What is Duplicate Content and How to Deal with It
The URLs are different, but the content of the pages is the same. Is this ever acceptable? After all, it is just a couple of identical pages on the site! Well, duplicate content can be problematic.
Not only does duplicate content make SEO promotion difficult, but it can also have a negative impact on page rankings in Google SERPs. To avoid this, you need to know how to get rid of internal duplicate pages.
The concept of duplicate pages and their types
Duplicates: multiple URLs for the same content
Duplicate content is individual site pages that have completely or partially the same content. In essence, these are copies of an entire page or a specific part of it, accessible via unique URLs.
What causes duplicates to appear on the site?
- Automatic generation of duplicate pages by the web resource's content management system (CMS) engine. For example:
- https://website.net/press-centre/cat/view/identifier/novosti/;
- https://website.net/press-centre/novosti/.
- Mistakes made by webmasters. For example, when the same product is presented in several categories and is available on different pages:
- https://website.net/category-1/product-1/;
- https://website.net/category-2/product-1/.
- Changes in site structure that occur when existing pages are assigned new addresses, but their duplicates with the old addresses are preserved. For example:
- https://website.net/catalog/product;
- https://website.net/catalog/category/product.
There are two types of duplicates: full and partial.
What are full duplicates?
These are pages that have the same content but are accessible through unique, dissimilar addresses. Examples of full duplicates:
- Page URLs with and without slashes ("/", "//", "///"):
- https://website.net/catalog///product
- https://website.net/catalog//////product
- HTTP and HTTPS pages:
- https://website.net
- http://website.net
- Addresses with and without "www":
- http://www.website.net
- http://website.net
- Page URLs with index.php, index.html, index.htm, default.asp, default.aspx, home:
- https://website.net/index.html
- https://website.net/index.php
- https://website.net/home
- Page URLs in upper and lower case:
- https://website.net/example/
- https://website.net/EXAMPLE/
- https://website.net/Example/
- Changes in the hierarchical structure of URLs. For example, if the product is available at several different URLs:
- https://website.net/catalog/dir/goods
- https://website.net/catalog/goods
- https://website.net/products
- https://website.net/dir/goods
- Additional parameters and tags in the URL.
- URLs with GET parameters. For instance, see https://website.net/index.php?example=10&product=25. This page is completely identical to the following page: https://website.net/index.php?example=25&cat=10.
- Availability of utm-tags and gclid parameters. Utm tags help provide information to the analytics system for analyzing and tracking various traffic parameters. The URLs of the landing pages that have utm tags added look like this: https://www.website.net/?utm_source=adsite&utm_campaign=adcampaign&utm_term=adkeyword.
- GCLID (Google Click Identifier) parameters. These are target URL tags that are automatically added to track company, channel, and keyword data in Google Analytics. For example, if someone clicks on your ad for https://website.net, the click-through address of the visitor will look like this: https://website.net/?gclid=123xyz.
- The yclid tag. This tag helps you track the effectiveness of advertising campaigns in Yandex Metrics. The tag allows you to track the actions of visitors who come to the site through an advertisement. Here's what the click-through address looks like: https://website.net/?yclid=321.
- Openstat tags. These are universal and are also used to analyze the effectiveness of advertising campaigns, monitor site traffic, and track user behavior on the site. Here is a link with the openstat tag: https://website.net/?_openstat=231645789.
- Duplicates that are created by a referral link. A referral link is a special link with your identifier that other sites use to recognize where the new visitor came from. For example:
https://website.net/register/?refid=398992
https://website.net/index.php?cf=reg-newr&ref=Uncertainty
- The first page of the product catalog of an online store, bulletin board, or blog. It often corresponds to a page of a category or a general page of a pageall section:
- https://website.net/catalog
- https://website.net/catalog/page1
- Incorrect 404 error settings can cause numerous duplicates to appear. For example:
- https://website.net/rococro-23489-rocoroc
- https://website.net/8888-??
The bold text may contain some characters and/or numbers. Pages of this kind should either return a 404 server response code (not 200) or redirect to the actual page.
What are partial duplicates?
In SEO, pages that are partial duplicates have the same content but with slight differences in the elements.
Types of partial duplicates:
- Duplicates on product cards and category pages (catalogs). Here, duplicates occur because of the product descriptions. The descriptions are presented on the general pages of products in the catalog, and the same texts are again presented on the product card pages. For example, there is a description under each product in the catalog on the category page and the same description text is used on the product page.
To avoid this type of duplicate, don't show the full product information on the category (catalog) page. Alternatively, use a non-repeating description.
- Duplicates on filter, sorting, search, and pagination pages, where there is similar content. Only the order of placement changes, while the description texts and titles are not changed.
- Duplicates on pages meant for printing or downloading, the data of which fully correspond to the main pages. For example:
- https://site.net/news/news-1
- https://site.net/news/news-1/print
Partial duplicates are harder to detect. But they have far-reaching consequences and can negatively affect the ranking of the website.
What issues can duplicate content lead to?
According to several technical SEO experts, duplicate content can appear regardless of the age of the site and the number of pages it has. While duplicate content will not prevent site visitors from accessing the necessary information, the situation is quite different with search engines robots. Since the URL parameters are different, search engines perceive these pages to be different.
Here are some of the consequences of having a large amount of duplicate content:
- Indexing problems. Duplicate pages increase the overall size of the site. When bots index unnecessary duplicate pages, the crawling budget of the owner of the web resource is inefficiently spent. As a result, the pages that actually need to be crawled might not even get into the index at all. As a reminder, the crawling budget refers to the number of pages that a search bot can scan during a single site visit.
- Changes in the relevance of the page in the search results. The search engine algorithm may decide that the double is more relevant to the query. Therefore, in the search results, it will show the wrong page that wasn’t meant to be promoted. Another undesirable outcome: due to competition between the duplicate pages, none of them will get into the search results.
- Loss of link weight of pages being promoted. Visitors may link to the duplicates rather than the original pages. The result is a loss of natural link mass.
Catalog of tools for finding duplicate pages
So, we have covered what duplicates are, what causes them, and what they lead to. Now let's move on to the important part — how to detect duplicates. Here are several methods that have been proven effective by technical SEO experts.
Finding duplicates with the help of special SEO programs
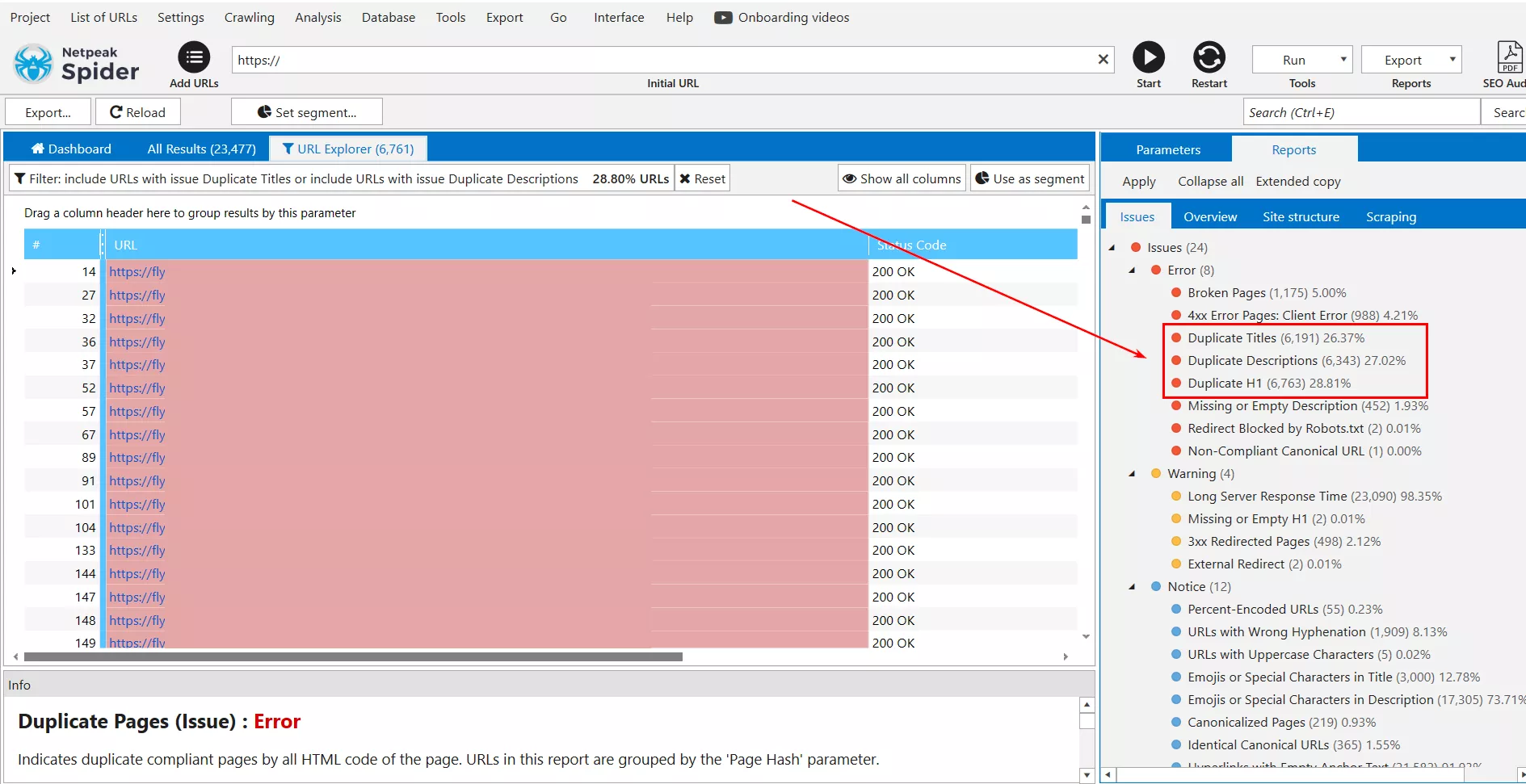
Netpeak Spider. By using the scanning feature, you can detect pages with duplicate content: full page duplicates, duplicate pages based on <body> block content, repeated "Title" tags, and "Description" meta tags.
Find duplicates using Netpeak Spider
Using search operators
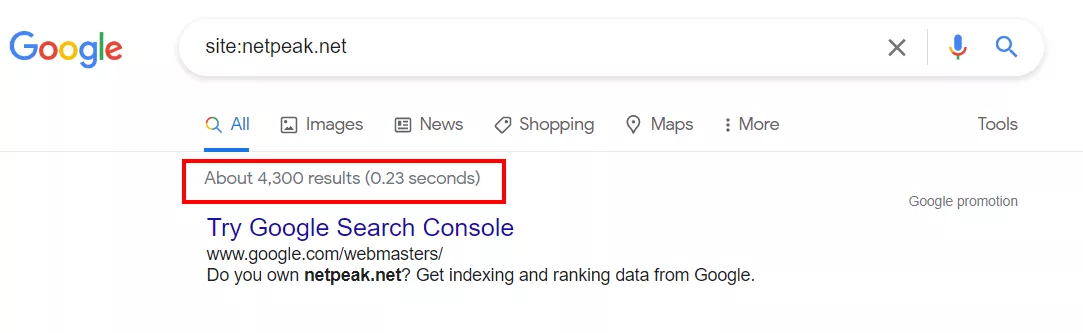
To find duplicates, you can analyze pages that are already indexed using the "site:" search operator. To do so, enter "site:examplesite.net" into a search box such as Google. It will show the pages of the site in the general index. Examine the number of pages in the output and see if it differs much from the number of pages found by the spider or in the XML map.
Next, look through the output to find recurring pages and "trash" pages that should be removed from the index.
You can also use the search function to analyze the output for a particular fragment of text from pages that may have duplicates. To do this, take part of the text in quotation marks, add a space after it, add the operator "site:", and enter it into the search box. It is necessary to specify your site to find pages that have this text. For example:
"A snippet of text from a site that may have duplicates" site:examplesite.net
If there is only one page in the search results, then the page has no duplicates. If there are several pages in the results, it is necessary to analyze them and determine the reasons for the duplicate text. Perhaps, there are duplicate pages that need to be removed.
In a similar way, using the "intitle:" operator, we can analyze the content of the "Title" on the pages in the rendering. A duplicate "Title" is sometimes a sign of duplicate pages. To check this, use the search operator "site:". An example of a search query:
site:examplesite.net intitle:full or partial Title tag text
Using the "site" and "inurl" operators, you can detect duplicate pages that appear on sort pages (sort) or on filter and search pages (filter, search).
For example, to search for sort pages, in the search box, you would type: site:examplesite.net inurl:sort.
To search for filter and search pages, type the following: site:examplesite.net inurl:filter, search.
Remember, search operators only show duplicates that have already been indexed. Therefore, you should not rely solely on this method.
How to get rid of duplicates
We have looked at what duplicates are, their types, their consequences, and how to find them. Now, let's move on to the most interesting thing — how to prevent duplicates from hurting SEO optimization. Here are some methods to eliminate duplicate pages:
301 redirect
This is considered to be the main method of eliminating complete duplicates. A 301 redirect performs an automatic redirect from one page of the site to another. When a 301 redirect is configured, bots will see that this URL page is no longer available and has been moved to another address.
A 301 redirect allows you to transfer the link weight from the duplicate page to the main page.
This method is useful to eliminate duplicates that appear because of:
- URLs in different registers.
- URL hierarchy.
- Definition of the main mirror website.
- Problems with the use of slashes in the URL.
For example, a 301 redirect can be used to redirect from these pages:
- https://site.net/catalog///product
- https://site.net/catalog//////product
- https://site.net/product to https://site.net/catalog/product
Robots.txt file
This method allows you to tell the search engine bots which pages or files should not be crawled.
In the robots.txt file, use the "Disallow" directive to prohibit search bots from accessing unnecessary pages.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /page
Please note that even if a page is specified in the robots.txt with the Disallow directive, this page may still appear in the results. Why? It has been indexed earlier or it may contain internal or external links. The robots.txt file contains instructions for search bots to scan the site, and it does not guarantee that duplicates will be removed.
Meta tag <meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow> and <meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow>
The <meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow"> meta tag tells the robot not to index the document and not to follow the links. Unlike robots.txt, this meta tag is a direct command and will not be ignored by search engine robots.
The <meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow"> meta tag tells the robot not to index the document, but still follow the links placed in it.
But according to Google's Search Advocate John Mueller, the "noindex, follow" meta tag will eventually be perceived by the search engine as "noindex, nofollow".
If the bot visits for the first time and sees the "noindex, follow" directive, then it will not index the page, but there is still a probability of clicks on internal links. But if the bot comes back after some time and again sees "noindex, follow", then the page is completely removed from the index, the bot stops visiting it and stops taking into account the links placed on the page. Essentially, in the long term, there is no difference between "noindex, follow" and "noindex, nofollow" meta tags.
To use this method, you should place one of the meta tags on the duplicate pages in the <head> block:
- <meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow" />
- <meta name="robots" content="none" />
- <meta name="robots" content="noindex, follow" />
Rel="canonical" attribute
Use this technical SEO method when you can't remove the page and it must be left open for viewing.
This attribute can help eliminate duplicates on filter pages, sort pages, and pages with get-parameters and utm tags. It is used for pages meant for printing, for different language versions, and across different domains. However, not all search engines support the rel="canonical" attribute for different domains. While it is clear for Google, Yandex will ignore it.
By specifying a canonical link, we are specifying the address of the page we prefer to be indexed. For example, the website has a category called "Laptops”. It has filters that show different selection parameters, such as brand, color, screen resolution, case material, and so on. If these filter pages are not meant for promotion, then specify a common category page for their canonical attribute.
How to specify the canonical page? Place rel="canonical" attribute between <head>...</head> tags in the HTML code of the current page. For example, for pages:
- https://site.net/index.php?example=10&product=25
- https://site.net/example?filter1=one
- https://site.net/example/print
The canonical page will be https://site.net/example.
In the HTML code, it will look like this: <link rel="canonical" href="https://site.net/example" />
The canonical page: the best representative page of a group of duplicates
Best Practices
Avoid duplicate content on pages with different URL parameters
This is the most common mistake that leads to the generation of duplicate pages on the site.
It occurs most often on e-commerce sites where product cards are presented with minimal distinction. For example, phone covers of different colors from one manufacturer for a certain model of iPhone.
If your website has a separate page with its own URL address for each product variant (i.e., color), but the content (description, characteristics) of the different pages is almost the same — this will lead to the appearance of duplicates. An example of this error:
- https://domain.com/case1-for-iphone-black
- https://domain.com/case1-for-iphone-red
- https://domain.com/case1-for-iphone-white
To avoid this issue, you can either display all dynamic attributes on the same URL or create unique content for each product variant.
Also, this problem applies to search results within the website:
The URLs of internal search results pages can and will be different, but the content of such pages (search results) will be very similar. Having such pages indexed will result in the generation of hundreds of duplicate pages. Example:
- https://domain.com/search-results/?text=smartphone
- https://domain.com/search-results/?text=smartphones
- https://domain.com/search-results/?text=smart+phones
Keep track of the number of pages in the index
As described earlier, the easiest way to identify the number of indexed pages is to use the search operator "site:yourdomain.com".
If you have access to Google Search Console, you can additionally check the number of pages in the search using the "Index" category.
If the number of pages in the index is much higher than the number of manually created pages, it indicates that URLS are being automatically generated and indexed. As a rule, the content on such pages differs minimally, which makes them duplicate pages.
Choose the main mirror of the site and ensure that redirects are set correctly
It is important to remember that duplicates are not limited to site pages. The entire website can be duplicated.
That said, such cases are rare and often associated with incorrectly configured redirects to the main version of the site. For example, the versions:
- http://domain.com / https://domain.com
- www.domain.com / domain.com
Just remember that all alternate versions of the site should redirect to the main site to avoid problems with SEO promotion.
Set up 301 redirects
The easiest way to deal with duplicate pages on your site is to use 301 redirects.
If there are duplicates on your site, set up a 301 redirect to the main page.
With this method, Googlebot won't be able to get to the duplicate pages and will index the pages you want.
Create unique content
As mentioned,duplicate content can be full or partial duplicates.
If you have a New York apartment cleaning page and a New Jersey apartment cleaning page, Google may perceive them differently as they are technically different pages. This is known as a partial duplicate.
Our advice is to create 101% original content, at least for the main pages of your site. It may be difficult and costly, but it is worth it as unique content will produce great results in the long run.
Configure the Canonical tag
The rel=canonical tag is highly useful. It signals search engines that this particular page, out of many similar pages on your website, is the original page and should be ranked in Google’s SERP.
Combine similar content
If you have pages with similar but technically different content that compete with each other in search engine rankings, try combining them into one page. For example, here are three articles that may compete with each other:
- How to choose a quadcopter.
- How to choose a quadcopter for blogging.
- How to choose a quadcopter for photography.
Combine them into one mega guide! You will get rid of partial takes, and Google will see your content as the most complete and potentially more useful than your competitors’ content.
Keep WordPress tags and category pages from being indexed
WordPress can automatically generate new tags and category pages. Such pages are the source of a lot of duplicate content.
That said, these pages are often necessary to preserve the usability of the site, so exclude them from search engines using the "noindex" tag. Thus, the pages will remain accessible to users but will be hidden from search engine robots. Alternatively, disable the creation of such pages on WordPress.
Frequently asked questions
Are there search engine penalties for duplicate content?
There are no explicit penalties as such for duplicating content. However, the presence of duplicates makes it difficult to promote the website and negatively affects the ranking of the site's pages.
The intentional use of a large amount of someone else's content may be a basis for taking action against your site if Google determines that the purpose of the duplicate content is to deceive and manipulate search engine results.
Will fixing duplicate content issues improve my site's rankings in the Google SERP?
Absolutely! Getting rid of duplicates will help search engines better understand which pages are original and which need to be indexed and ranked.
In addition, eliminating duplicates is better for the crawl budget. Search engines will spend your crawl budget on processing the truly important pages that you want to promote.
Can duplicate content ever be acceptable?
There is no official answer to this question from Google. In any case, duplicate pages make it difficult to promote your website and negatively affect rankings. One thing can be said for sure: the more unique content, the better.
Is duplicate content harmful?
Yes, duplicate content is definitely harmful. In most cases, duplicate pages do not lead to sanctions from search engines, but pages with similar content will indirectly (and negatively) affect page promotion and worsen the ranking of your website's pages in Google SERP.
Conclusions
- Duplicates are separate website pages that have completely or partially the same content.
- Why do duplicates occur? Automatic generation, mistakes made by webmasters, and changes in the site structure are the most common reasons.
- Why are duplicates problematic? Indexation becomes worse, pages in search results undergo harmful changes in relevance, and the natural reference mass of the established pages is lost.
- How can you find duplicates? The easiest ways are to use spider programs (Netpeak Spider) or the “site:” search operator.
- How to get rid of duplicates? Techniques include using appropriate commands in the file robots.txt, using tags such as tag meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow" and tag rel="canonical", and implementing 301 redirects.
Have you eliminated duplicate content from your website? If you have, well done! Now, take another look at the website, and you can evaluate the benefits of eliminating duplicates and the effectiveness of the chosen method. Going forward, for timely detection and elimination of errors, it is recommended that website analysis is regularly performed to check for duplicates.
Related Articles
How to Set Up Consent Mode in GA4 on Your Website with Google Tag Manager
Let's explore how to properly integrate consent mode in GA4, configure it for effective data collection, and at the same time comply with GDPR and other legal regulations
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers