Transactional emails are automated emails that are sent to users in response to their interactions with a website or application. These can include delivery notifications, payment receipts, and other messages that ensure user information and support.
These emails help businesses enhance customer interaction. When used skillfully, they are a powerful tool that can expand the company’s influence and generate profit.
In this article, I will explain what makes an email transactional, the different types of transactional emails, how they differ from marketing emails, and how to evaluate their effectiveness.
What makes an email transactional?
An email is considered transactional if it contains information directly related to the user’s action, such as order confirmation or payment failure notification. In other words, transactional emails do not promote products or services; they aim to inform the user.
Here are some of the key characteristics of transactional emails:
- Personalized content. Transactional emails contain personalized information about specific user actions, such as order confirmation, delivery notifications, or password reset instructions.
- Response to user action. These emails are automatically sent in response to specific user actions, such as a purchase, registration, or password recovery request. They are part of the interaction chain between the user and the service.
- informational purpose. The main purpose of transactional emails is to provide users with important information necessary to complete a transaction or resolve issues. Unlike marketing emails, transactional emails are not intended to promote products or services and are focused on increasing loyalty and building trust.
- Relevant and important. Because these emails are directly related to the user’s actions, they have a high degree of relevance and importance to the recipient. This gives them higher open rates and engagement compared to regular marketing emails.
- Automated sending. Transactional emails are sent automatically through systems integrated with the website or application. This ensures timely delivery of messages without the need for manual intervention.
Transactional emails play a crucial role in ensuring a positive user experience, providing necessary information, and maintaining ongoing communication between the company and the customer.
Transactional versus marketing emails
There are a few key differences between these two common types of emails.
Transactional emails are sent in response to specific user actions and contain information that is essential for completing a transaction or carrying out another action. These emails are sent in response to user requests and do not require user consent.
Marketing emails are aimed at promoting the company’s products or services. They often contain promotional offers, and users have to consent to receiving them.
|
Key Differences |
Transactional Emails |
Marketing Emails |
|
Purpose |
Inform the user about the status of a transaction, send a password reset link, email verification request, refund request form, or the completion of a purchase. |
Promote products and services and increase sales. |
|
Content |
Personalized and relevant to a specific user action. |
Promotional content that may be targeted but is not always related to a specific action. |
|
Automation |
Sent automatically in response to user actions. |
Often sent as part of pre-scheduled campaigns or based on audience segmentation. |
|
Open Rate |
Usually have a high open rate due to their importance and relevance. |
Often have a lower open rate. These emails may also have lower engagement rates because they often lack strong customer involvement. Additional incentives are needed to encourage email opens. |
Examples of marketing emails include promotional campaigns, product recommendations, holiday offers, newsletters, and updates, as well as invitations to participate in webinars and events. Trigger emails can also be promotional. For example, they can be used for reactivating purchases, offering to buy a follow-up or extended service, or reminding the customer of the need to renew a purchase.
Types of transactional emails
Transactional emails are essential tools for communication between businesses and their customers. They provide critical information and updates related to the customer’s interactions with a company. Below is an in-depth look at various types of transactional emails, each serving a unique purpose in the customer journey.
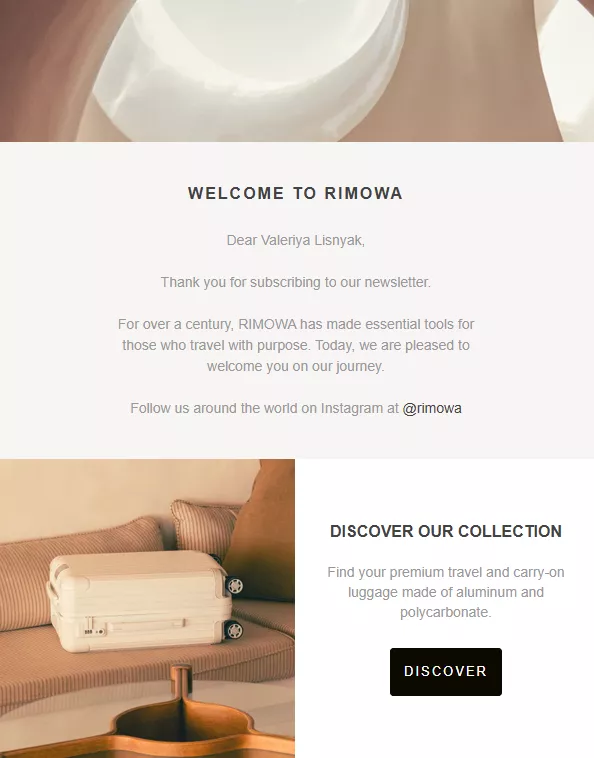
Welcome emails
Purpose: Emails about successful subscription and registration are the first point of contact between a business and a new subscriber or customer. They set the tone for the relationship and enable businesses to make a positive first impression.
Content: Typically, a welcome email includes a warm greeting, an introduction to the brand, and a summary of what the customer can expect going forward. It might also offer a special discount or a guide to getting started with the service or product.
Best Practices: Personalize the email by including the customer’s name, and ensure that the design is consistent with your brand’s identity. Mentioning the next steps and including links to helpful resources can further enhance the customer’s onboarding experience.
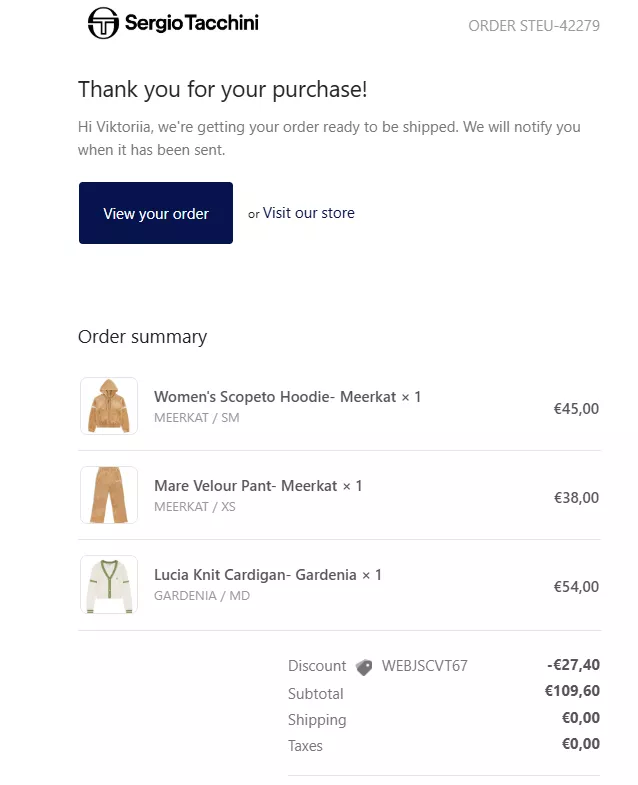
Order confirmation emails
Purpose: Sent immediately after a customer places an order, these emails confirm the details of the purchase. They reassure customers that their order has been successfully received. It’s also about customer care, allowing the client to review all details, ensure accuracy, and report any errors in the order if necessary.
Content: Order confirmation emails should include a summary of the purchased items, the total cost, payment details, and an estimated delivery date. It often includes a link to track the order or view the order status on the company’s website.
Best Practices: Ensure all order details are accurate, and include a strong call to action, such as tracking the order or contacting customer support if there are any issues.
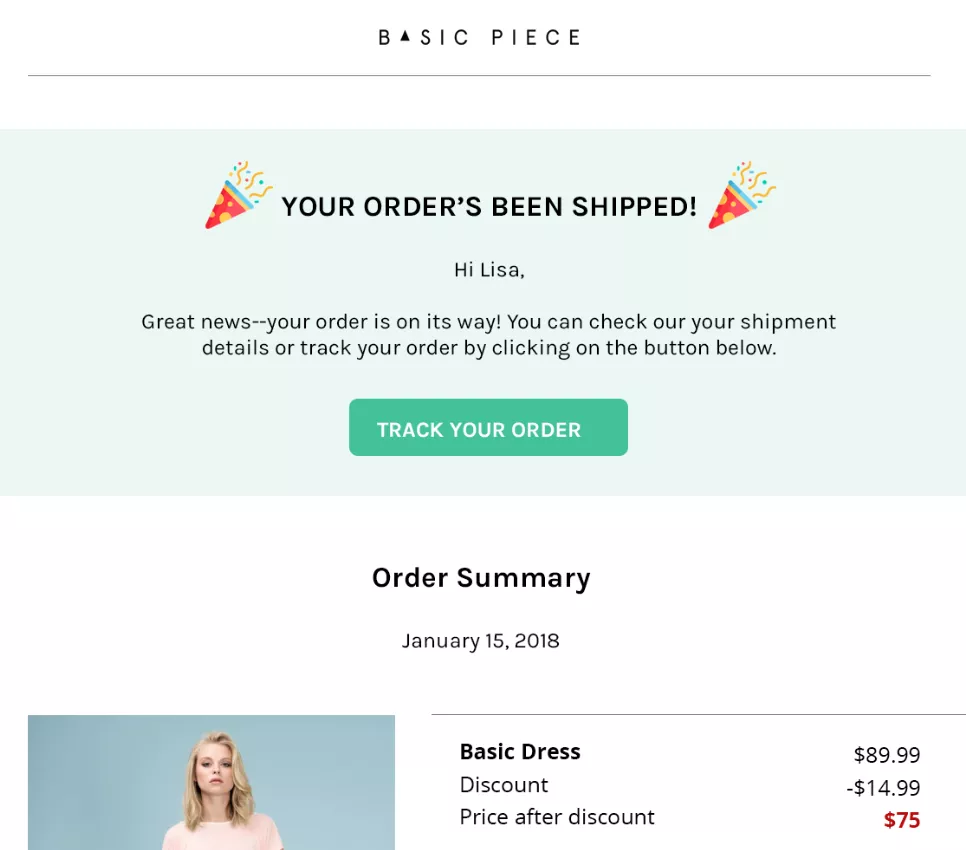
Shipping confirmation emails
Purpose: Once an order has been shipped, a shipping confirmation email is sent to inform the customer that their order is on its way.
Content: This email typically includes the shipping carrier’s name, a tracking number, and an expected delivery date. It may also contain a summary of the items being shipped and the shipping address.
Best Practices: Provide clear tracking information and a direct link to the carrier’s tracking page. Include contact information for customer support in case of delivery issues to further enhance the customer experience.
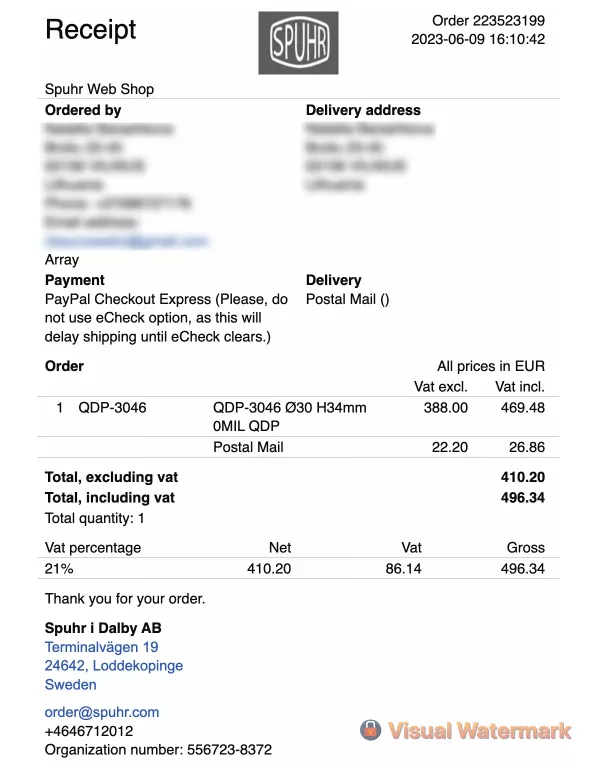
Payment invoice emails
Purpose: Payment invoice emails are sent to customers to confirm that their payment has been successfully processed. These emails serve as an official record of the transaction.
Content: The email includes details such as the amount charged, payment method, date of the transaction, and any applicable taxes or discounts. It often acts as a receipt for the customer’s records.
Best Practices: Ensure that the invoice is clear and easy to understand. If possible, include a downloadable PDF version of the invoice for the customer’s convenience.
Purchase receipt emails
Purpose: Similar to payment invoice emails, purchase receipt emails confirm the details of a completed purchase and provide a record of the transaction.
Content: These emails typically include a breakdown of the purchase, including itemized costs, payment details, and a confirmation number. They may also contain information on how to return or exchange the items.
Best Practices: Clearly differentiate between a receipt and an invoice if both are sent. Provide easy access to customer support or return policies directly within the email.
Payment failure notifications
Purpose: When a payment fails to process, it’s crucial to notify the customer promptly. Payment failure emails alert customers to issues with their payment method and provide steps to resolve the problem.
Content: These emails explain the reason for the payment failure, such as insufficient funds or an expired credit card. They should guide the customer through updating their payment information or retrying the transaction.
Best Practices: Use clear and concise language to explain the issue. Include direct links for customers to update their payment information or contact support for assistance.
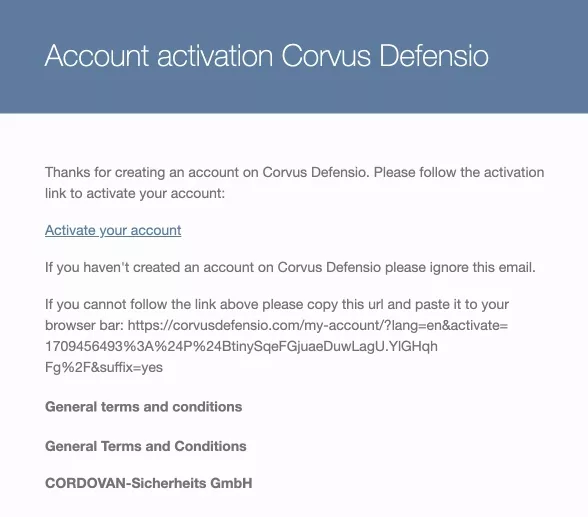
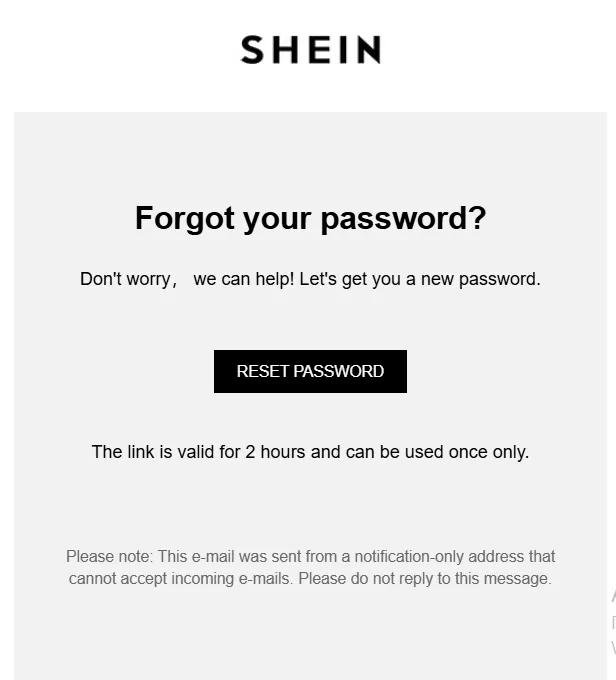
Password reset emails
Purpose: Password reset emails are sent when a customer wants to change their account password. These emails ensure account security and help customers regain access to their accounts.
Content: The email usually includes a secure link to reset the password, along with instructions for creating a new one. For security purposes, the link is often time-sensitive.
Best Practices: Emphasize the importance of using a strong password and provide tips on creating one. Ensure that the reset link is secure and expires after a certain period.
Account update emails
Purpose: These emails inform customers about changes made to their accounts, such as updates to personal information, payment methods, or subscription plans.
Content: Account update emails typically summarize the changes made and include a confirmation that the update was successful. They might also provide instructions on how to revert the changes if they were not authorized.
Best Practices: Confirm the details of the changes and include a contact method for the customer to report any discrepancies or unauthorized actions.
Subscription renewal emails
Purpose: Subscription renewal reminder emails notify customers when their subscription is about to expire and offer options for renewal.
Content: These emails usually include the expiry date, the cost of renewal, and instructions on how to renew or cancel the subscription. Some companies also offer incentives, such as discounts, for early renewals.
Best Practices: Send these reminders well in advance of the renewal date and provide a seamless process for renewal or cancellation. Consider including a link to view the subscription details or change the plan.
Event reminder emails
Purpose: Event reminder emails are sent to remind customers of upcoming events they have registered for, such as webinars, in-person conferences, or online workshops.
Content: The email should include the event date, time, and location (or online access details). It may also provide a brief overview of what to expect and any materials the customer should prepare in advance.
Best Practices: Ensure that the reminder is sent at an appropriate time, such as a few days before the event. It can also be helpful to include a calendar invite or a link to add the event to the customer’s schedule.
Feedback request emails
Purpose: Sent after a transaction or interaction, feedback request emails ask customers to share their experiences. These emails can provide valuable insights into customer satisfaction.
Content: Feedback request emails typically include a survey link or a simple question with rating options. They might also encourage customers to leave reviews on specific platforms.
Best Practices: Keep the request short and easy to complete. Offering an incentive, such as a discount on future purchases, can increase the conversion rate for the next purchase or order.
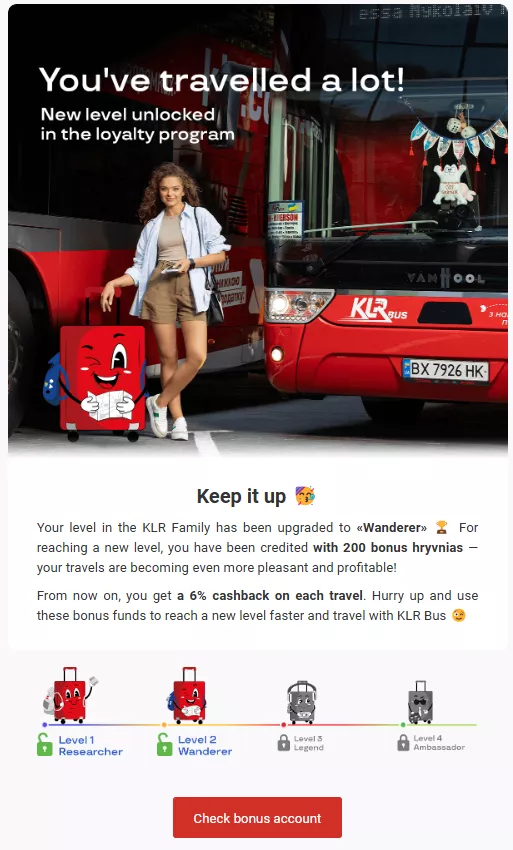
Loyalty program updates
Purpose: Loyalty program update emails keep customers informed about their rewards status, new benefits, or changes to the loyalty program.
Content: These emails usually detail the customer’s current points balance, recent transactions, and how close they are to earning a reward. They may also highlight new ways to earn or redeem points.
Best Practices: Personalize the email with the customer’s name and current status. Encourage further engagement with the program, as this will increase loyalty and motivate repeat purchases.
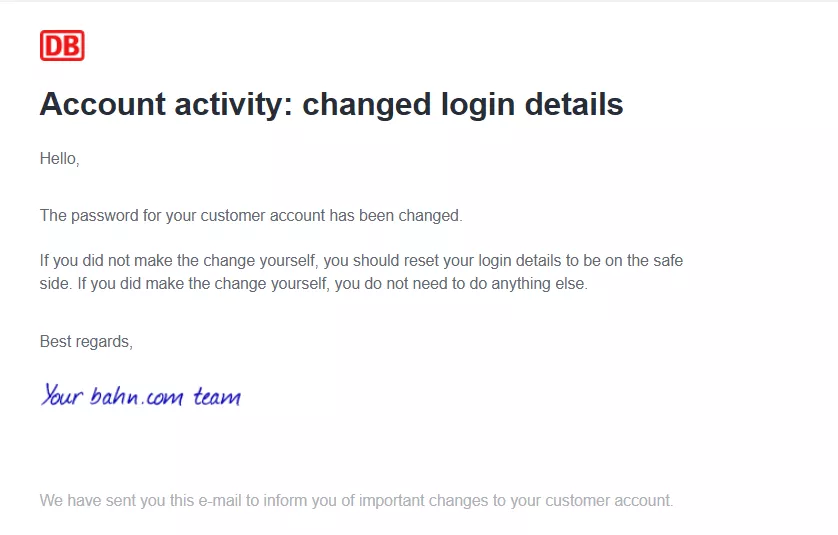
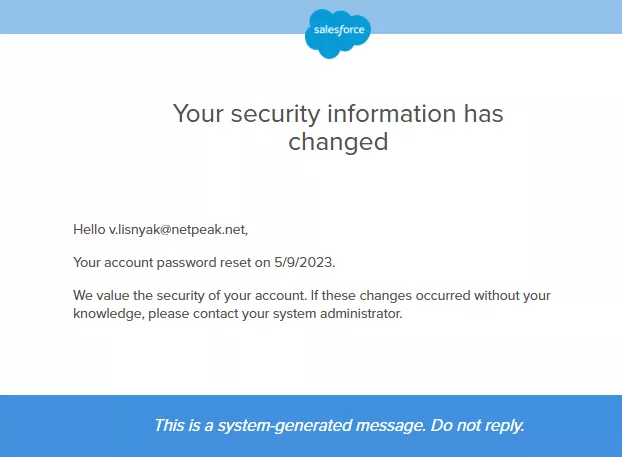
Security alerts
Purpose: Security alert emails notify customers of potential security issues with their accounts, such as unauthorized login attempts or changes to security settings.
Content: The email should provide details of the suspicious activity and mention steps the customer can take to secure their account, such as changing their password or enabling two-factor authentication.
Best Practices: Act quickly to send these alerts, as timing is critical in preventing security breaches. Include clear instructions and a direct link to the necessary security settings.
Order cancellation emails
Purpose: If an order is canceled, an order cancellation email informs the customer and provides details about the cancellation process.
Content: The email should include the order number, the reason for cancellation (if applicable), the contents of the canceled order (if the order was partially modified or canceled), and the next steps, such as processing a refund or purchasing an alternative item.
Best Practices: Clearly explain the reasons for the cancellation and offer assistance if the customer needs further help. Provide contact information for customer support.
Sometimes, order cancellations could occur due to brand-related reasons (e.g., the item is out of stock). In such situations, consider including a “sorry” promo code for the customer’s next purchase.
Why are transactional emails important?
Transactional emails are essential because they ensure timely and accurate communication with users regarding their accounts or purchases. This improves the user experience, enhances trust in the brand, and contributes to increased customer loyalty.
- Provides users with information. Transactional emails give users important information about actions they have taken on a website or app. This can include order confirmations, shipping notifications, payment invoices, or purchase receipts. Such emails keep users informed about the current status of their interactions with the service.
- Builds trust and customer loyalty. When customers receive timely and accurate notifications about their transactions, it strengthens their trust in the company. Users feel that their needs are being cared for, which helps reinforce loyalty and encourages repeat purchases.
- Enhances the user experience. Transactional emails make interactions with the service more transparent and convenient. Users can easily obtain information about their orders and payments, reducing the number of inquiries with customer support.
- Minimizes errors and misunderstandings. Automatic notifications about the status of orders, payments, and other actions help prevent misunderstandings and errors. Users receive clear instructions and information, allowing them to act quickly and efficiently.
- Provides additional information. Transactional emails can be used to provide additional information, such as product usage instructions, care tips, or support advice, which contributes to a fuller and more correct use of purchased products or services.
- Cross-selling and upselling. Transactional emails can include offers for related products or services (cross-selling) and suggestions to upgrade to a more expensive option (upselling). This can help increase the average order value and offer customers useful additional products.
- Supports communication. Transactional emails help maintain ongoing communication with customers by providing them with up-to-date information and updates. This helps maintain high levels of user engagement and enhances their overall impression of the brand.
- Legal and financial aspects. Some transactional emails, such as payment invoices and receipts, are necessary to fulfill the company’s legal and financial obligations. They provide customers with official documents that confirm the fact of purchase or payment.
Best practices when working with transactional emails
- Personalization. A transactional email should be personalized because it responds to each customer request or action. Ensure it contains unique content tailored specifically for each recipient.
- Upsell and cross-sell. This is the perfect opportunity to include offers for additional or complementary products. It can help increase the average order value and provide the user with other useful products or services.
- Provide links. Add useful links to help pages, user profiles, or order tracking. This enhances the user experience and makes interacting with the email more convenient.
How Transactional Emails Work
Transactional emails are typically sent automatically using specialized systems or integrations with a website. When a user performs an action, the system generates an email and sends it to the specified email address. This happens instantly and does not require manual intervention.
Transactional emails are a crucial tool for automated and timely interactions with users. They work based on the following principles:
- Event Initiation.
A transactional email is sent in response to a specific user action. This can include:
- Registering on the website.
- Placing an order.
- Requesting a password reset.
- Making a payment.
- Updating a profile.
When a user performs one of these actions, the system records the event and initiates the email sending process.
- Email Generation.
First, the developer needs to manually set up the integration of the website with a CRM or ESP. After the event is triggered, the CRM system or ESP generates the transactional email based on the previously prepared template.
The email contains personalized information, such as the user’s name (optional and only if we have this info in the database), order number, payment amount, and other details related to the user’s action.
- Automatic Sending.
The CRM or ESP automatically sends the email to the email address provided by the user. This happens instantly or with minimal delay to ensure the email is relevant and timely. An ESP should have IPs with a good reputation to avoid damaging the sending company’s domain reputation. Otherwise, you might end up having to rescue your domain from the spam.
- Email Delivery.
The email is delivered to the user through the chosen email service (SMTP server). It is important that the email provider is reliable and has a high deliverability rate. This will prevent emails from landing in the spam folder and ensure they reach the intended recipients.
However, the delivery depends not only on the ESP but also on whether the domain has all the necessary domain authentication records (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) configured. It is recommended to have two separate IPs for sending promo and transactional emails. This ensures that the reputation of the promo IP does not affect the reputation of the transactional IP, because the deliverability of the latter is more important.
Valeriya Lisnyak, Senior Retention Marketing Specialist in the Netpeak Agencies Group
- Tracking and Analysis.
After the transactional email is sent, the system tracks its delivery and the user’s interaction with the email.
Tools for sending transactional emails
Many tools and services help automate the process of sending transactional emails and are useful for sending emails in general. Here are some of them:
- SendPulse. A convenient tool for sending newsletters that also offers many other useful features.
- Hubspot, SalesForce. Some CRMs also have a mailing function.
- Google Analytics. Allows you to track email campaign clicks to your website and analyze user behavior.
- Postmaster. Monitors domain and IP reputation and has a spam rate metric.
- MXTool. Tracks errors in domain record (DNS) settings.
- Postman. Tests the correctness of API requests (events from the website to CRM or ESP to trigger email sending).
- Yespo. An omnichannel marketing automation platform that enables personalized customer engagement through email, SMS, web push notifications, and other communication channels.
Read our blog on How to Choose the Best Email Marketing Service.
Measuring the success of transactional emails
Evaluating the success of transactional emails is a crucial aspect of understanding their effectiveness and impact on users. Various metrics and tools can be used to identify the strengths and weaknesses of these emails. Here are the key indicators to consider:
- Delivery Rate.
This metric shows the percentage of emails successfully delivered to users’ inboxes. A high delivery rate indicates a quality address database and correctly configured email service.
Delivery Rate = (Number of Emails Delivered / Number of Emails Sent) × 100
- Open Rate.
The open rate indicates the percentage of recipients who opened your email. This metric shows how interesting and relevant the email subject is to your users.
Open Rate = (Number of Emails Opened / Number of Emails Delivered) × 100
- Click-Through Rate (CTR).
This metric shows how many users clicked on a link in the email. A high CTR indicates that the email content interested the recipients and prompted them to take action.
CTR = (Number of Clicks / Number of Emails Delivered) × 100
- Click-Through Open Rate (CToR).
This metric calculates the percentage of email recipients who clicked on a link after opening the email. It helps measure the effectiveness of your email content in driving engagement among those who actually opened the message.
CToR = (Number of Clicks / Number of Opens) × 100
- Conversion Rate.
The conversion rate indicates how many users performed the desired action after clicking a link in the email, such as making a purchase or registering on the website. This is one of the most important metrics, as it indicates the actual effectiveness of your email campaign.
Conversion Rate = (Number of Conversions / Number of Clicks) × 100
Optionally, it may be sometimes better to use sessions on the website as the denominator if such tracking is available. This is because clicks can be accidental or occur on non-target buttons.
Valeriya Lisnyak, Senior Retention Marketing Specialist in the Netpeak Agencies Group
- Bounce Rate.
The bounce rate shows the percentage of sent emails that were not delivered due to various reasons (nonexistent address, technical problems, etc.). A high bounce rate may indicate issues with the address database or technical settings.
Bounce Rate = (Number of Bounces / Number of Emails Sent) × 100
- Unsubscribe Rate.
This metric shows how many users unsubscribed from your mailing list after receiving an email. A high unsubscribe rate may indicate that your content does not meet recipients’ expectations or is sent too frequently.
Unsubscribe Rate = (Number of Unsubscribes / Number of Emails Delivered) × 100
- Spam Complaint Rate.
This metric reflects the proportion of users who marked your emails as spam. A high spam complaint rate can cause your domain or IP address to be blocked by email services.
Spam Complaint Rate = (Number of Spam Complaints / Number of Emails Delivered) × 100
Read more in our blog about How to Measure Your Newsletter Performance: 10 Key Email Marketing Metrics.
Conclusion
- Transactional emails are automated emails sent in response to specific user actions on a website or application. These emails play a crucial role in enhancing customer interaction, ensuring timely communication, and supporting the overall user experience.
- An email is considered transactional if it provides information directly related to a user’s action, such as order confirmation or payment failure notification. The primary purpose of these emails is to inform users, not to promote products or services.
- Transactional emails are highly personalized and automated based on user actions. Due to their relevance and importance, they typically have a higher open rate.
- There are various types of transactional emails, and each serves a unique purpose in the customer journey. These include:
- Welcome emails
- Order confirmation emails
- Shipping confirmation emails
- Payment invoice emails
- Purchase receipt emails
- Payment failure notifications
- Password reset emails
- Account update emails
- Subscription renewal reminders
- Event reminder emails
- Feedback request emails
- Loyalty program updates
- Security alerts
- Order cancellation emails
- Transactional emails are essential for ensuring timely and accurate communication with users regarding their accounts or purchases. They enhance the user experience, build trust, and encourage customer loyalty.
- There are several best practices for optimizing the effectiveness of transactional emails. These include personalization, upsell and cross-sell opportunities, and providing helpful links.
- Transactional emails are automatically generated and sent in response to specific user actions, ensuring timely and relevant communication without manual intervention. The process includes event initiation, email generation, automatic sending, delivery, and tracking and analysis.
- There are various tools available for automating transactional emails, including Yespo, SendPulse, Hubspot, SalesForce, Google Analytics, Postmaster, MXTool, and Postman.
- Key metrics for evaluating the success of transactional emails include delivery rate, open rate, click-through rate (CTR), click-through open rate (CToR), conversion rate, bounce rate, unsubscribe rate, and spam complaint rate. These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of your email campaigns and help you identify areas for improvement.
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses