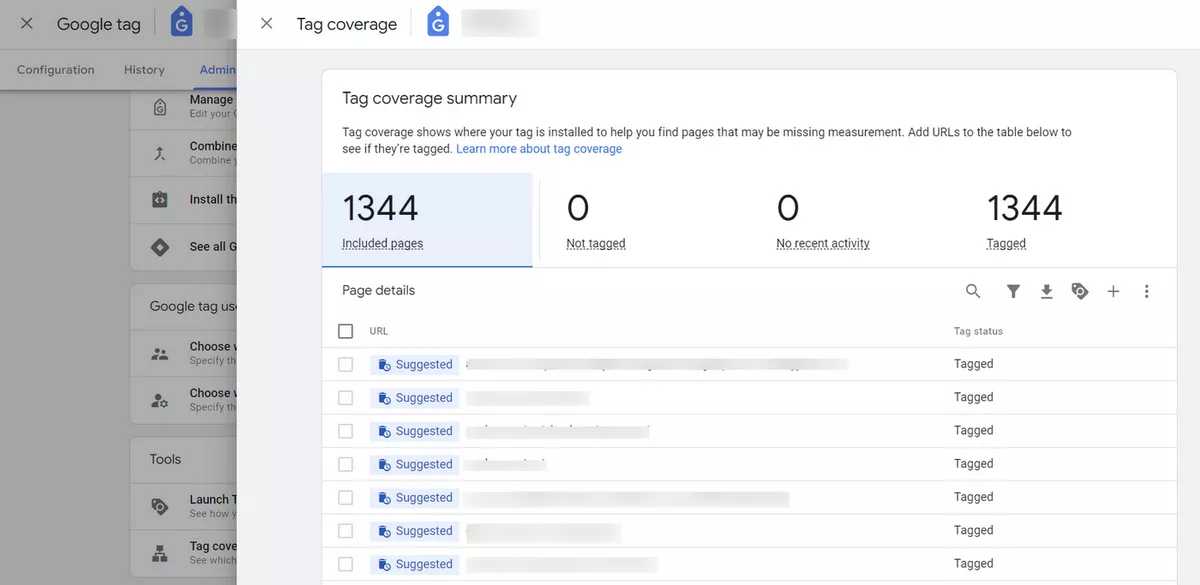
Also, you can see here where your tag is installed to help you find pages that may be missing measurements. You need to click on "Tag coverage".
In the Configuration tab, click to "Show all" you can find a lot of interesting things there. Below are the details about these things.
1. Manage automatic event detection
Here you can configure which types of events your Google Tag should automatically detect for measurement in associated destinations.
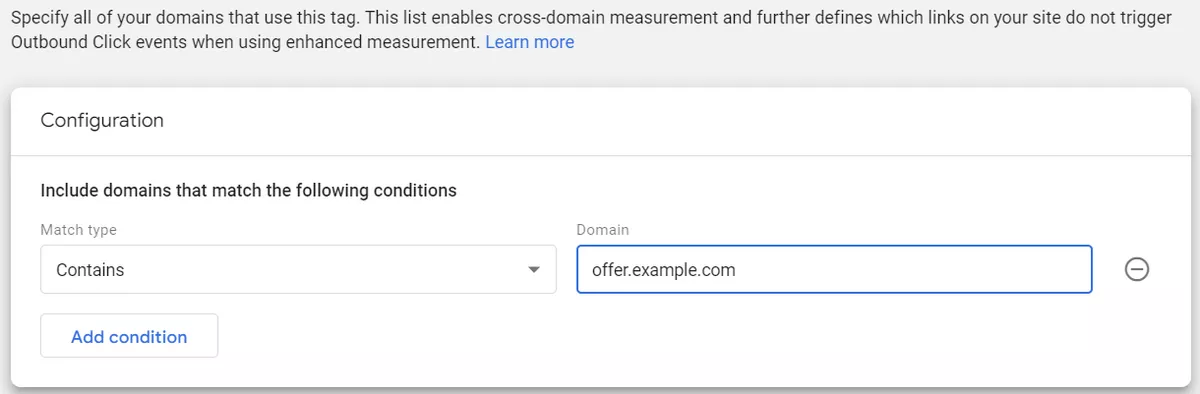
2. Configure your domains (Cross-domain tracking)
This setting allows GA4 to track users across different domains. For example, if your website has multiple subdomains, cross-domain tracking will enable GA4 to track users as they move between these subdomains.
To set up cross-domain tracking you must update the configuration of your GA4 property to include the additional domains you want to track.
To do this, сlick on "Configure your domains", enter the domains you want to track, and click "Save".
Verify your cross-domain tracking setup by checking the real-time reports in GA4.
You should see data for users moving between your domains.
3. Allow user-provided data capabilities
The main point of this allows is that user-provided data can help improve measurement and provide more insights, but it is important to ensure that the data collection complies with the terms of service of the destination product. Google will only use the data you share to provide services and will not share it with others.
4. Collect Universal Analytics events
Turn on if you want to collect an event each time a ga() custom event, timing, or exception call from Universal Analytics occurs on your website
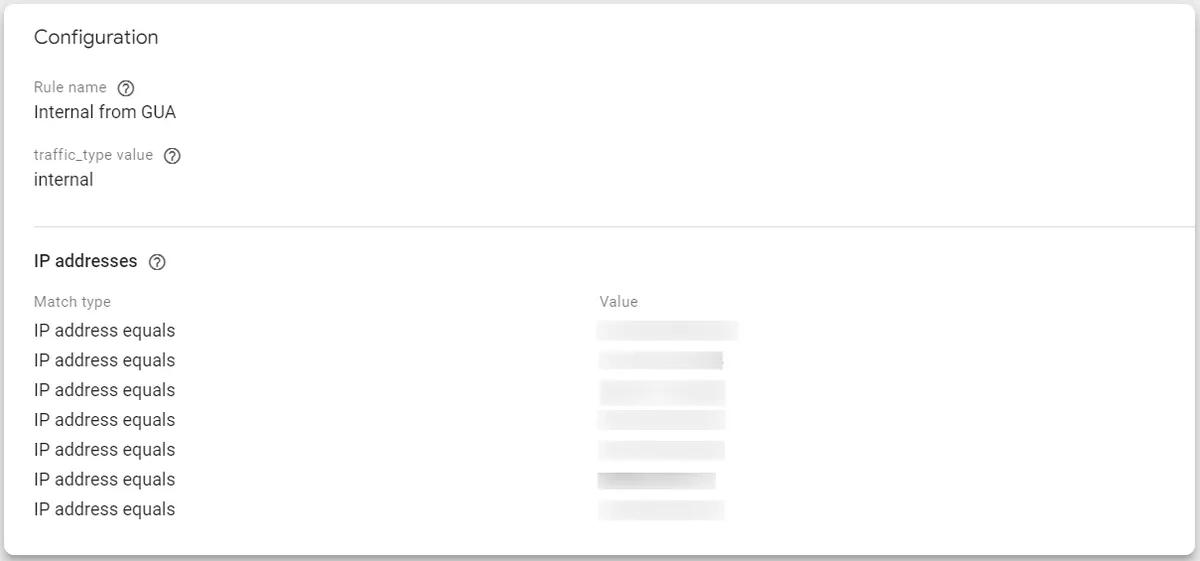
5. Define internal traffic
In order to ensure accurate reporting, it is important to exclude internal traffic data generated by users such as employees, developers, or contractors. This can be achieved by using IP filters to remove such data from your reports.
It is important to note that applying a data filter has a permanent effect on the data. Therefore, if you wish to temporarily hide data from certain reports, you can use report filters instead.
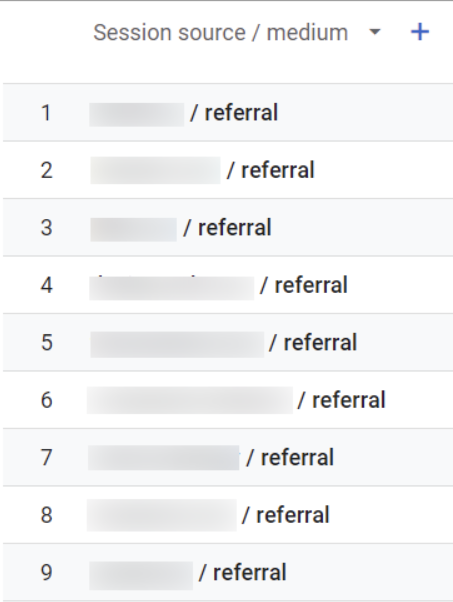
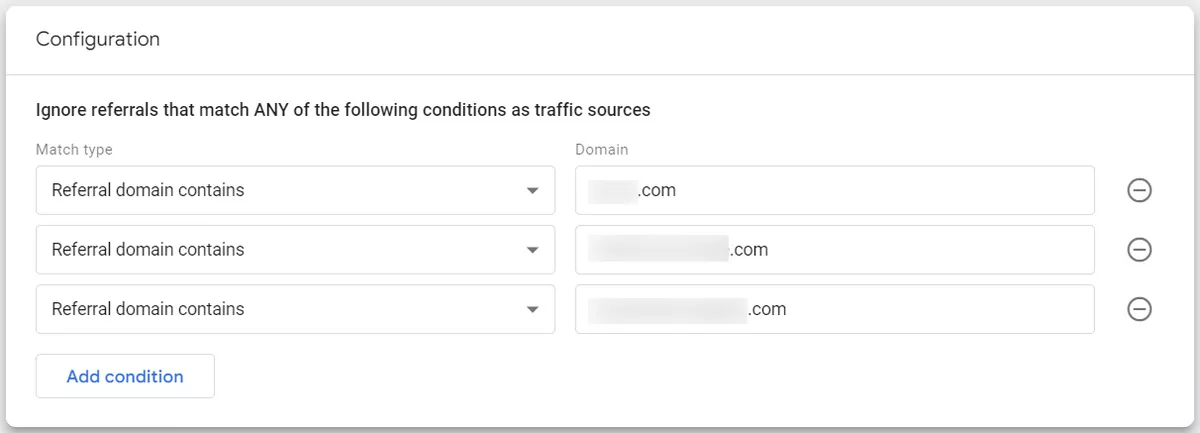
6. List unwanted referrals
In Google Analytics, referrals are traffic that comes to your website from external sources, such as links on other domains, transfers from payment systems, etc.
To better understand referral traffic, Google Analytics identifies the source of the incoming traffic and displays the domain names of these sites as referral traffic sources in your reports.
However, to ensure the accuracy of your data, you may want to exclude certain referrals from your reports. In this setting, you can create a set of conditions that identify the domains whose traffic you don't want to be included as referrals.
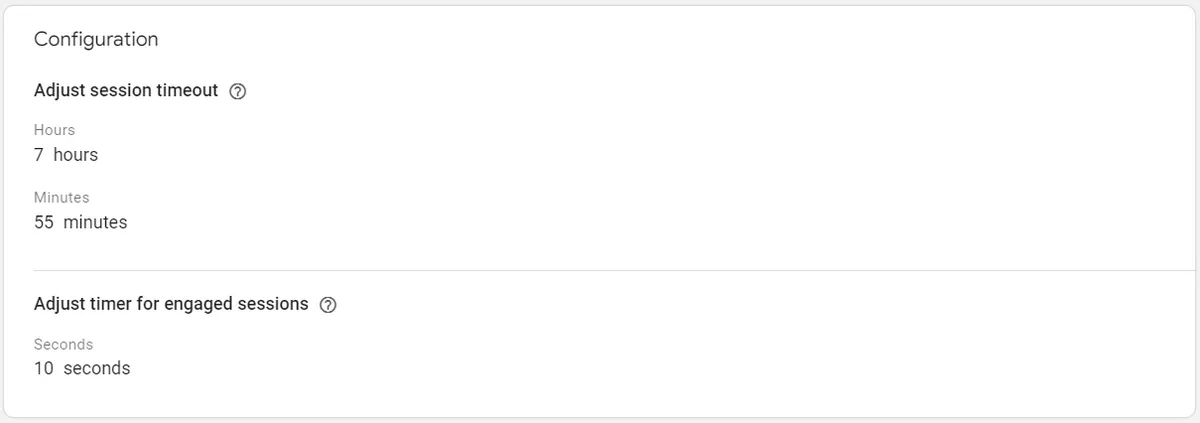
7. Adjust session timeout
You can adjust how long it takes before sessions expire due to inactivity or become engaged sessions.
By default, the session timeout is set to 30 minutes of inactivity. This means that if a user is inactive on your site or app for more than 30 minutes, the session will end, and a new session will begin when the user resumes their activity.
GA4 allows you to set the minimum as 5 minutes and the maximum as 7 hours 55 minutes session timeout intervals, you may want to adjust the session timeout to better suit your needs.
Additionally, GA4 also provides a timer for engaged sessions. This timer keeps track of the duration of active engagement with your website and resets the session timeout whenever there is user engagement. This means that if a user is actively engaging with your site or app, their session will not end after 30 minutes of inactivity but rather when they are no longer engaged.
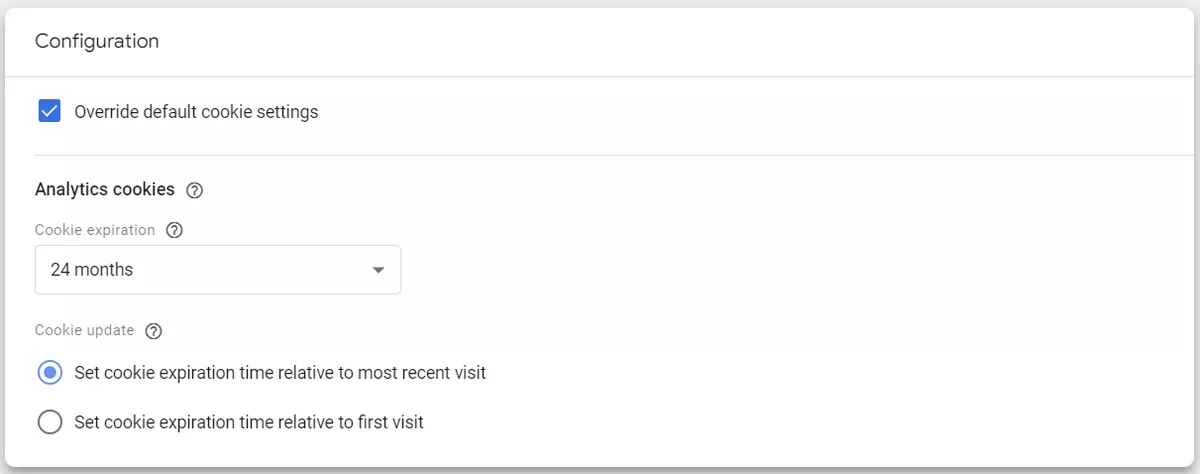
8. Override cookie settings
Google tags use first-party cookies for various purposes. These cookies have default expiration and update settings, but you can customize these settings by overriding them.
App data stream
App data streams in GA4 are critical to understanding user behavior within your mobile app.
If you integrate Google Analytics 4 with Firebase – app data streams are automatically created to send users data to GA4. However, you also have the option to create them separately if necessary.
The primary settings for app data streams GA4 include:
- Measurement Protocol API secrets.
- Modify events and create custom events.
These settings are the same as in web data streams and perform the same task.
Editing Data Streams
You can edit the data stream at any time by following these steps:
- Select the GA4 property that contains the data stream you want to edit.
- Click on the Data Streams tab in the Admin navigation menu.
- Click on the data stream you want to edit.
- Make the desired changes to the properties of the data stream.
- Click the "Save" button to apply your changes.
Deleting Data Streams
If you no longer need a data stream, you can delete it by following these steps:
- Log into your Google Analytics account and select the GA4 property that contains the data stream you want to delete.
- Click on the Data Streams tab in the navigation menu.
- Click on the data stream you want to delete.
- Click the top on the right "Delete stream" button.
- Confirm the deletion by clicking "Delete Stream" in the confirmation dialog.
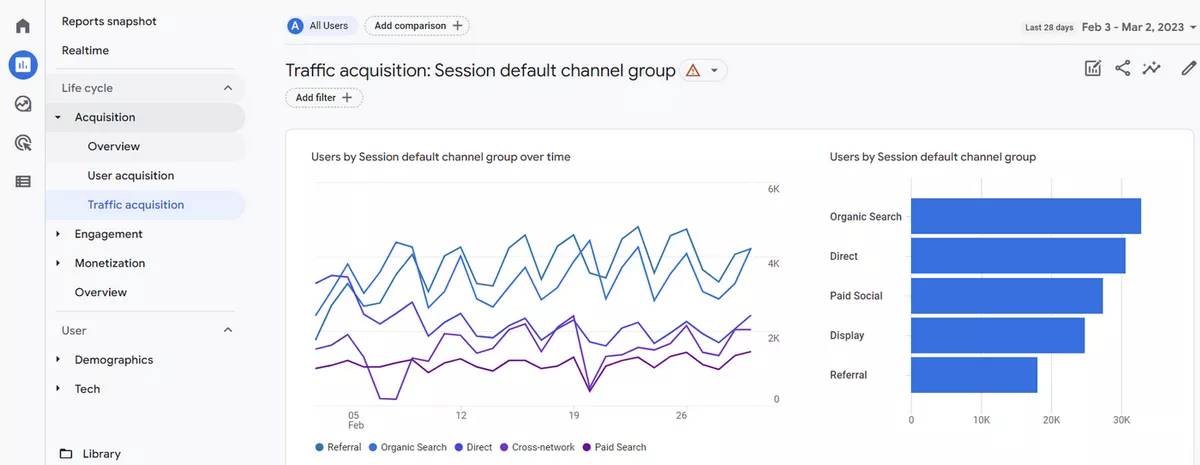
How to choose data streams in reports?
If you have more than one data stream in a GA4 account, as you might want to either see data for all the streams or any single one of them.
You can apply different data streams to any standard reports or Explore reports
To view data streams in standard reports, you need to go to your reports section in GA4 and select the report where you want to see the stream's data.
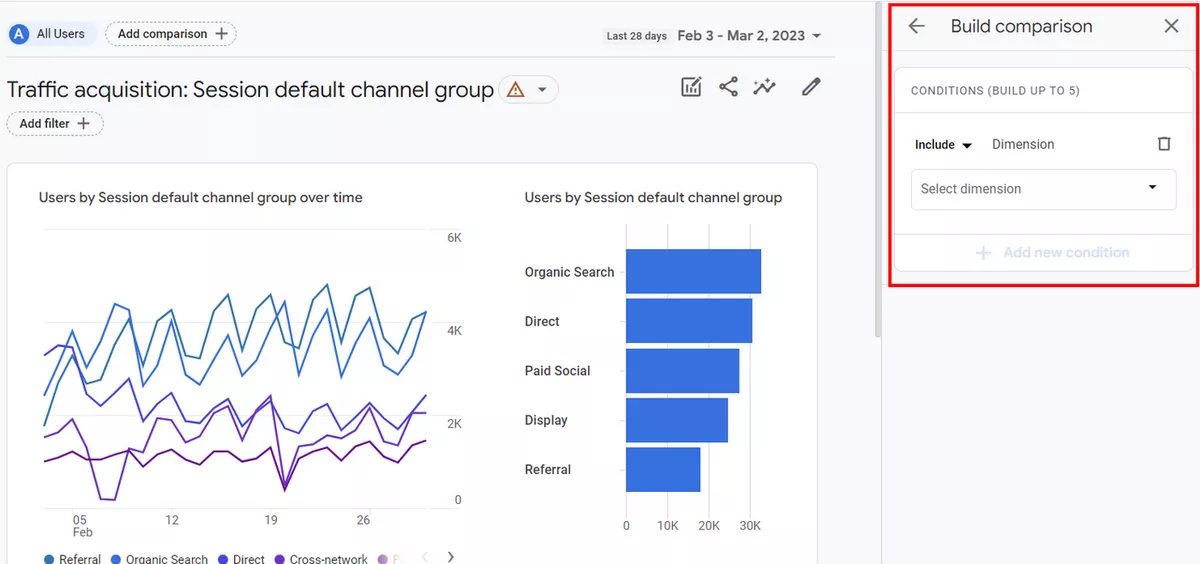
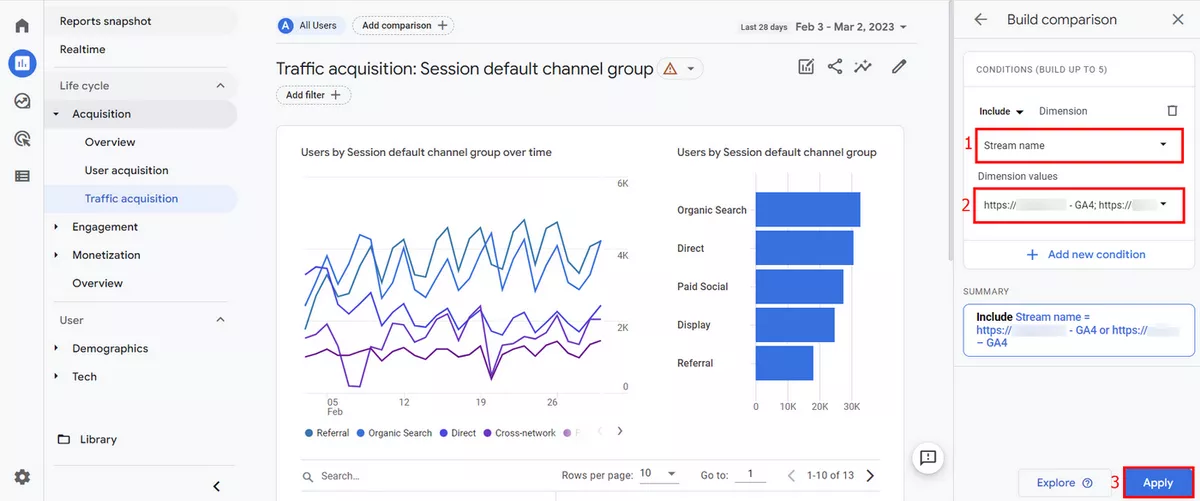
Next, click on the "Add Comparison+" button at the top of the report. This will open a small Build comparison configuration tab on the right side.
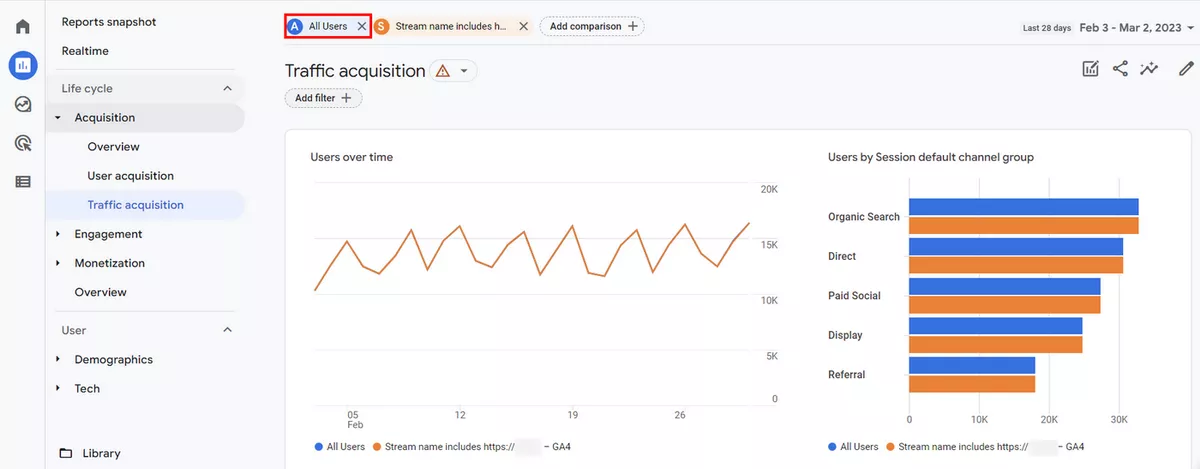
In the Build comparison configuration tab, select the Stream Name in Dimension and choose the streams in Dimension values. Once you have selected the streams, click on Apply.
You will now see a comparison of All Users and the streams you selected. If you only want to see the data for the selected streams, you can remove All Users from the top.
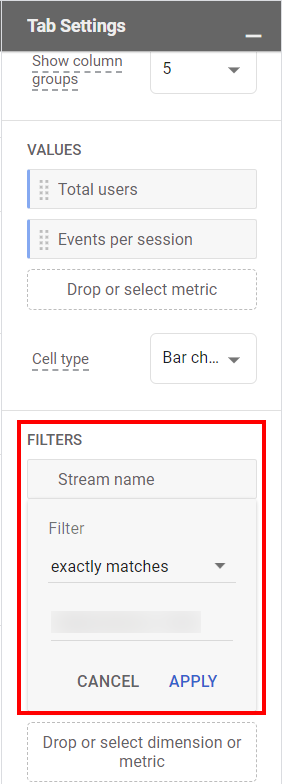
To configure data streams in Explore reports, open the report in the Explore section of GA4, and follow these steps:
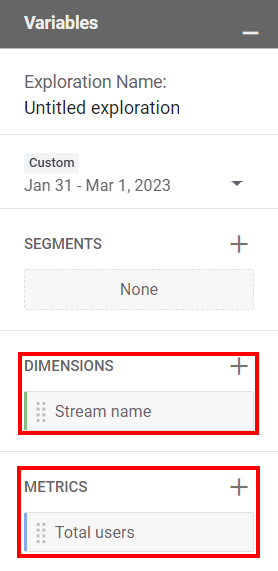
- Add "Stream Name" as a Dimension in the Variables column.
- Add the metric(s) you want the data for in the Variables column.
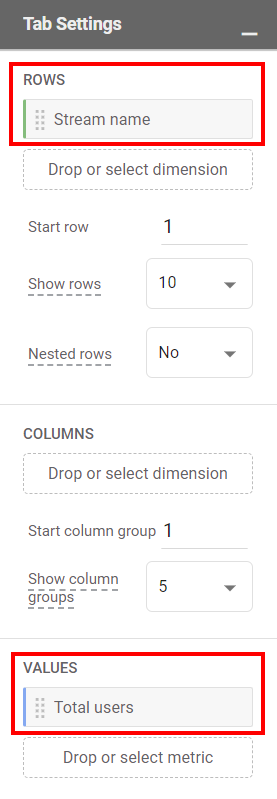
- Use Stream name in Rows under the Tab settings column.
- Add the Metric(s) in the Values under the Tab settings column.
- If you want to view the data for single streams, you can use the filters under the Tab Settings column.
By following these steps, you can configure the report for the stream and the data you want to see.
Examples of Using Data Streams
Let's look at some instances of how data streams may be utilized to better analyze user behavior and enhance the performance of your digital assets now that you are familiar with the fundamentals of managing data streams in GA4.
Monitoring Certain User Behaviors. You may track user behavior more precisely by building data streams for particular pages or features on your website or mobile app. To examine how customers are traveling through the checkout process and spot any bottlenecks that might be leading users to abandon their purchases, for instance, you can construct a data stream for your checkout page.
Data Segmentation by Source. You may use data streams to segment your data by source if you have various websites or mobile apps by creating unique data streams for each one. You can then utilize this information to see how consumers are interacting with each specific source and decide how to enhance their experiences based on statistics.
Comparison of User Behavior on Several Platforms. If you have both a website and a mobile app, you can generate distinct data streams for each and compare user behavior on each platform separately. By doing so, you'll be better able to comprehend how people are interacting with your digital domains and decide how to enhance their experiences based on data.
Conclusion
Now you have an understanding of how to manage data streams in GA4 and examples of how and where you can use it to better analyze and understand the behavior of users of your website or mobile application. Performing a comprehensive Google Analytics 4 audit can further refine your data management practices and ensure that you're leveraging the full potential of GA4 to optimize user experience and drive business growth.
Recommended theme posts
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses