All About Google Search Console, and How to Use It
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool from Google. It helps you understand how Google shows your website in search results, and you can use it to optimize your website performance. In this article, I will discuss what GSC is, how to set up this tool, and what functions it performs.
- What is Google Search Console?
- Google Search Console domain registration
- Key features of Google Search Console
- Best practices for using GSC
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console provides important information about website performance, including data on search queries, click-through rate (CTR), and overall visibility in search results. Through the GSC, users can see
- the queries bringing visitors to the site;
- how well the pages work in search;
- whether there are problems with speed;
- how the site is indexed;
- scanning statistics;
- number of backlinks, etc.
According to the My Codeless Website, proper use of Google Search Console increases organic traffic by 28%.
Google Search Console domain registration
There are a few steps to set up and use Google Search Console (GSC).
1. Sign in to Google Search Console.
2. Click Start now.
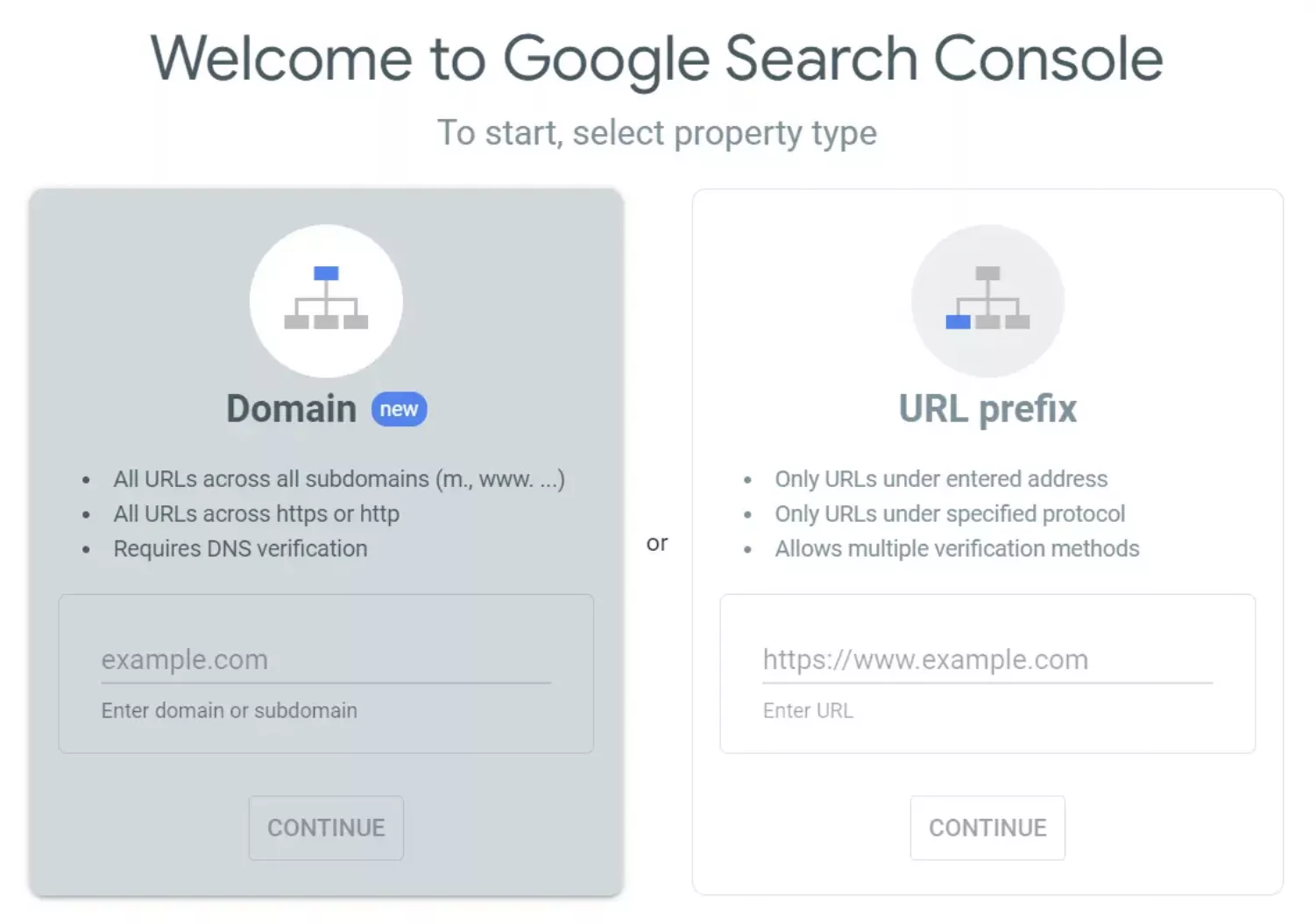
3. Select the Property Type from the two options:
- Domain: This option covers URLs in all subdomains and protocols (HTTP and HTTPS). This method is comprehensive but requires DNS (Domain Name System) verification.
- URL prefix: This option covers only URLs at the entered address and in the specified protocol (for example, https://www.example.com). It allows multiple verification methods.
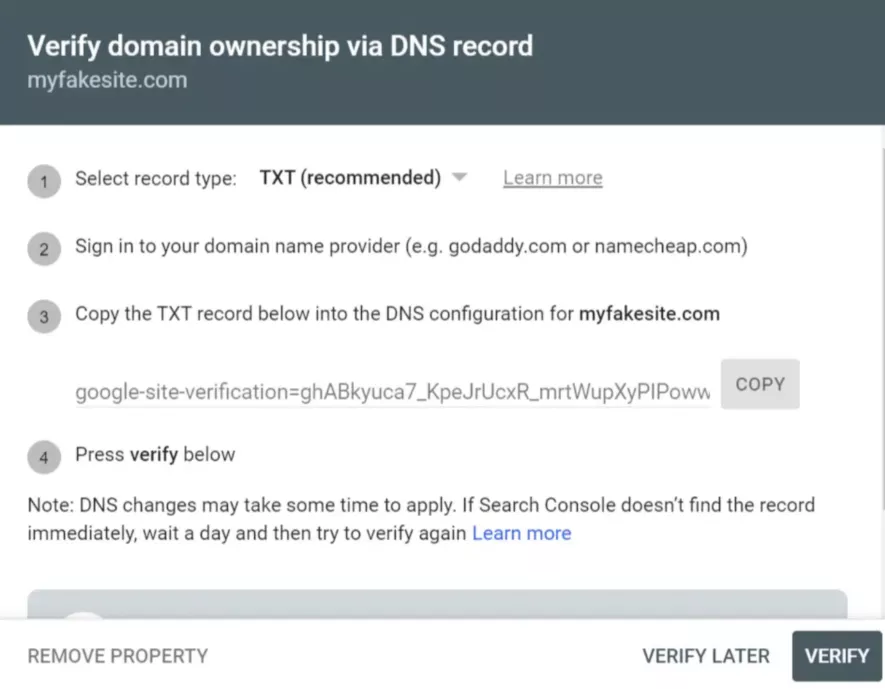
4. Verify the site to prove that you are the owner. There are two main types of verification: DNS verification and URL prefix verification.
- Select Domain as the resource type.
- Copy the TXT record provided by GSC.
- Go to the domain name provider (e.g., GoDaddy, Namecheap).
- Add the TXT record to the DNS configuration.
- Return to GSC and click Verify.
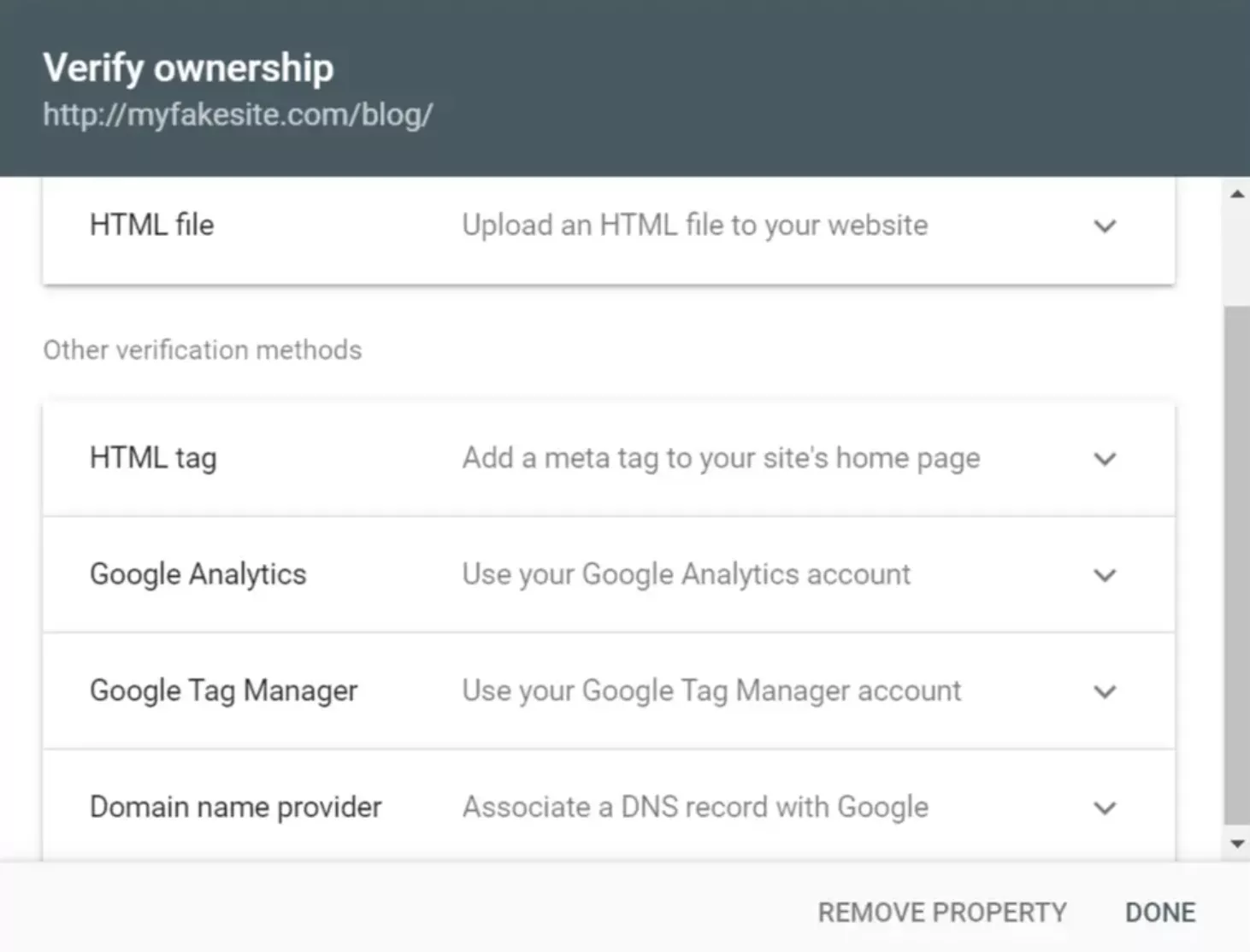
The recommended method of verification is to download an HTML file:
- Select URL Prefix as the resource type.
- Upload the verification HTML file provided by GSC.
- Add the file to the site’s root directory.
- Click Verify in GSC.
There are also several other ways to verify site ownership.
Adding a meta tag to your site’s home page:
- Copy the suggested meta tag and paste it on the homepage. It should appear in the <head> section before the first <body> section.
- Click Confirm.
Using a Google Analytics account:
- Add the analytics.js or gtag.js snippet to your website’s homepage.
- Place the tracking code in the <head> section of the page.
- Make sure you have editing rights.
- Click Confirm.
Using a Google Tag Manager account:
- Use the container snippet.
- Make sure you have publishing permissions.
- Click Confirm.
Associating a DNS record with Google:
- Select the domain name provider from the list.
- Click Start verification.
Once the verification process is complete, Google will notify you if it was successful. If not, try to prove ownership again.
Key features of Google Search Console
Performance report
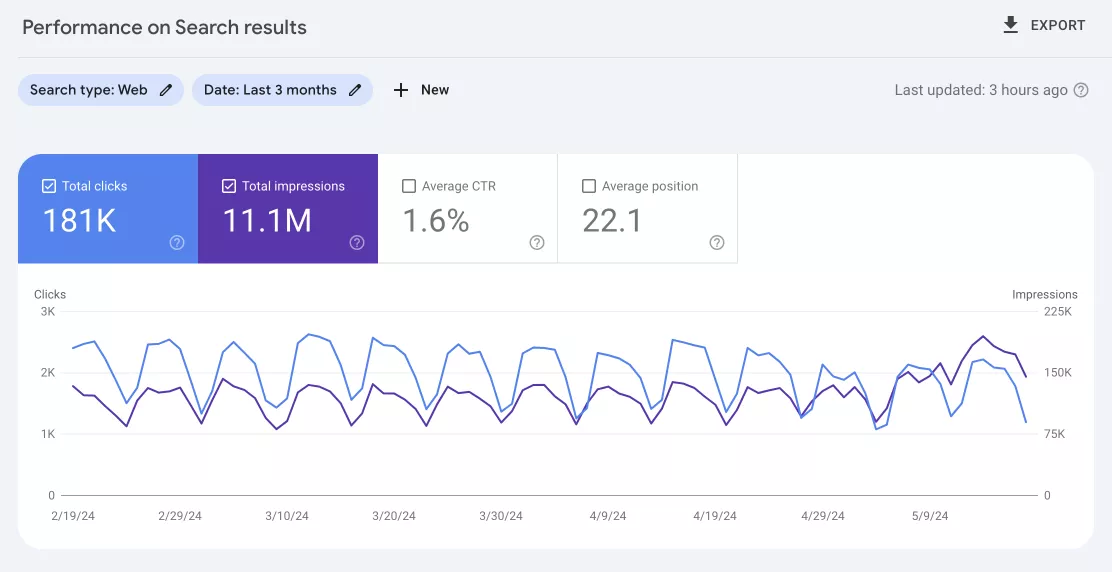
This report includes information on tracking search traffic, identifying trends, and optimizing your website. You will find the following metrics on a Performance report:
1. Total clicks. The number of times users clicked on a URL from Google search results. Clicks are a direct indicator of the quality of traffic from search, and they show what queries lead users to the site.
2. Total impressions. The number of times a URL from a website has appeared in Google search results.
3. Average click-through rate (CTR). The ratio of clicks to impressions is expressed as a percentage.
4. Average position. The average ranking of website URLs by search queries. It helps you understand how well the site ranks in general and identify opportunities for improving specific pages.
5. Queries. Google search terms entered by users that led to impressions and clicks on the site. You can get an idea of what users are looking for and optimize your content according to their intentions.
6. Pages. Individual pages of a website that appear in search results. Identifying the pages that are performing well helps you repeat successful strategies and improve pages that aren’t bringing results.
The number of clicks on queries and the number of clicks on pages will be different because Google hides some of the clicks on queries.
7. Countries. These are the geographic locations from which impressions and clicks to the site originate. Knowing this information helps you adapt content and marketing strategies to target specific regions more effectively.
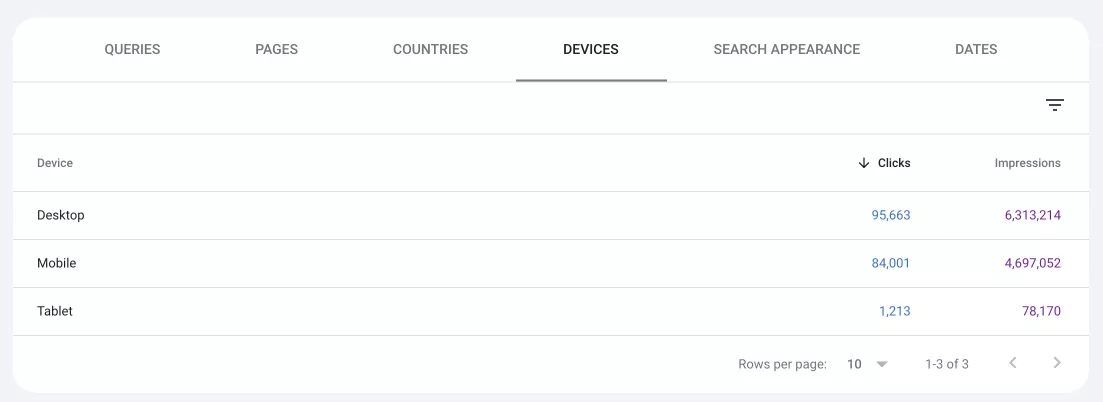
8. Devices. Types of devices (desktop, mobile, or tablet) used to access the website.
9. Dates. Analyzing indicators for different periods of time helps to identify trends, seasonality, and the impact of SEO efforts or algorithm updates.
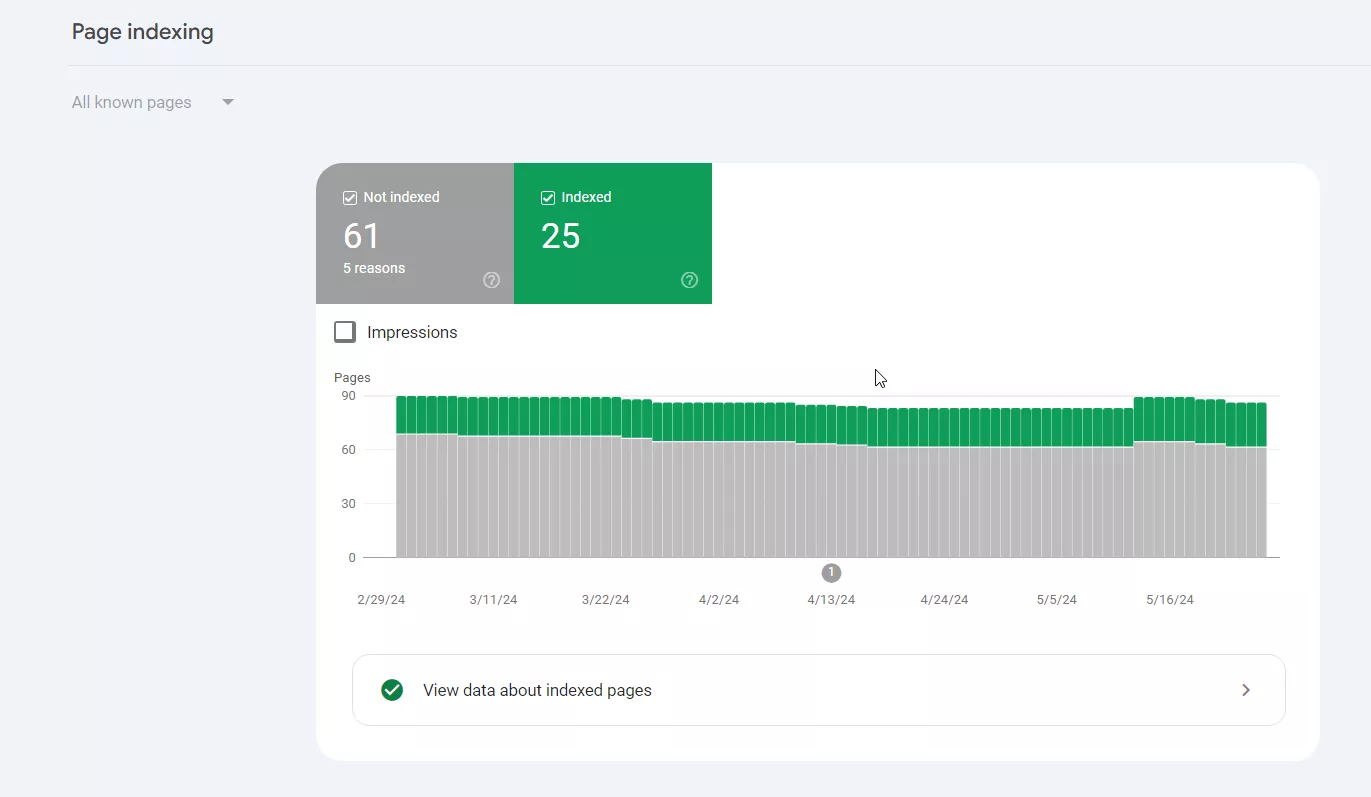
Indexing report
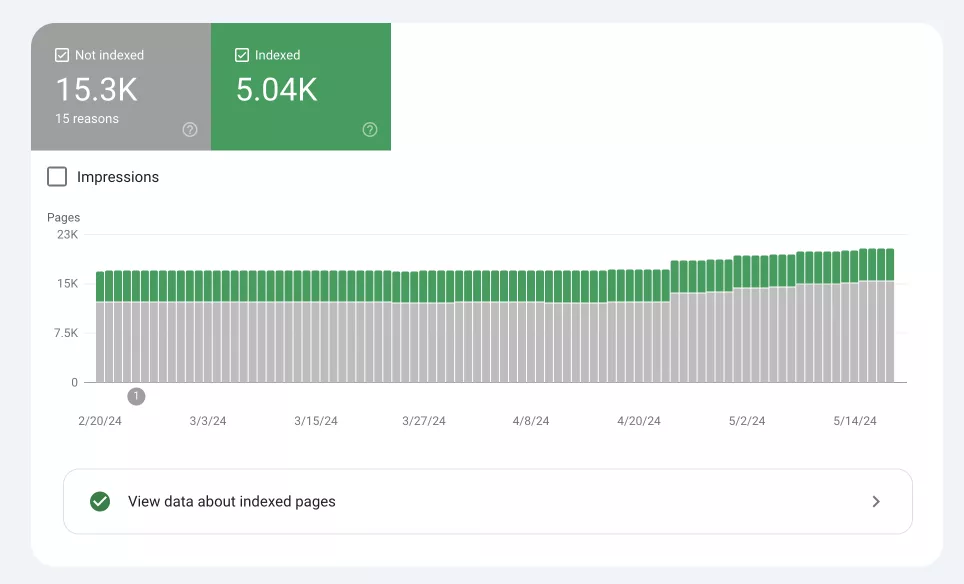
This report gives an idea of how well Google can index a website and highlights problems that prevent pages from being indexed. The indexing report categorizes pages into two main statuses:
- Indexed.
- Not indexed. These are pages that Google could not index due to serious problems, such as server errors (5xx), not found (404), redirect errors, etc.
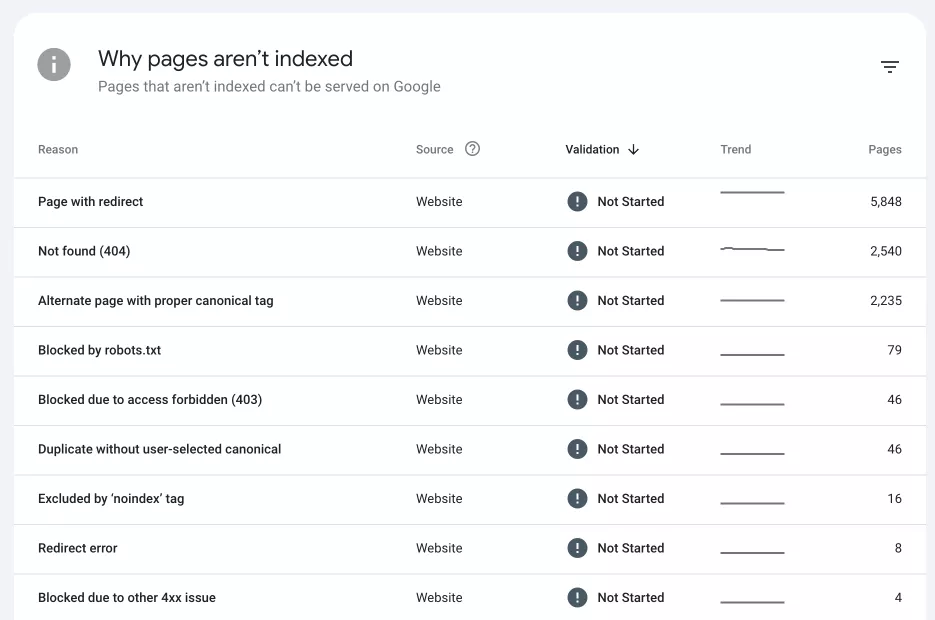
The report also contains information on why pages are not indexed, such as pages with no index tags, pages with duplicate content, or pages blocked by the robots.txt file.
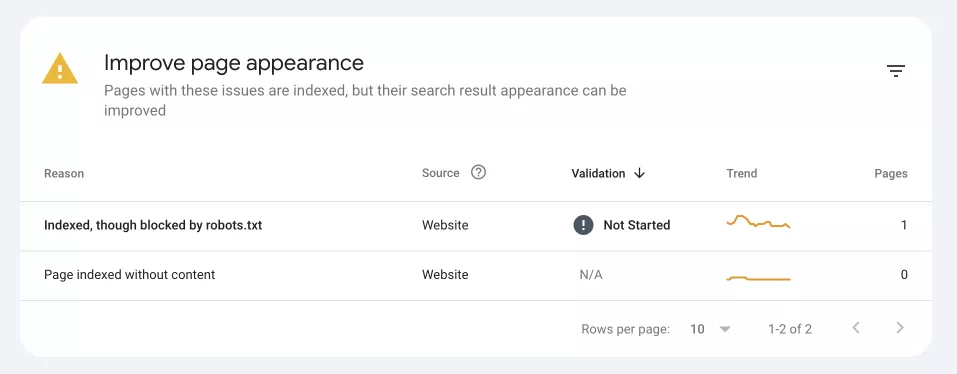
In addition, the report advises which pages should be improved. Such pages are indexed but have potential problems that need attention. For example, pages blocked by robots.txt or pages that lack content.
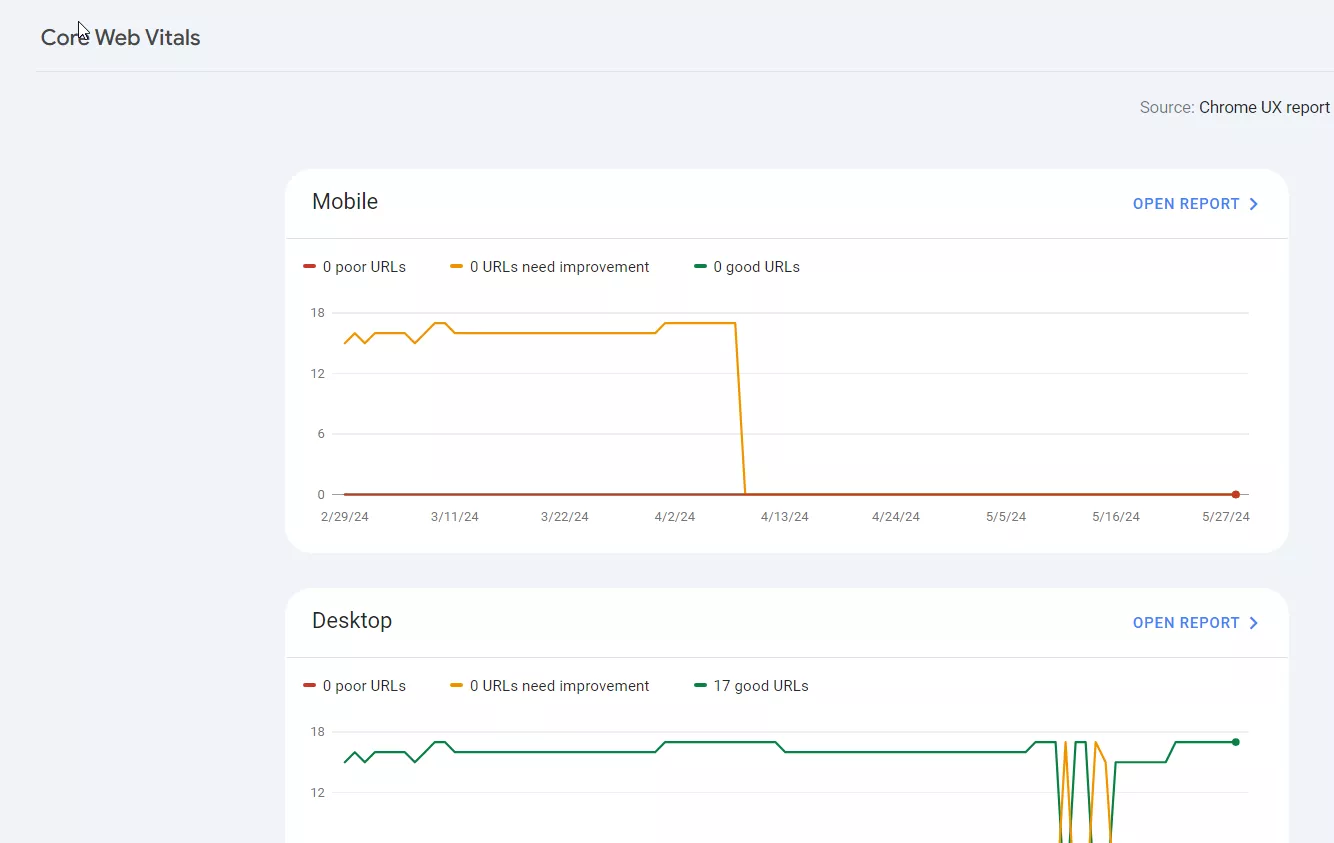
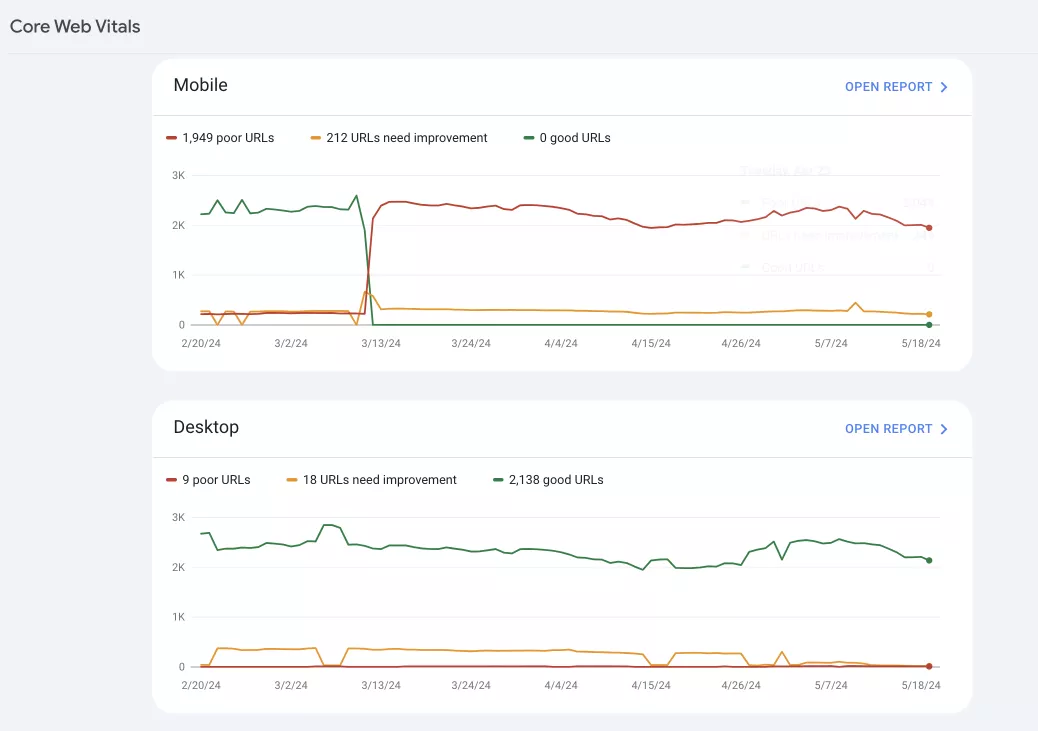
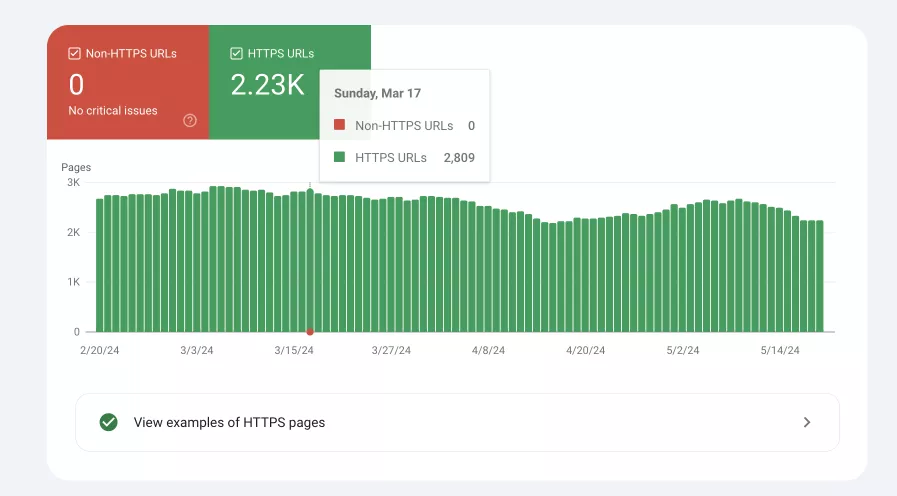
Experience report
This report helps identify and fix problems that can negatively affect the user experience on the site. It focuses on two aspects:
1. Core web vitals. Shows the quality of pages on the desktop and mobile versions of the site.
2. HTTPS. Shows the number of URLs that use a secure connection protocol.
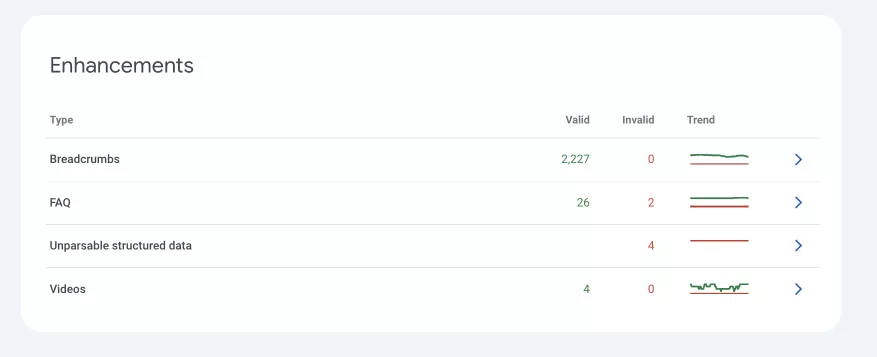
Enhancements report
This report provides information on how to improve your site’s presence in search results.
Key components of an Enhancements report:
- Breadcrumbs. They show the way to a particular page. The introduction of the breadcrumb markup allows Google to display this navigation in search results. The report shows the number of pages where it is implemented correctly.
- FAQ. Structured data in the FAQ format allows you to display questions and answers directly in search results.
- Unparsable structured data. This states errors that prevent Google from understanding and using structured data.
- Videos. This section shows problems related to structured video data on the site and helps ensure that video content meets the criteria for Google’s extended search results.
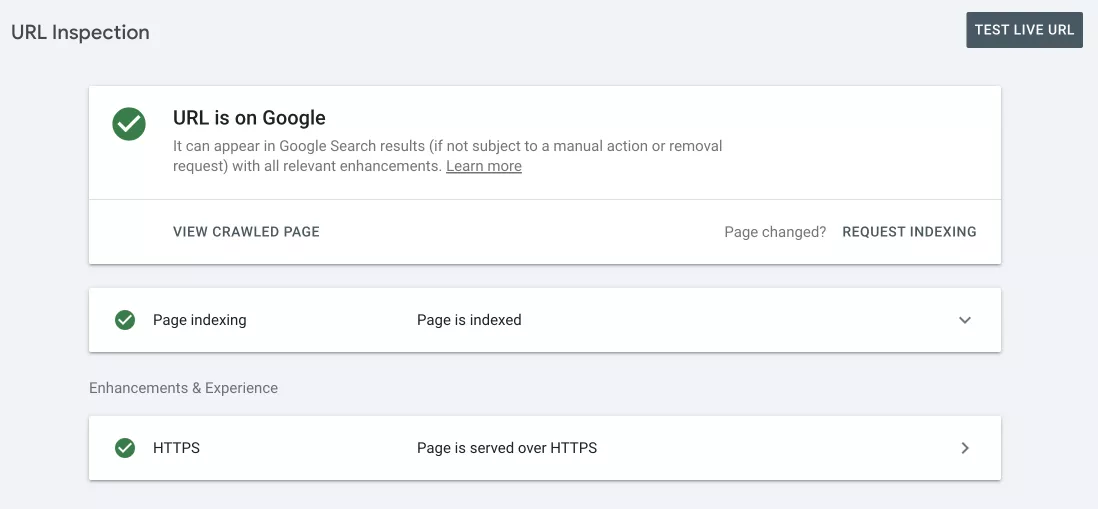
URL checker tool
This tool is designed to provide detailed information about the status of a particular URL on a website. It helps to understand how Google perceives the page and identify problems that prevent it from being indexed or displayed correctly in search results.
What can the URL checker tool do?
- Check if the URL is indexed by Google and included in the search results.
- Find out how Googlebot crawled the URL and when it was last crawled.
- Determine if there are any problems with the way Google displays the page.
If the URL is not indexed, you can request that Google crawl it again and try to index it.
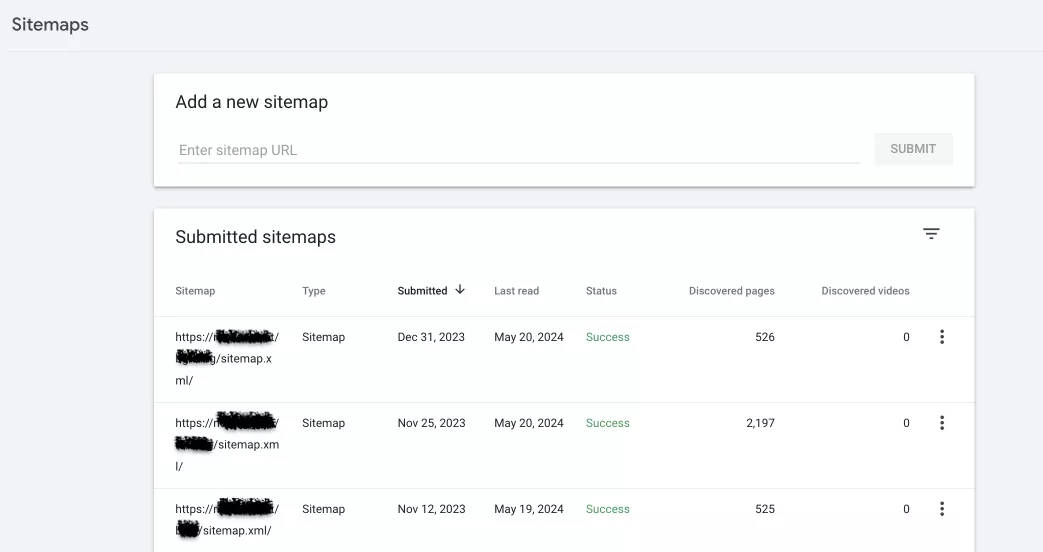
Sitemaps
Sitemaps are XML files that contain a list of URLs on a website and additional metadata about each URL, such as the date it was last updated, how often it was changed, and its importance in relation to other URLs on the site.
What is the purpose of a sitemap?
- Help search engines understand the structure of the site and find all the pages that are worth indexing.
- Allow search engines to crawl the site more intelligently, especially if there are a lot of pages or if the site is new with few backlinks.
- Ensure that important pages and new or updated content are quickly discovered and indexed by search engines.
The report shows the available sitemaps, their status, and the number of URLs.
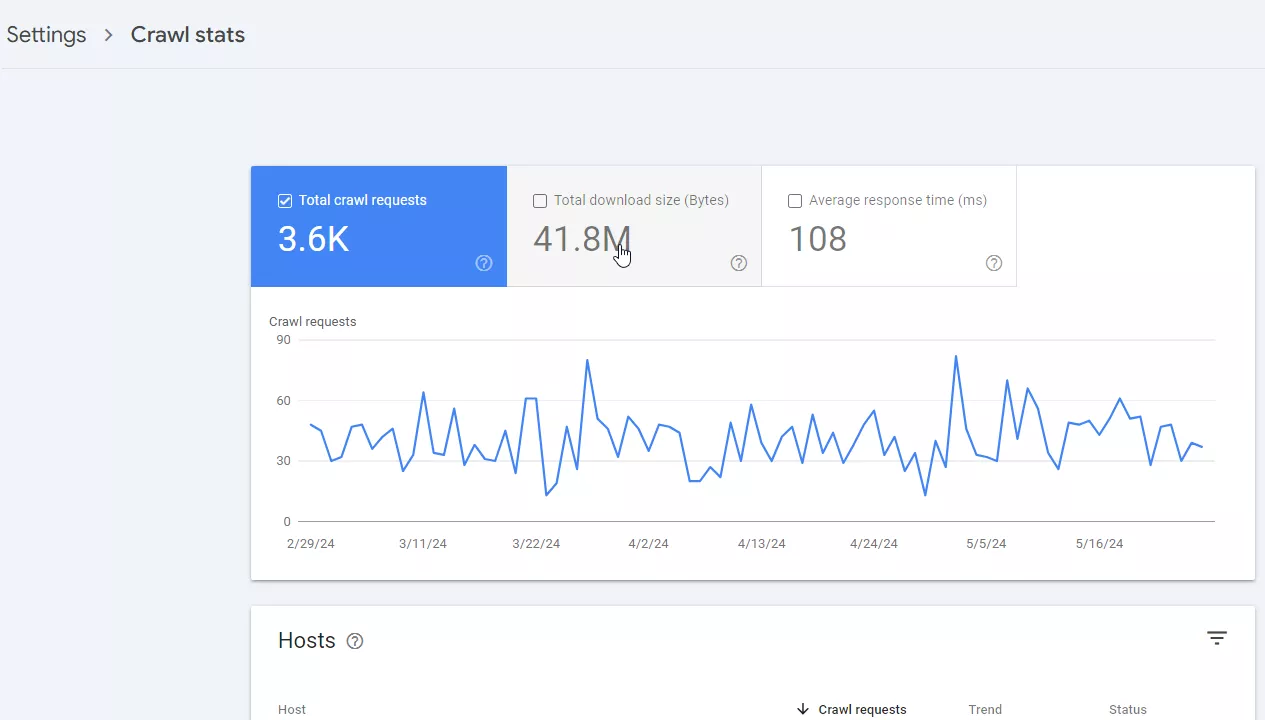
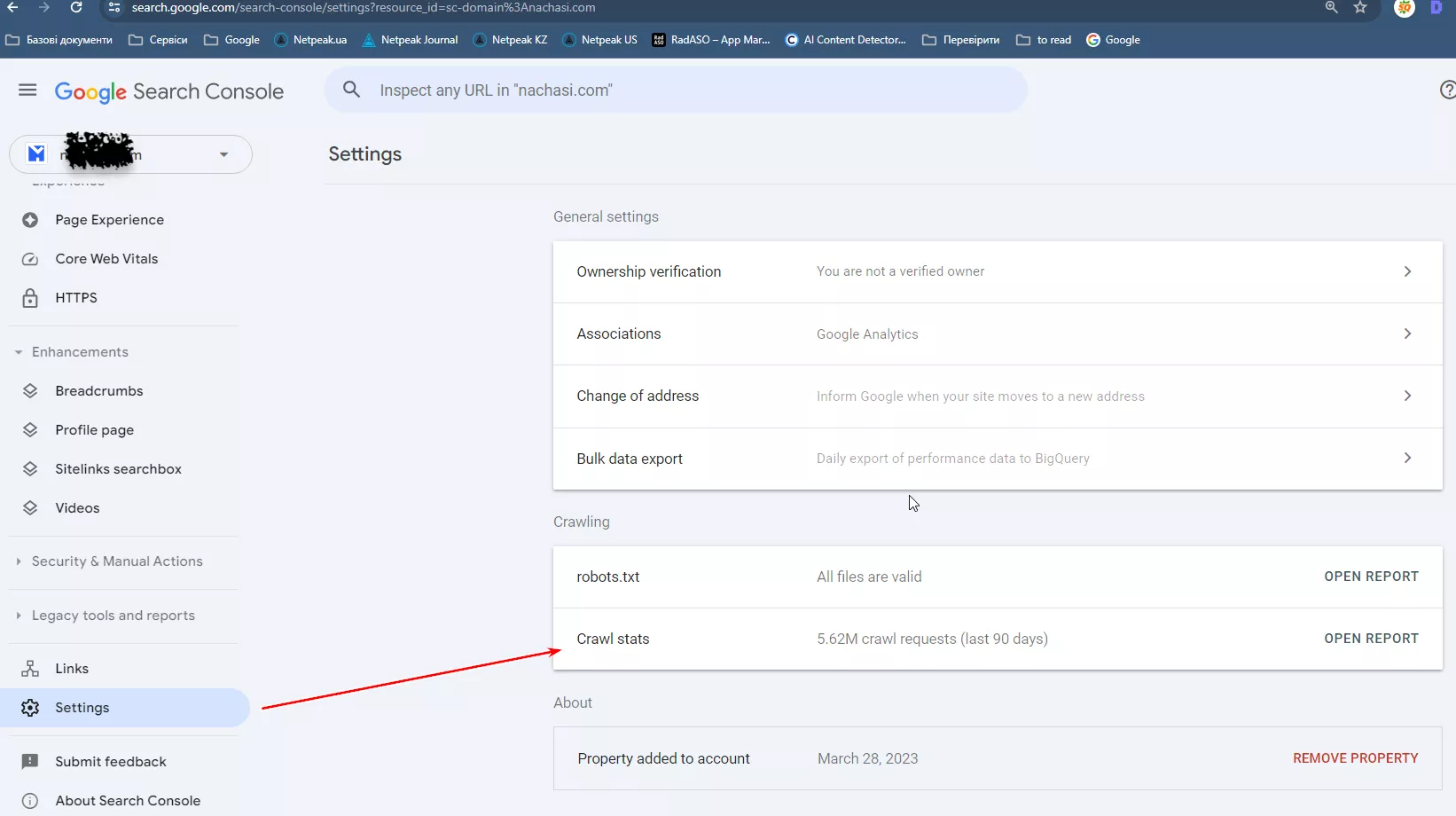
Crawl stats report
Provides information about how Google search robots access and interact with your site. It shows how often Googlebot crawls the site and how it processes server requests. This information allows you to identify potential problems that affect the indexing and visibility of the site in search.
This report shows:
- The total number of requests made by Googlebot during the selected period.
- The amount of data downloaded by Googlebot during the crawl in bytes.
- The average time it takes for the server to respond to Googlebot requests.
- Whether Googlebot successfully reached the server or encountered errors.
Best practices for using GSC
To maximize the benefits of GSC, monitor reports regularly, resolve issues quickly, and stay up to date with new features and changes.
Optimize based on Google Search Console data
Google Search Console (GSC) provides a wealth of data that you can use to optimize your site’s performance.
Use the data in the Performance report to:
- Find queries with a high number of impressions but low CTR. If a query has 10,000 impressions but a CTR of 0.5%, you should improve its title and description to better match the search intent of users.
- Look for keywords with an Average Position between 5 and 15. They are close to the top positions, and working on them will pay off.
- Analyze pages with a high number of clicks but a low average position. For example, a page that receives a lot of traffic but is ranked at position 12 may need a better content structure and additional backlinks to move up, etc.
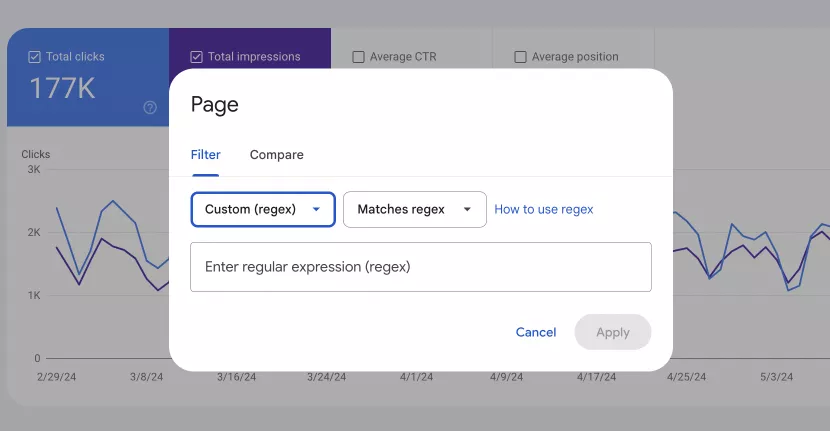
Using redex
Google Search Console offers advanced filtering capabilities using regular expressions (regex) to help you analyze patterns and trends in your search data. Regex can be used to filter by keywords (queries) or pages (URLs).
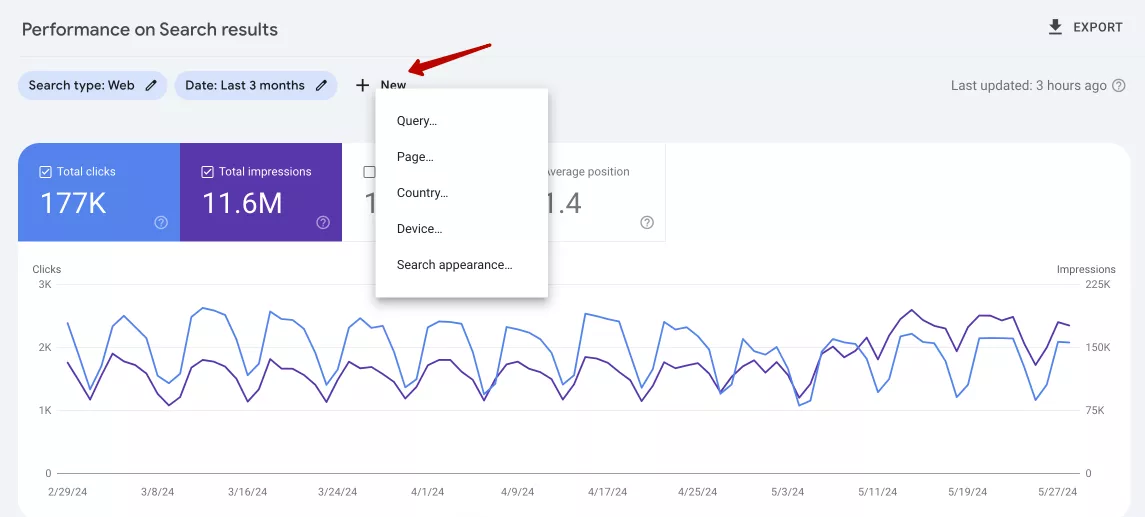
To use Regex in GSC:
- Sign in to your GSC account.
- Navigate to the Performance report.
- Click the New button to add a new filter.
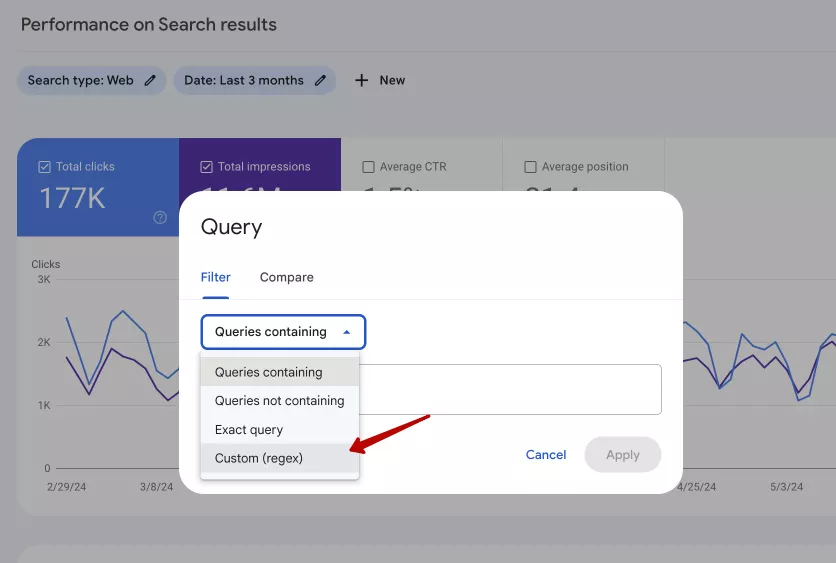
Filter by query:
- Select Query and then Сustom (regex) from the filtering options.
- Enter a regex pattern to filter searches that match the specified pattern.
Example: To filter queries that contain the words “buy” or “purchase,” you can use the regex “buy|purchase.”
Filter by page:
- Select Page and then Custom (regex) from the filtering options.
- Enter a regex pattern to filter pages (URLs) that match the specified pattern.
Example: To filter URLs that end in “.html” or “.php,” you would use “ \.html$|\.php$.”
Read more about GSC on our blog:
- Google Search Console Integration with Analytics 4: A Comprehensive Guide
- How to Create HTML Sitemap
- Connecting Search Console API to Google Spreadsheets
Conclusion
- Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool from Google that provides important information about website performance.
- The key functions of Google Search Console include Performance, Indexing, Experience, and Enhancement reports, a URL checker, and Sitemaps.
- Best practices for using GSC include regular monitoring and analysis of GSC reports, promptly fixing any problems that arise, and quick familiarization with new features and updates from Google.
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses