What is SEO friendly URL – Guide for Beginners
There are many SEO factors that influence the final result of search engine promotion. One of the ranking factors is URL optimization.
Google Developers Documentation contains a separate section about URL optimization. In this beginners guide we will talk about what URLs are, their types and influence on SEO, and how to make SEO friendly URLs for website pages.
What is a URL?
URL is a unified resource locator. It is a unique set of symbols that can identify all kinds of resources on the Internet (website pages, files, images, video and so on). It shows where a particular site is located on the web and how it can be accessed.
What is URL structure?
A special standard was created to unify all web addresses, so that all URLs have a simple and clear path to file storage.
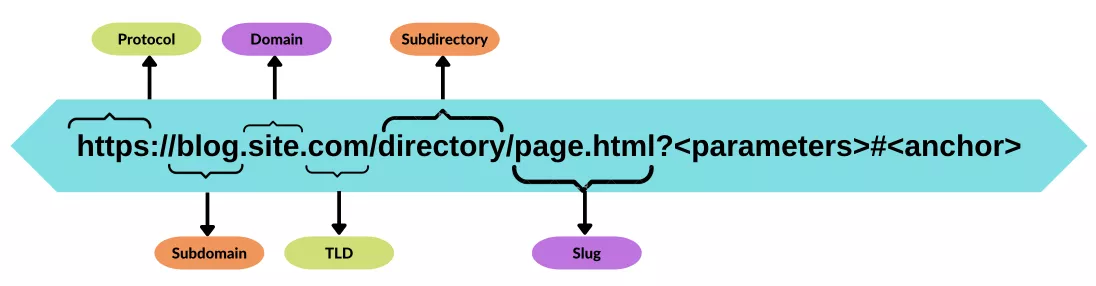
The special characters we see in the address bar are the URL. The URL structure looks like this:
Protocol is a data transfer method. There are a huge number of protocols, but the most common are:
- FTP:// (File Transfer Protocol) provides remote hosting access, transferring data from the server to the user's device and vice versa;
- HTTP:// (HyperText Transfer Protocol) is a hypertext transfer protocol for transporting arbitrary data (initially in HTML format).
- HTTPS:// (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) – HTTP protocol, using SSL and TLS transport mechanisms for better security.
- SMTP:// (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is a mail transfer protocol in TCP/IP networks.
Subdomain is a part of the domain name. It is used to organize different sections of the site. In our example blog.site.com is a part of a big website site.com.
Domain is the name of the website. Do not confuse the domain and URL. The domain is just a part of the URL.
TLD or Top-Level Domain is the part of the domain name that comes after the dot. It contains extra information to the domain associated with it. This could be the website’s purpose (.edu, .gov), the geographical area (.us, .de, .fr) and others.
Subdirectory is a part of the url that shows a folder where the web page is located. Another way to describe it would be the name of a specific section of your site. It can be a category of products for online shops or a type of pages like /blog/ or /news/.
Slug is the part of the url that identifies a specific page. This part is usually optimized for search engines. The slug helps users and crawlers understand what content is on the exact page.
The parameters and anchor are additional parts of the URL.
Parameters are special data that a browser tells a web-server. Generally, parameters are specified after the "?" sign and separated by an "&". Anything that goes before the “?” is the main URL, the part that goes after are additional parameters. https://site.com/cat332t1.html?sort_direction=desc&sort_by=price_desc
Anchor is a type of bookmark on a page, which directs a user to a certain part of the page (marked code fragment). It is implemented with "#" symbol: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/URL#Syntax.
The impact of URLs on SEO
There are many ranking factors that affect the promotion of websites which help in achieving the desired results in website ranking.
All other things being equal, a properly optimized page URL gives an advantage over sites with URLs generated by a CMS system.
The degree of importance of optimized URLs in on page SEO depends on the frequency of queries and competition. As a rule, the main categories of the site are promoted by high-frequency queries and URL optimization does not have much impact on them. But for low-frequency queries correctly composed URLs are important and significantly help site ranking in search results.
Types of URLs
There are two types of URLs: static and dynamic.
A static URL is a permanent web address which does not contain any additional parameters and does not change over time (or changes very rarely). Static URL example:
Dynamic URL means that a page path is generated in response to a specific user request.
Dynamic URLs have special characters like "?", "=", "&". These characters are followed by additional page parameters. Dynamic URLs are usually generated after selecting filters, sorting products, searching the site and other.
Dynamic URLs have some disadvantages:
- it is difficult to remember them;
- their CTR is lower than static URLs;
- they do not take keywords into account;
- users do not understand what content will be shown on the page;
- they are difficult to copy – they can be cut off.
URL structure for different types of pages
One of the most frequently asked questions on SEO concerns proper URL structure. Let's take online shops as an example and review the different options for building URL structure.
1. Section/category page. This is quite simple because the domain is immediately followed by the section/category page:
2. Subcategory page. Let’s consider two frequently used methods:
- repeat the structure of the site:
- remove intermediate folders in URL:
3. Product page.
- keep the page hierarchy by adding a product card to the URL:
4. Advantages:
- you can show search engine bots the site's structure and content, which will have a positive impact on indexation;
- you can track traffic in analytics, because you can see from which section/category the user came;
- users see which section of the site they are in – it's easier for them to navigate the site.
5. Disadvantages:
- long URL reduces the weight of keywords in URL;
- some CMS systems do not allow you to create additional sections/subcategories;
- there is a high probability of duplicate pages. For example, one product can be in two categories. This leads to duplicate pages. For example, iPhone XS can be located in several sections at once: https://site.com./smartphones/iphonexs/; https://site.com./smartphones/apple/iphonexs/.
Another method is to not link the product card to a specific category and store everything in the root of the site: https://site.com/product/.
6. Advantages:
- products are not attached to pages of specific categories, which eliminates the possibility of duplicate pages;
- increased weight of keywords in URL on a certain category;
- optimum URL length by eliminating intermediate categories/subcategories.
7. Disadvantages:
- not every content management system has the ability to remove unnecessary folders for URLs;
- there is no way to track traffic in analytics: this way the product won't be assigned to a specific section/category.
When should you use the first method, and when the second? It all depends on the subject and the capabilities of the site. If this is a small online shop, in which the product card is assigned to a particular category/subcategory, then you can use the first.
The second is recommended when the product can belong to different categories. Goods will not be assigned to categories and this way you can solve the problem of page duplicates.
URL structures for different websites
The URL structure depends on the website needs. The URLs of eCommerce differ from the blog URLs and it’s OK. Or the international website URLs will contain the multilanguage part.
You can choose the URL structure depending on your website needs and user experience. But always remember the common best practices for URL structure.
Using keywords in URLs
There is no exact information about how keywords in URL impact the page ranking in search results. In the past there was an idea that keywords in URLs increase the CTR. But now this is not actual.
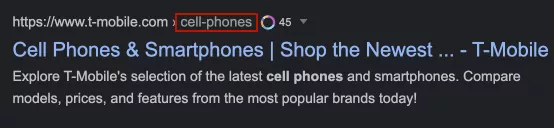
Today Google uses the breadcrumb navigation or breadcrumb structured data in search results. So the keywords in the URL are not visible.
Example of breadcrumbs navigation in search results:
Using the keywords in URL actual for websites that do not have the breadcrumbs navigation or breadcrumbs structured data.
But it doesn't mean that you shouldn’t use keywords in URLs. They help users understand what content will be shown on the page.
Using keywords in category URL structure
It is recommended to use relevant keywords as the category name in the URL. Sometimes the high frequency keywords don't show what the certain page contains. So be attentive to choose the category names that properly describe the information on the page.
Mistakes to avoid in URLs
Rude mistakes in URL handling:
- changing URLs without a 301 redirect.
If you are going to change or you have already created new page URLs, you need to set up 301 redirects to avoid duplicate pages. The same goes for other versions of the site (with www, http and https, upper and under case and so on);
- different URLs but the same content.
For example, two filter parameters such as color and size. A visitor can filter products by color and then by size, or vice versa, by size and color. It's important here to follow the same logic of forming URLs for filter pages to avoid a huge amount of duplicate content.
Best practices for URL optimization
Search engines recommend the use of human readable URLs, also known as SEO friendly URLs. They are page paths that let the user and search engine bots know what information can be found via a link.
For generating SEO friendly URLs it is necessary to follow generally accepted rules:
Use the hyphens to separate words:
- do not use the other punctuation symbols;
- two or more consecutive hyphens or underscores should be replaced by a single hyphen;
- if a "-" appears at the beginning or end of the URL, then it should be removed;
- if the CMS system uses underscores, then leave it that way.
Use only lowercase letters.
URLs are case-sensitive. https://site.com/News/ and https://site.com/news/ are not the same page for search engines. So try to avoid capitalization in URL.
Short URLs are recommended.
Webmasters usually use no more than 3-5 words in an address. The fewer the better. Long URLs are cropped in search engine results, reducing the weight of keywords. They are also inconvenient for users because they are hard to remember and make site navigation more difficult. An exception is news sites, where the URL often contains more than three words.
An example of a cropped URL:
Page nesting level.
The structure of a URL should mirror the structure of the site itself, but this is not always useful if the pages are 4-5 folders away from the main URL. In such cases, reduce the level of nesting by hiding intermediate sections.
Use a logical URL structure to improve your user experience.
Simple, readable URL with relevant keywords that describe the page content is SEO friendly.
Use of the "#" symbol in URLs.
Search engines do not take into account the parts of the URL that come after the hashtag. This is why they can be used to improve user navigation. Typically, the hashtag is used on article pages and one-page sites to create an anchor menu. If it is a sequence of two "#!" characters, known as a shebang or hashbang, then the URL will be indexed.
Use ".html/.php" or the right slash "/" at the end of the URL.
These options do not affect ranking and indexing. So you can use both but remember the shorter the URL the better so I recommend using the right slash in URL.
Avoid using parameters if possible.
Parameters make URLs longer, can cause problems with duplicate content, and are simply unreadable by the user.
Use https protocol.
Google considers https protocol as a lightweight ranking factor from 2014. So it will be better to use it both for data security and SEO optimization.
Avoid using dates.
Sometimes CMS’s could automatically add dates in URLs:
And it is not a good idea. For the first, the date makes URLs longer. And we already know that SEO friendly URLs need to be as short as possible.
The second reason is that it is harder to update the content of the page. Changing or adding new information to the page causes that the URL will not be relevant to page content and we will have to set up the 301 redirect.
So it is better not to use date in the URLs at all.
No spam.
Using keywords in URLs will help your site ranking in search results a little better. But don't abuse them in the URL, because search engine crawlers may think the site is using spammy promotion techniques;
Conclusions
- A URL is the location of a particular website, page or file on the internet.
- URLs are a ranking factor, but not one of the most important, don't get too hung up on them.
- Make URLs for users. With their help, a person without going to the page will immediately see what content is on it.
- Build the URL structure depending on the type of your website to avoid any further additional work.
- Before optimizing URLs, be sure to check the recommendations of the search engines in which you are promoting.
FAQ
Q: What is an URL?
A: URL is a unified resource locator. It is a unique set of symbols that can identify all kinds of resources on the Internet (website pages, files, images, video and so on). It shows where a particular site is located on the web and how it can be accessed.
Q: Why is SEO friendly URL important for SEO?
A: SEO friendly URLs help to improve the user experience and better understand both humans and crawlers what the page is about.
Q: Are shorter URLs better for SEO?
A: Short URLs are recommended because Google can reduce the part of URL in search results. But using the logical site structure with relevant keywords in the URL is more important.
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses