Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is a powerful web analytics tool that can help you gain valuable insights into your website traffic, user behavior, and conversion performance. However, to make the most of GA4, it's important to ensure that your data collection is accurate and complete.
In this article, we'll guide you through the process of auditing GA4 and identifying common issues that can impact your data quality and reporting.
Check if the data is collected
Before you analyze your GA4 reports, make sure your data collection setup is error-free and technically sound.
To ensure your tracking infrastructure is fully optimized—and to catch any hidden technical misconfigurations—it’s worth conducting an In-depth Technical SEO Audit. This audit will go beyond analytics and help identify issues that might affect both data accuracy and site performance.
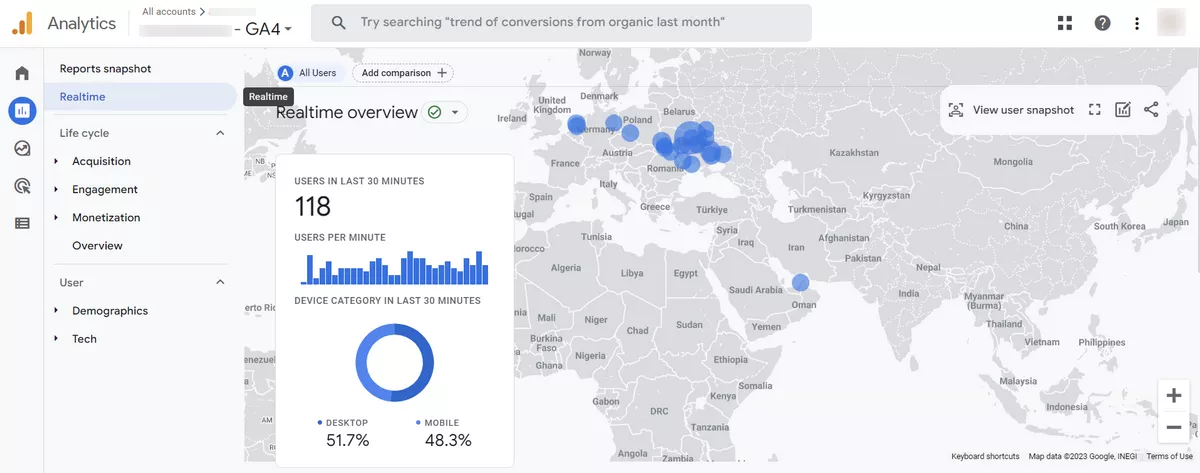
The first step in auditing GA4 is to verify that data is being collected from your website or app. You can do this by checking the Realtime report in GA4 and looking for active user sessions.
If you don't see any data, it's likely that your GA4 implementation is not working correctly. It is necessary to understand and check how your Google Analytics 4 was implemented.
Because there are several options for implementation:
- Integration with CMS.
- F Directly in the code.
- Via GTM.
You need to stick to one implementation option to have clean tracking.
If you prefer to implement it in code, then everything should be configured directly in the source code.
If you are using Google Tag Manager, it is recommended to configure all your tags through GTM. This way, you will ensure that your tags are clearly organized as well as efficiently tracked.
Web analytics underpins conversion optimization. What will CRO get you? Find out with Netpeak's calculator.
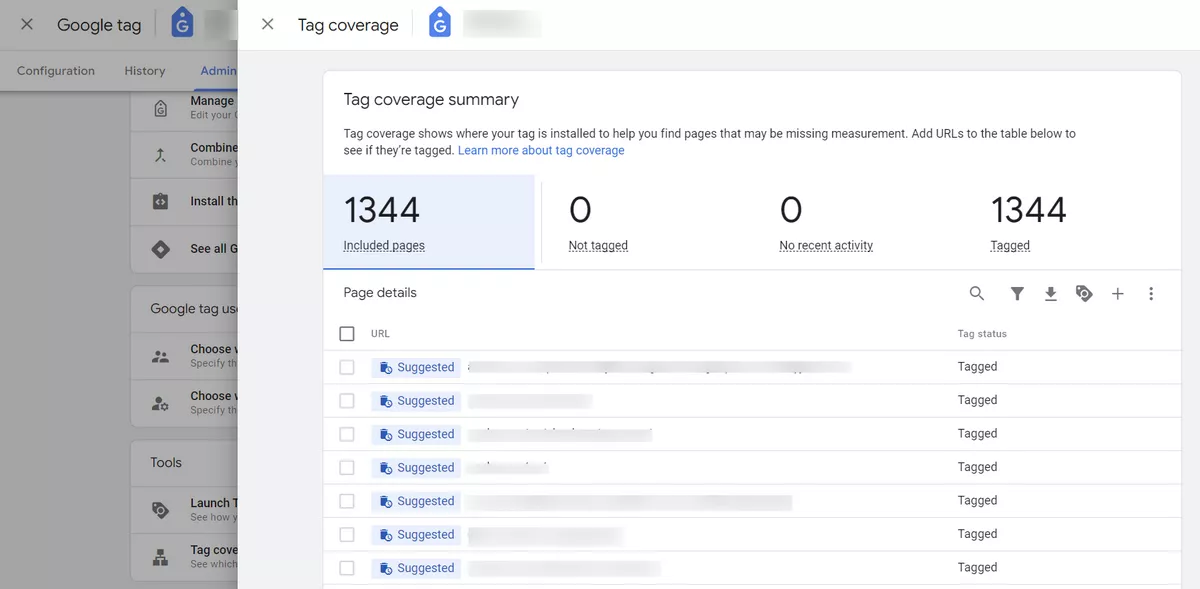
Are all pages tagged?
Another critical aspect of GA4 auditing is to ensure that all pages on your website are tagged with the appropriate data stream and event codes.
You can see it in Admin Property → Settings → Data Streams → Web Stream Details → Configure Tag Settings → Admin → Tag Coverage.
.
Most common issues
There are several common issues that can impact GA4 data quality and reporting.
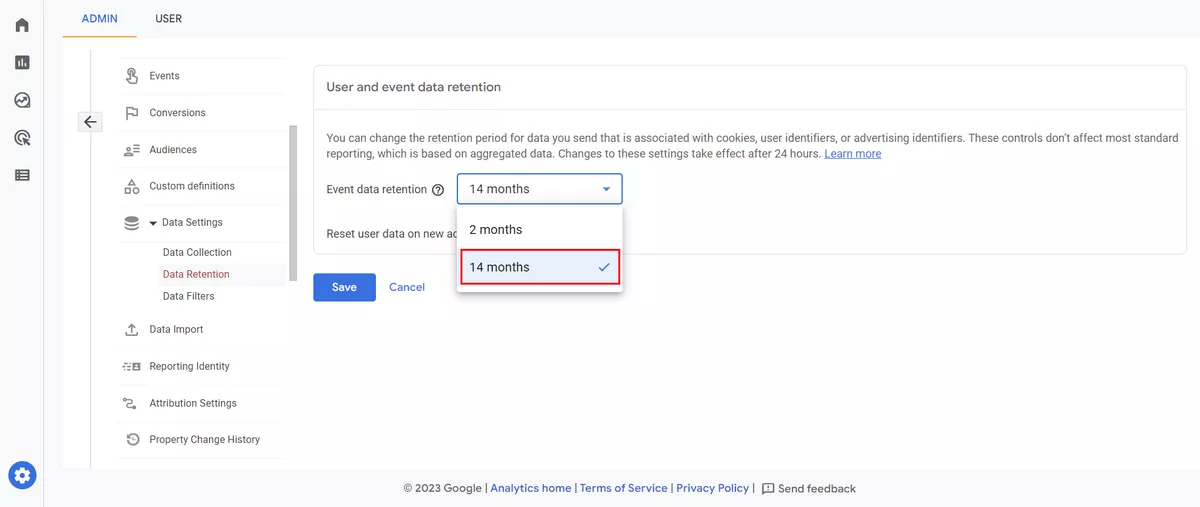
Data retention
Data retention settings allow you to control how long GA4 will retain user and event data. Make sure that you've adjusted your data retention settings to match your business needs and compliance requirements.
Your default setting for data retention is two months. You can change it to 14 months.
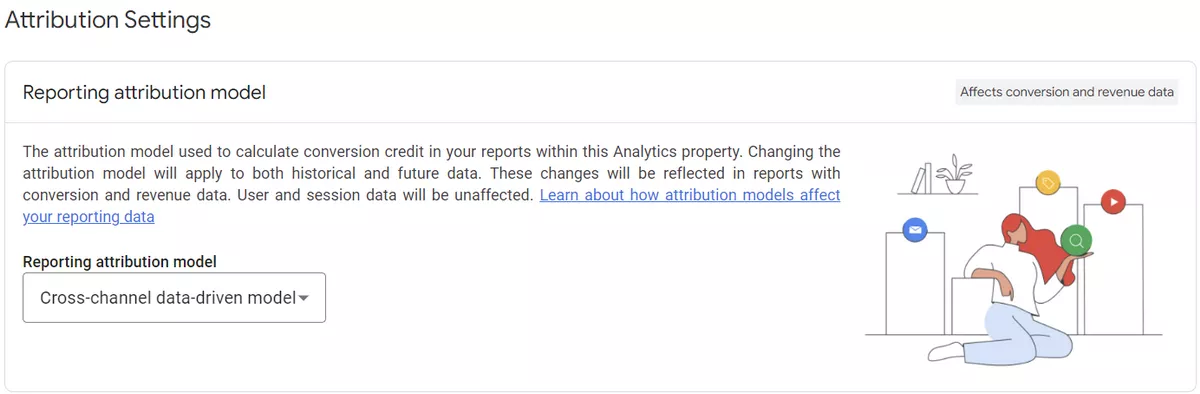
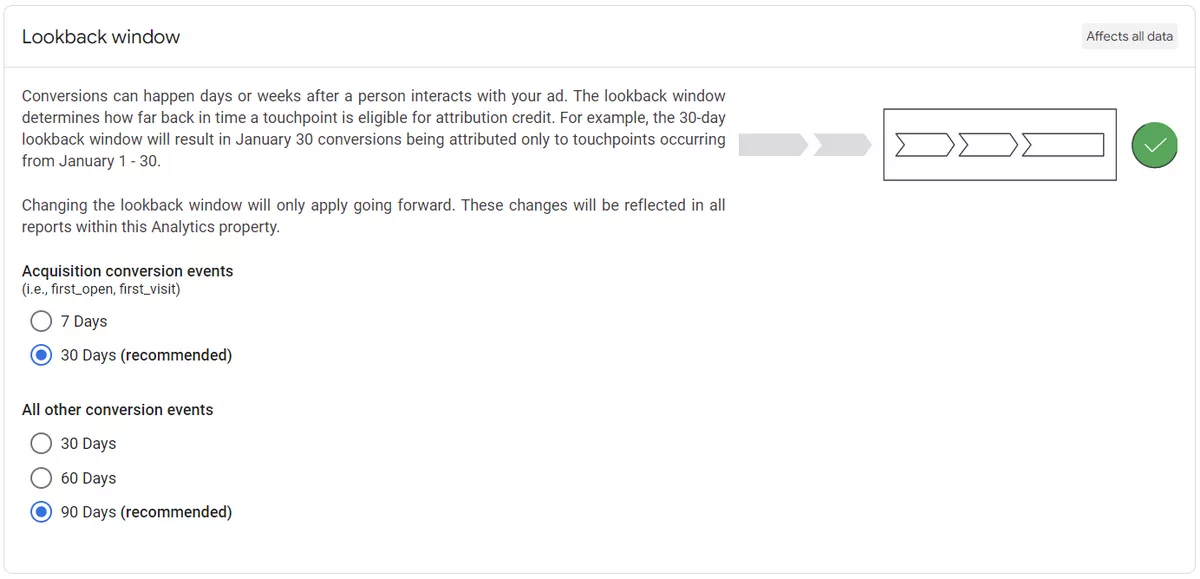
Attribution settings
Setting up attribution in GA4 allows you to track which marketing channels and traffic sources influence user behavior on your website, as well as understand which events and conversions were made thanks to these channels. This allows you to optimize your marketing campaigns and traffic acquisition more effectively.
You can choose one of the following attribution models: last click, first click, linear, time decay, position-based, and decreasing influence.
The attribution lookback window defines the period of time for which GA4 will attribute user actions to a particular campaign or source. Make sure that you've chosen the appropriate lookback window based on your business needs and conversion cycle.
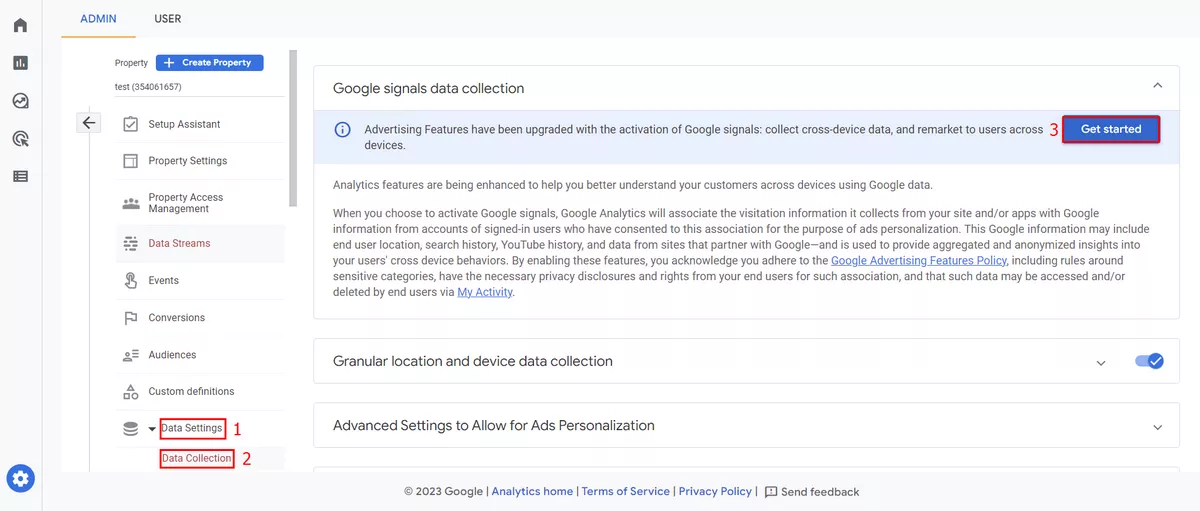
Do you use Google Signals?
Google Signals is a feature that allows you to track users across devices and platforms, providing a more complete view of user behavior. If you're using Google Signals, make sure that it's configured correctly and that you've enabled cross-device reporting in your GA4 property settings.
To activate Google Signals you need to go to Data Settings → Data Collection, and click Get Started.
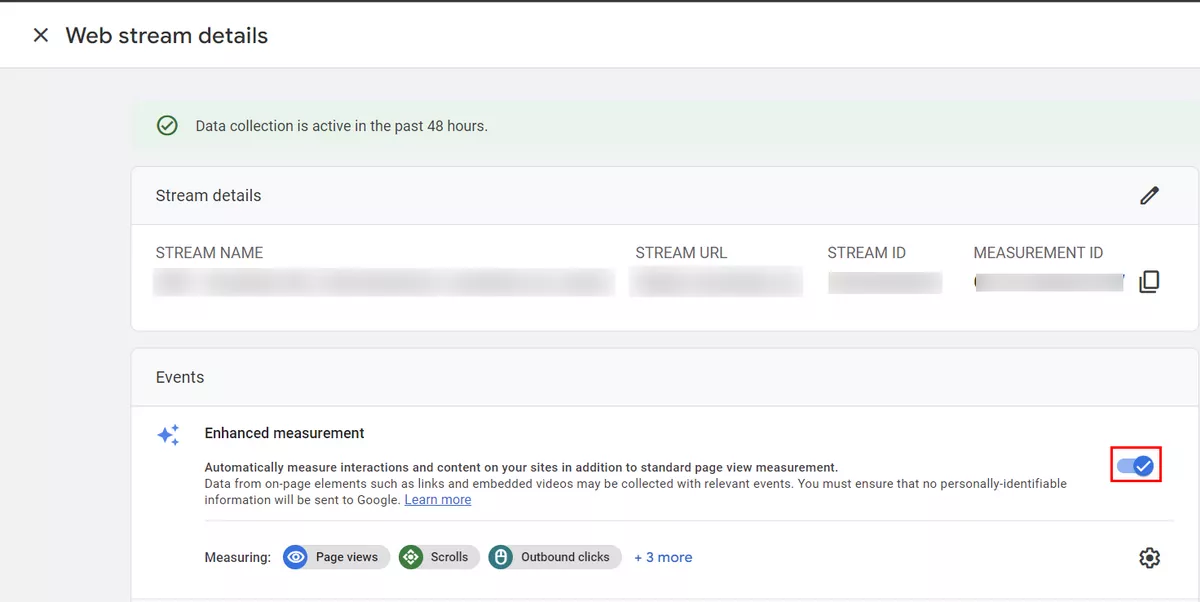
Are you using enhanced measurement?
Enhanced measurement provides additional tracking capabilities for certain user interactions, such as video plays and file downloads. Make sure that you've enabled enhanced measurement and configured it correctly.
404 page is not tracked
The problem of untagged 404 pages, can interrupt the user journey and result in unreliable metrics. Make sure that your 404 error page is tagged with the appropriate data stream and event codes so that you can track user behavior on this page.
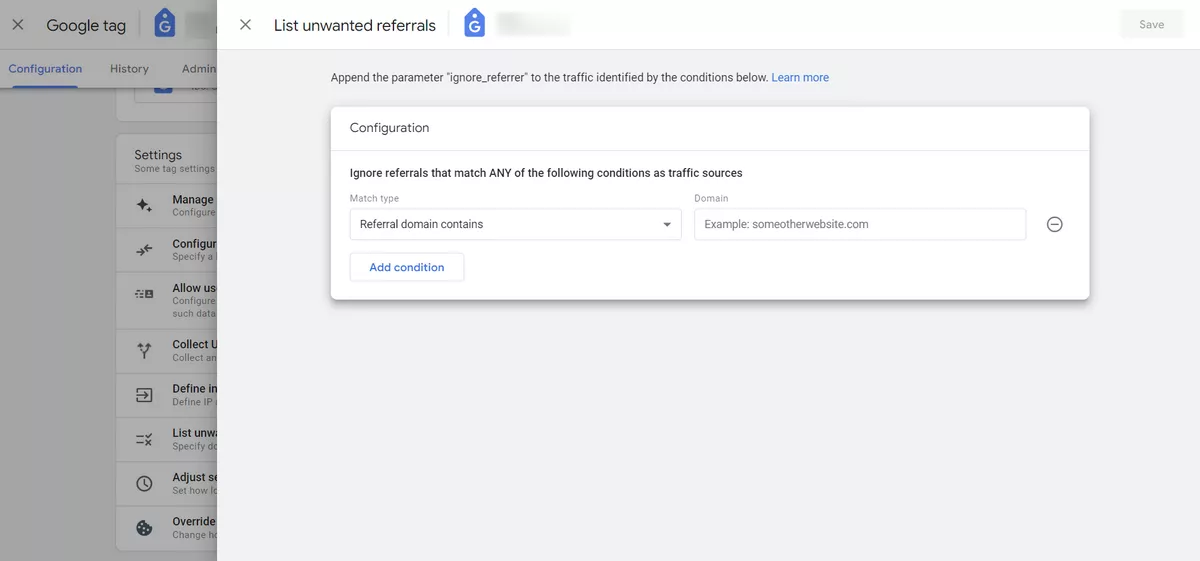
Self-referrals
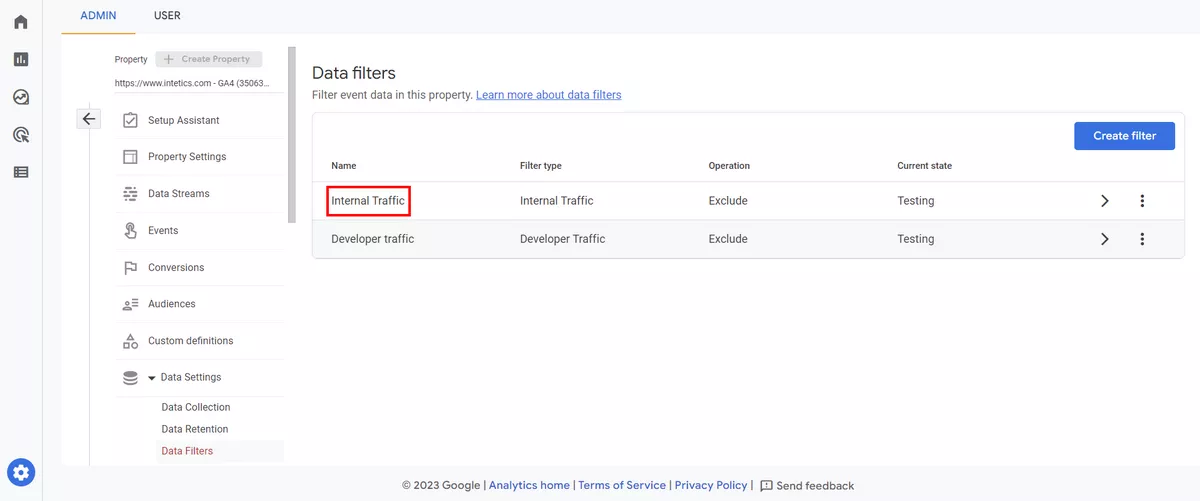
If your website or app is generating self-referrals, it can skew your traffic sources and attribution reporting. Use a filter to exclude self-referrals from your data.
You can find this filter here: Admin Property → Settings → Data Streams → Web Stream Details → Configure Tag Settings → Show All → List unwanted referrals.
Exclude internal traffic
To ensure accurate reporting, it's important to exclude traffic from internal users, such as employees or contractors. You can use IP filters or a custom dimension to exclude internal traffic.
Check your ecommerce events
If you have an ecommerce site it's very important to check that all eсommerce events for GA4 are being recorded correctly because ecommerce events in Google Analytics 4 have slightly different names compared to Universal Analytics. Such as "view promotion" and "select promotion" instead of "promo view" and "promo click," respectively. GA4 offers a more logical naming convention for ecommerce events, such as "view item list" instead of "impressions," and "select item" instead of "click item" or "impression click".
The purchase event is the most important ecommerce data in GA4, and the syntax for the event is slightly different from Universal Analytics.
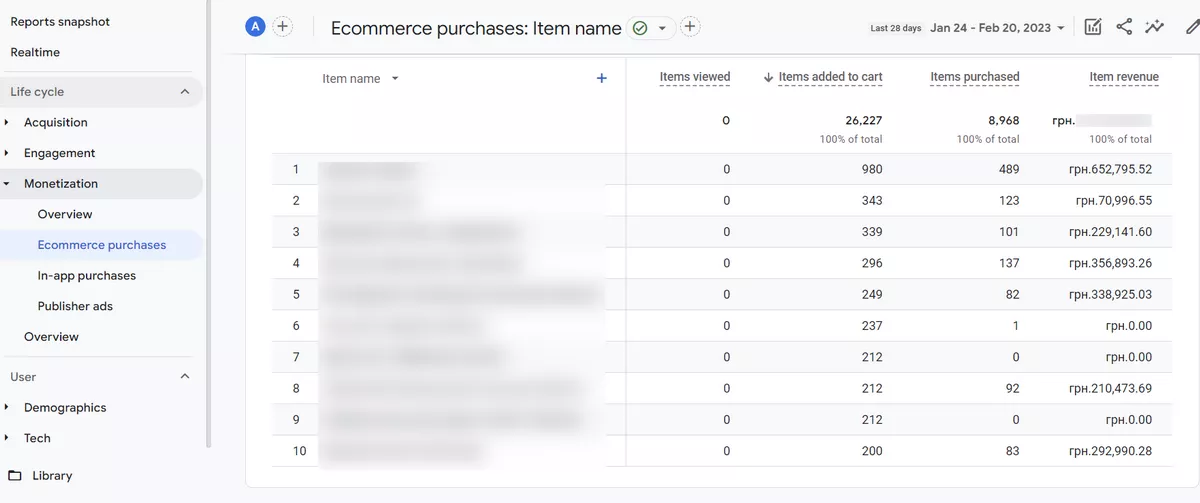
You can use the Monetization report in GA4 to verify that transaction and product data is being collected and reported accurately.
In this screenshot, you can see that the “items viewed” data are not transferred to the report.
Connect the products
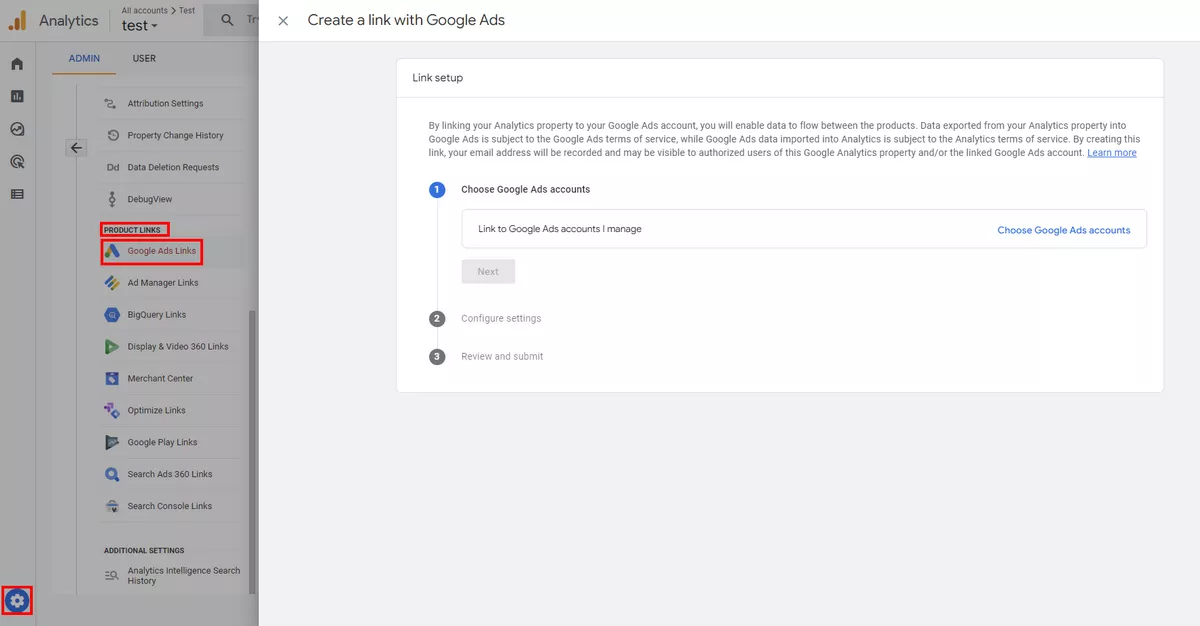
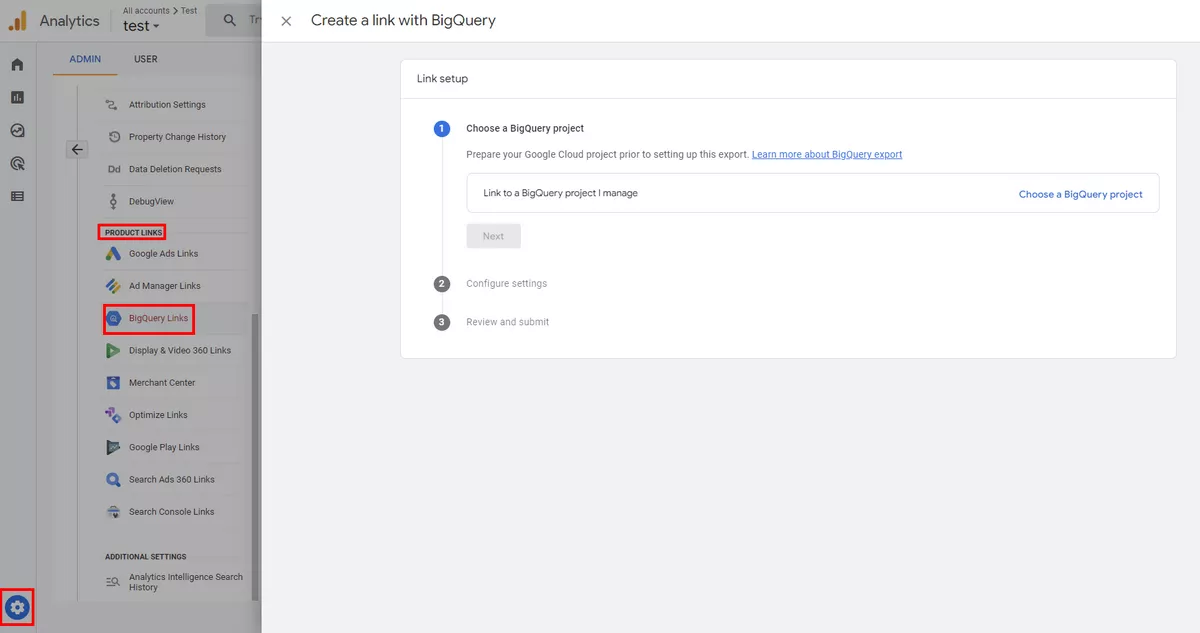
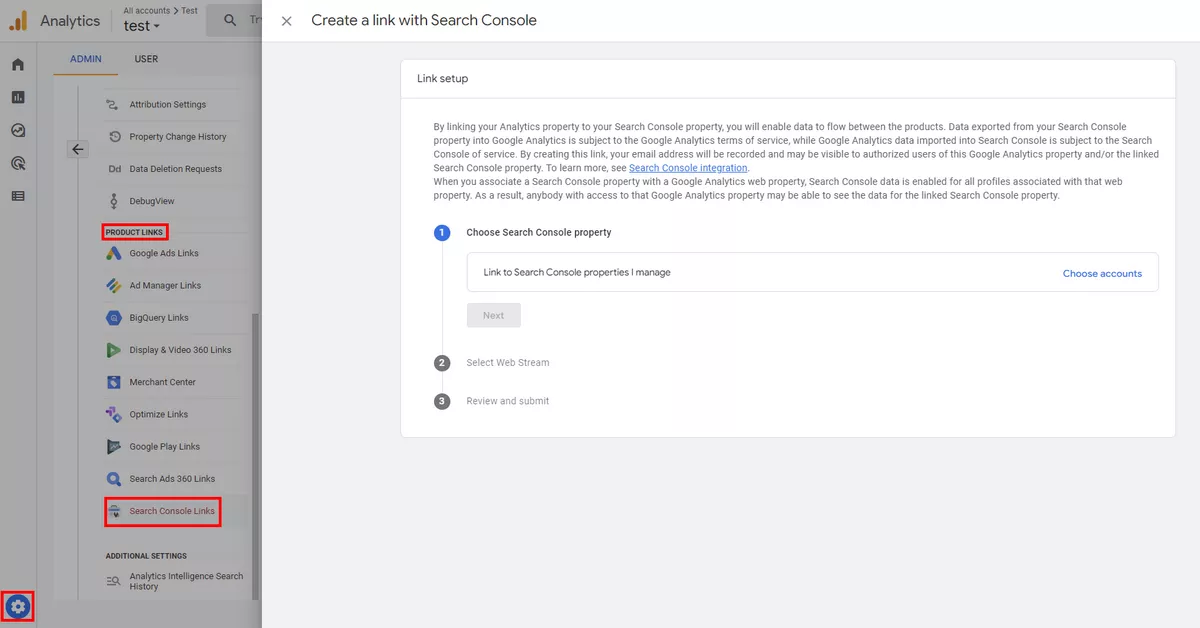
To see the settings for connections go to Admin then click Product Links and then select the product you are interested in.
Below are the main products that are a must-have when combined with GA4.
Google Ads
By linking GA4 with Google Ads, you can track the performance of your ads and gain insights into how they are driving traffic to your website.
Looking for ad monetization services? Netpeak has one.
Google BigQuery
Combining GA4 with BigQuery, you can export GA4 data to BigQuery for more in-depth analysis and reporting, and it is also beneficial because you can keep data longer than the 14-month retention period.
Search Console
By connecting GA4 with Search Console, you can see how your website is performing in to organic search and track user behavior on your website.
Also GA4 allows for easy integration with Google services, such as Display & Video 360, Merchant Center, Search Ads 360, Google Play, and Firebase.
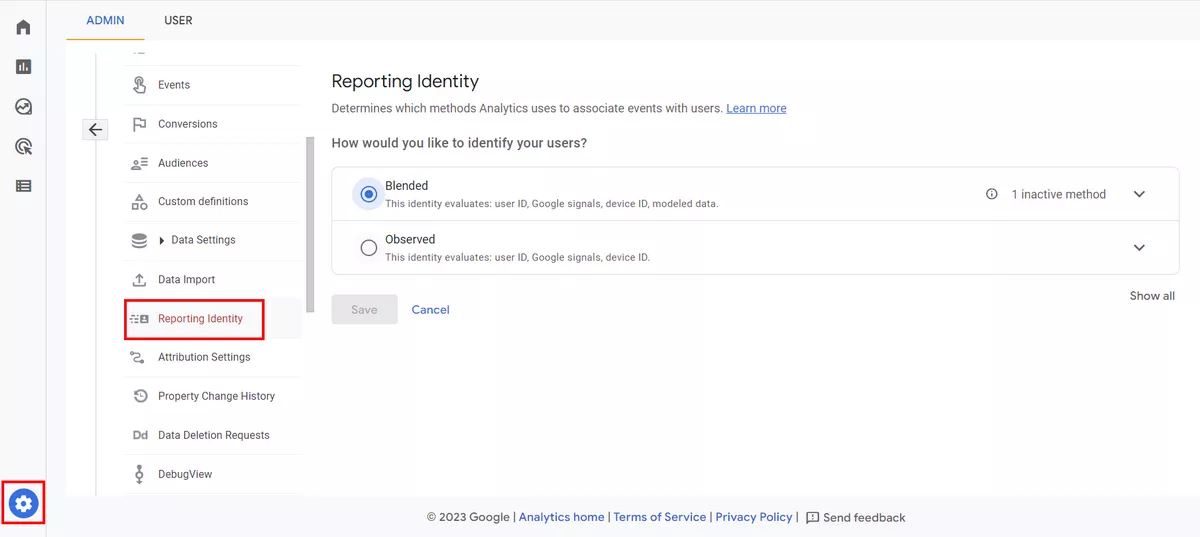
Choose your reporting identity
Reporting identity allows you to customize how user and session data is attributed to different dimensions, such as source/medium, campaign, or user ID. Make sure that you've chosen the appropriate reporting identity and that it's consistent across all reports.
Navigate to Admin, then choose Reporting Identity.
User ID
Using User ID you can track individual users across devices and sessions, and gain insights into their long-term behavior and preferences. This information can help you optimize your content and user experience, and ultimately drive more conversions.
Make sure that it's set up correctly and that user IDs are being passed correctly in your data stream. How to send a User ID to GA 4 you can read on the official Google Guide.
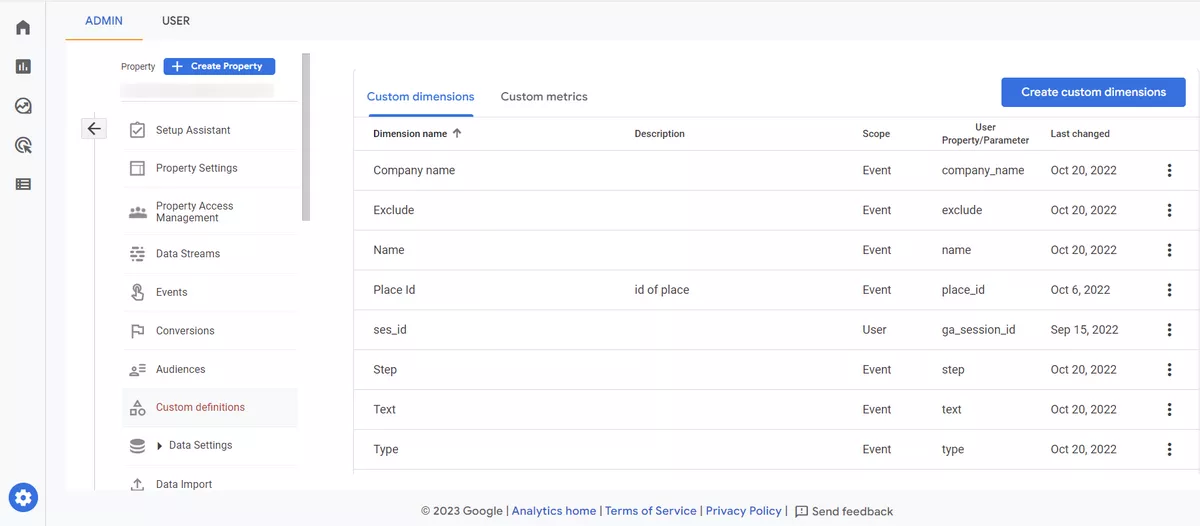
Use Custom Dimensions and Metrics
Your GA4 tracking should align with your business goals and objectives. This means that you should be tracking the key metrics and dimensions that are most important to your business. During your audit, you should evaluate your tracking plan to ensure that it accurately reflects your business goals and that you are tracking all of the key metrics and dimensions that are important to your business. Use custom metrics in conjunction with standard metrics to calculate KPIs that are unique to your business.
Keep traffic in the right channels
Very important to keep traffic in the proper channels.
Unlike Universal Analytics, GA4 doesn't have filters to quickly adjust and fix incorrectly tagged traffic sources. The most common issues are when the same traffic source is reported on different sources, such as when Facebook is spelled differently or written in different cases. To keep traffic consistently falling into the right source, users should look through Google's naming conventions, write clear UTM documentation, and run regular UTM audits to check for anomalies in traffic.
To ensure you implement it correctly, consider using Google Analytics 4 Services to set up tracking, reporting, and advanced configurations.
Checklist for auditing GA4
Below is a summary checklist for auditing GA4 based on the article:
- Verify that data is being collected from your website or app by checking the Realtime report in GA4.
- Ensure that all pages on your website are tagged with the appropriate data stream and event codes.
- Check and adjust data retention settings.
- Set up attribution in GA4.
- Configure Google Signals if you want to track users across devices and platforms.
- Enable enhanced measurement to provide additional tracking capabilities.
- Tag your 404 error page.
- Exclude self-referrals and internal traffic.
- Check that all e-commerce events for GA4 are being recorded correctly, paying attention to the different naming of events compared to Universal Analytics.
- Connect GA4 with essential products like Google Ads, Google BigQuery, and Search Console for better tracking and analysis.
- Choose a reporting identity.
- Set up User ID correctly to track individual users across devices and sessions.
- Use custom dimensions and metrics to track key metrics and dimensions unique to your business.
- Keep traffic in the proper channels by following Google's naming conventions and running regular UTM audits.
For a more structured and professional approach, consider our Google Analytics 4 Audit Services — we’ll help you uncover missed opportunities, fix misconfigurations, and maximize the value of your GA4 setup.
Conclusion
Auditing GA4 is an important part of ensuring accurate and complete data collection for your website or app. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can identify common issues that can impact your data quality and reporting and take corrective action to improve your GA4 implementation.
Regular auditing and monitoring of your GA4 data will help you gain more insights and make more informed decisions about your website or app performance.
FAQ
What is a GA audit?
A GA audit is the process of evaluating the setup and performance of Google Analytics (GA) on a website or app. It helps website, app owners and digital marketers identify any issues or areas for improvement in their GA implementation, ensuring that they are collecting accurate data and making informed decisions based on that data.
What should be included in a Google Analytics audit?
A thorough Google Analytics 4 audit should include an evaluation of the tracking code implementation, data quality and accuracy, events tracking and conversion setup, attribution modeling, and custom tracking configuration. It should also cover GA integrations with other platforms such as Google Ads, Search Console, BigQuery, and other Google services, as well as the reporting identity and user ID setup.
How to do a Google Analytics audit?
To perform a GA audit, you need to have a good understanding of Google Analytics, how it works, and its various features and functionalities. The audit can be done manually by reviewing the GA configuration and reports, or by using auditing tools and plugins. It's important to have a clear audit plan and checklist.
For businesses seeking expert guidance and support in conducting comprehensive Google Analytics audits and optimizing their web analytics setup, partnering with a specialized web analytics agency can provide tailored strategies and expertise to enhance data accuracy, reporting capabilities, and overall digital performance.
Recommended theme posts
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses