How to Set Up Filters in Google Analytics 4?
A filter in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is a tool that allows you to automatically filter incoming data by a certain parameter. It is very important to set filters up correctly because they exclude the actions of the team working on the project from analytics and allow you to analyze what real users have done.
What are the types of data filters?
Currently, there are two types of data filters in GA4:
- Internal traffic filters are used to exclude employee traffic.
- Developer traffic filters are used to exclude traffic coming from debugging devices.
Let's look at both types in detail.
What is an internal traffic filter in GA4?
Internal traffic is generated when copywriters, suppliers, managers, SEO specialists, etc., visit the site. These users are not the target audience, but if the team is large, the traffic volume will be significant and distort the data in the reports. An internal traffic filter will exclude them.
What is a developer traffic data filter in GA4?
Developer traffic comes from users setting up or tracking a resource in debug mode. It allows you to check if site settings are working correctly.
However, it also affects the indicators in reports, so it should be filtered. Using this filter, such data will remain only in the DebugView report, which is necessary for testing and allows you to check each change before deploying it in the working environment.
Filter modes in GA4
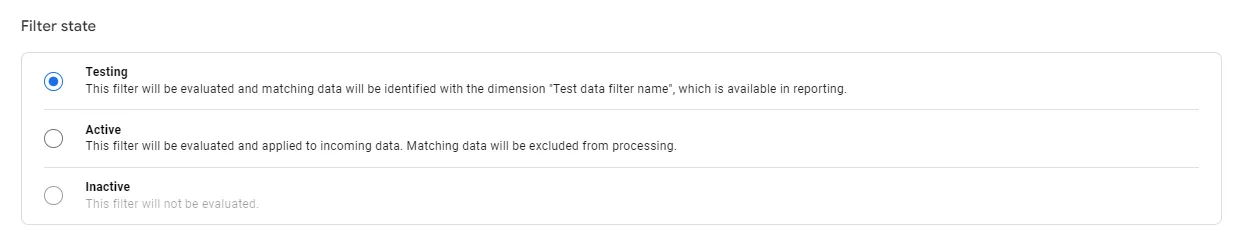
Filters can be in one of three modes: testing, active, or inactive.
Testing mode
It is crucial to test filters before activating them as they will irreversibly change the information. Once you cut off certain data, you will no longer see it in Analytics.
However, a filter in testing mode does not make irreversible changes, and you can analyze its performance. To do this, add a comparison to the report using the Test data filter name parameter.
Active mode
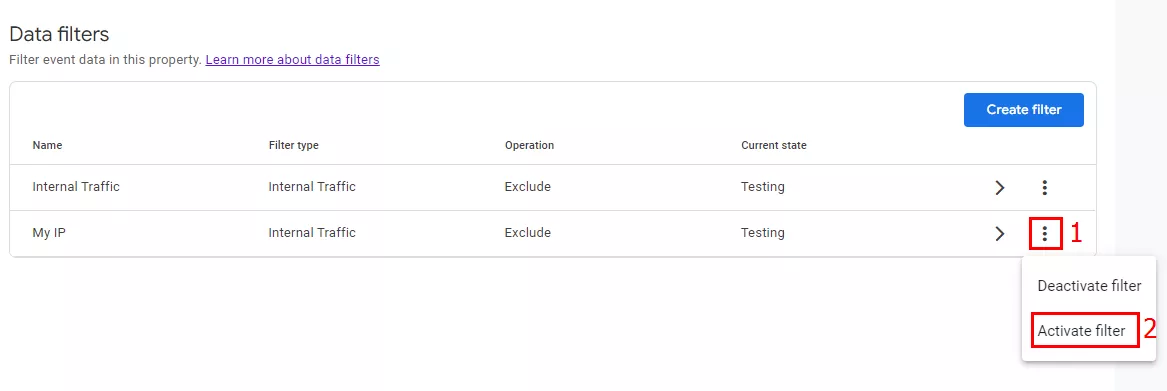
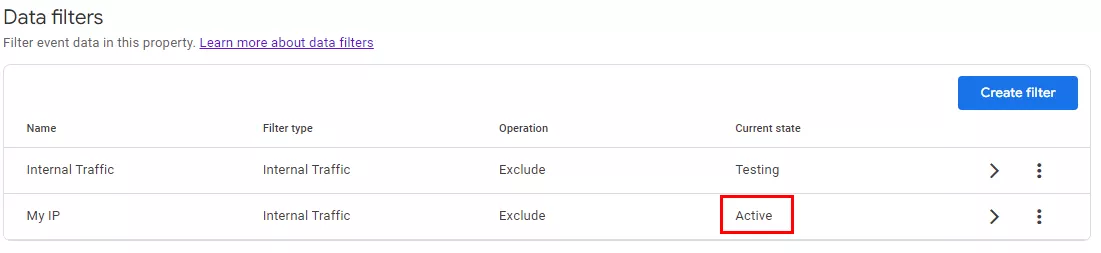
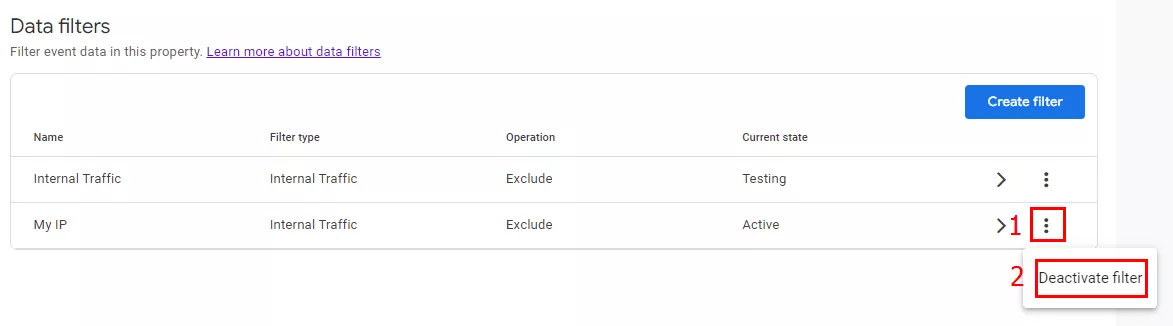
In this mode, the filter irreversibly changes the data. Click the three-dot options menu (1) > Activate filter (2) to activate it.
Analytics will then display a message warning you that the filters are irreversible. Confirm the activation to apply the filter.
Inactive mode
In this mode, the filter makes no changes to the data. To disable the filter, click the three-dot options menu (1) > Deactivate filter (2).
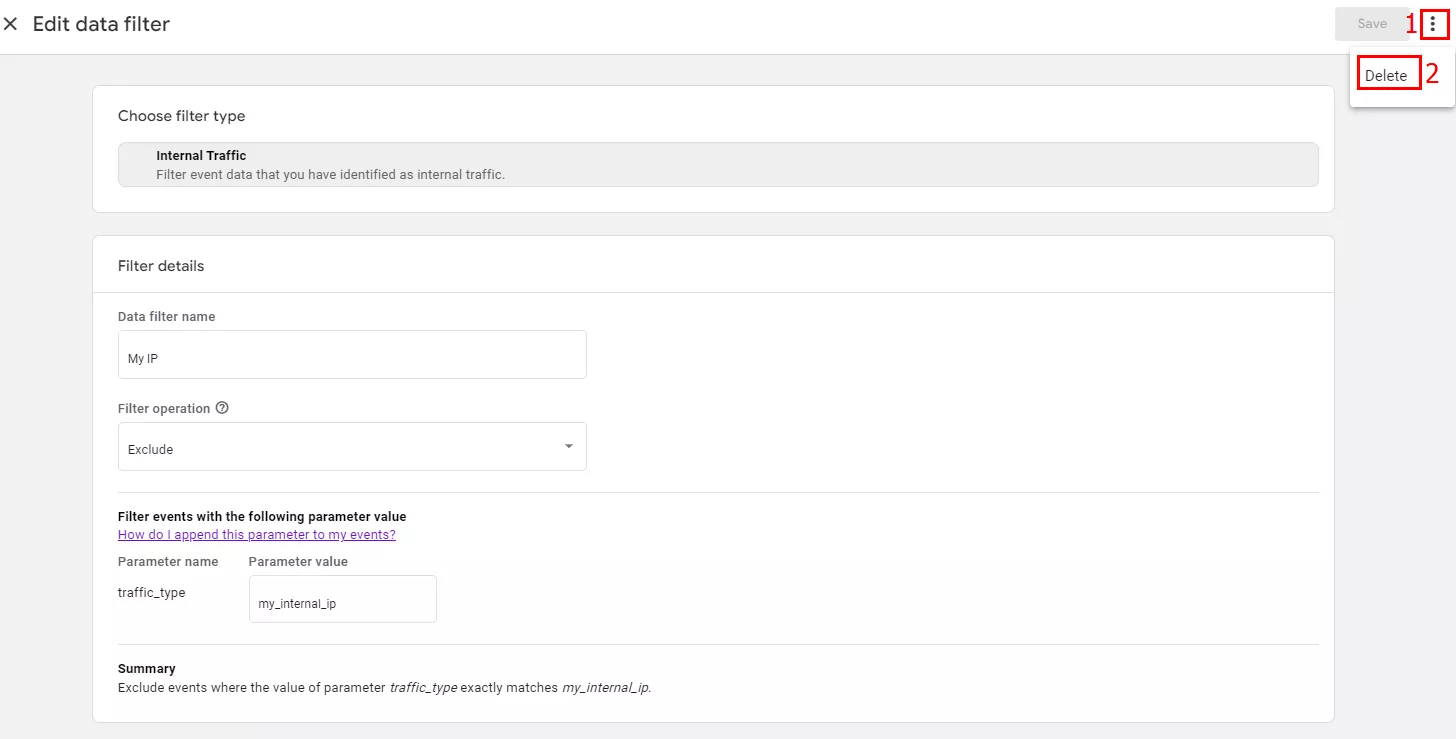
Filters can also be deleted. On the filter editing page, click the three-dot menu on the top right corner (1) > Delete (2).
How to set up an internal traffic filter in GA4?
Before setting up filters in Analytics, check your permissions. You'll need editor or admin access to the resource.
Defining internal traffic
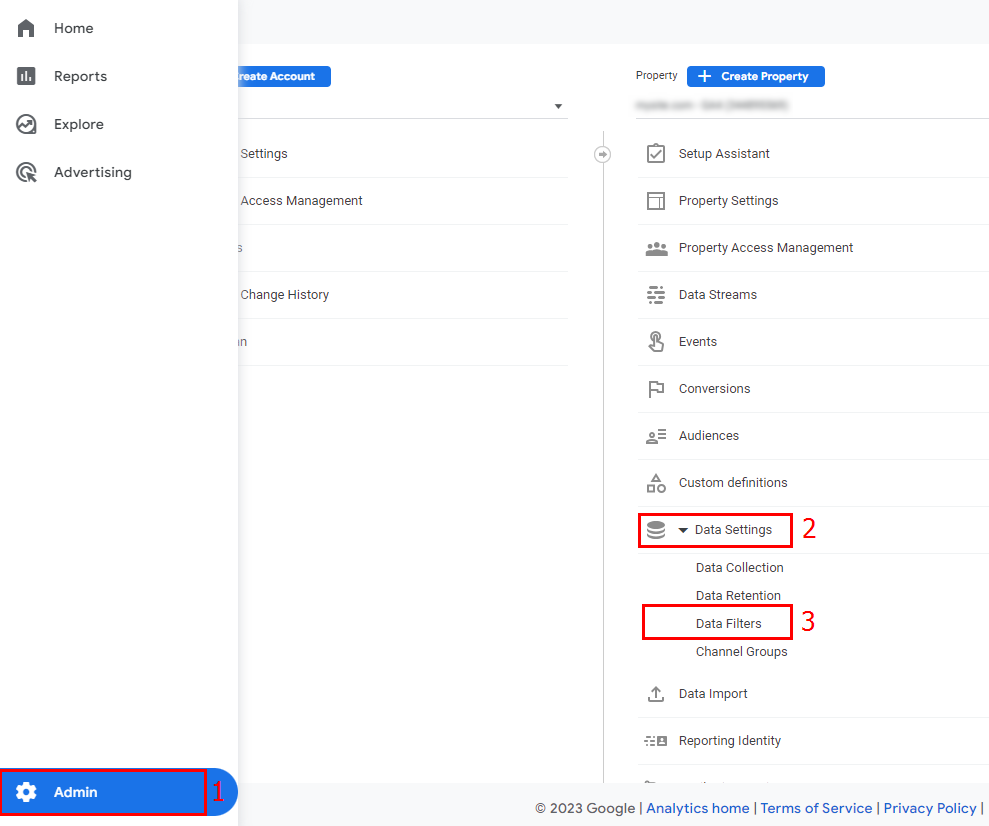
- This is the first step in customization. Go to Admin (1) > Property > Data Streams (2). Click on the arrow to the right of the desired stream name (3).
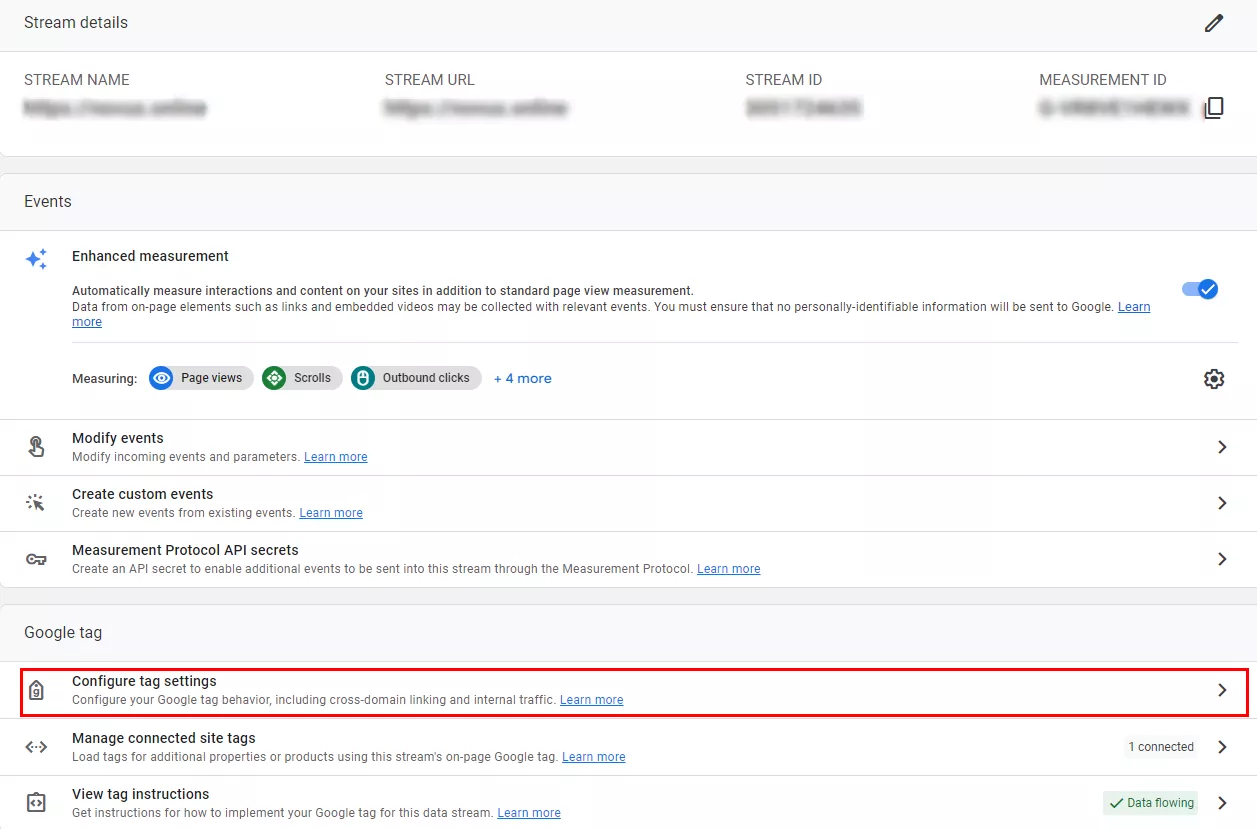
- Next, you'll see a window with the stream data. At the bottom of the window, select Configure tag settings.
-
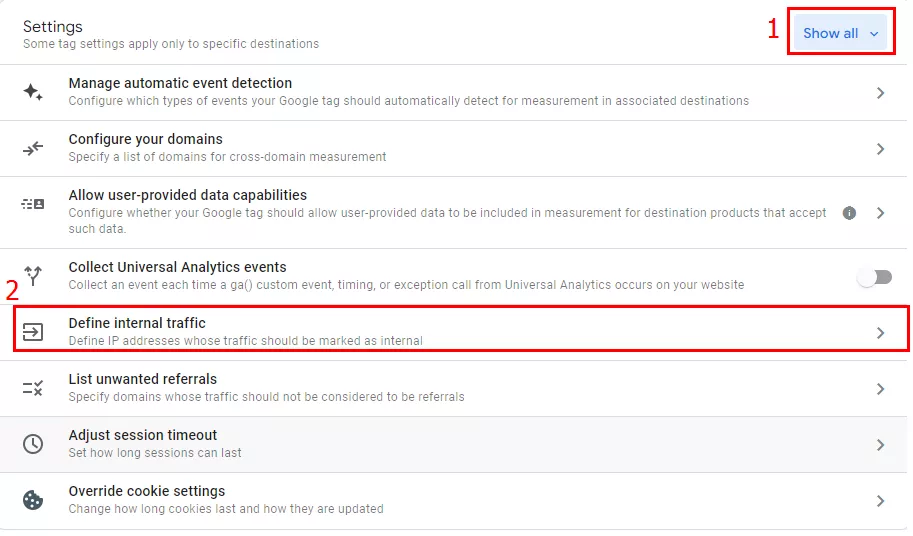
To see the settings, select Show all (1). From the drop-down menu, select Define internal traffic (2).
-
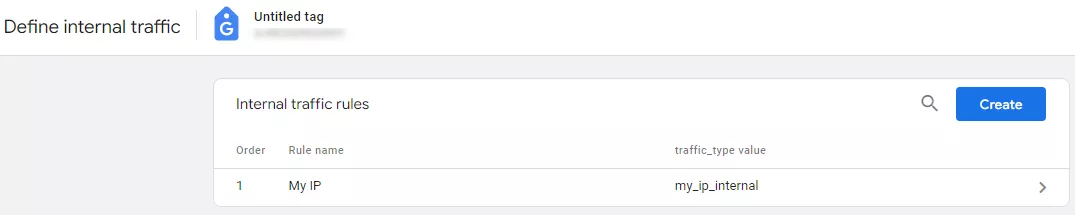
Next, you'll see a window containing the rules configured for this action.
If no rules are configured yet, GA4 will display a notification. To create a new rule, click Create (1). Conveniently, there is also a Learn more link (2).
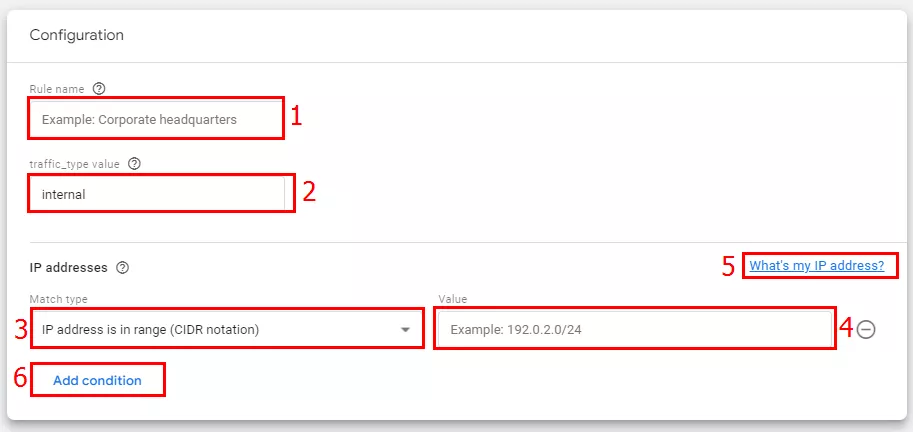
- In a new window, set the following rules.
- Specify the rule name (1).
- Next, write a name for the traffic_type value (2) that is easy to understand. Keep in mind that you will need different names for different types of traffic.
- From the drop-down menu (3), select the appropriate match type for the IP address.
- In the Value field (4), specify the IP addresses you want to exclude from GA reports. To exclude your IP, click What's my IP address? (5) and enter it in the appropriate field.
If you need to exclude multiple addresses, click Add condition (6).
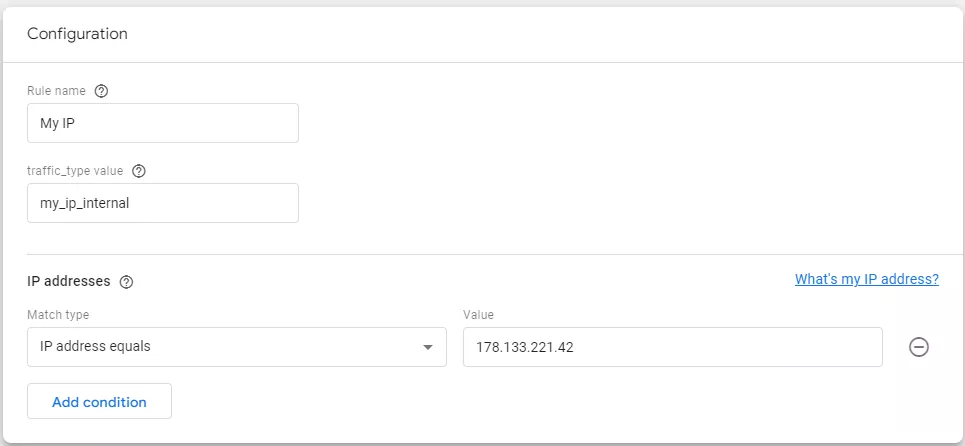
Here's an example of the configuration when specifying an internal traffic rule.
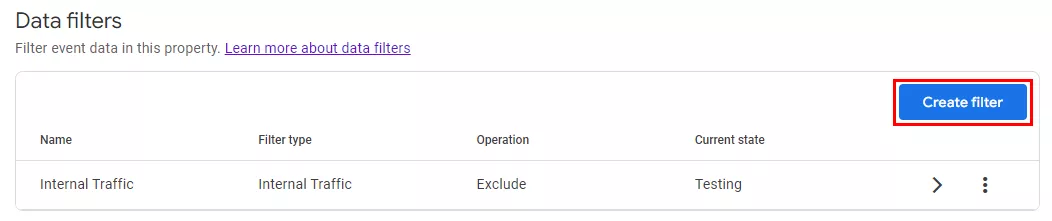
Data filter setup in GA4
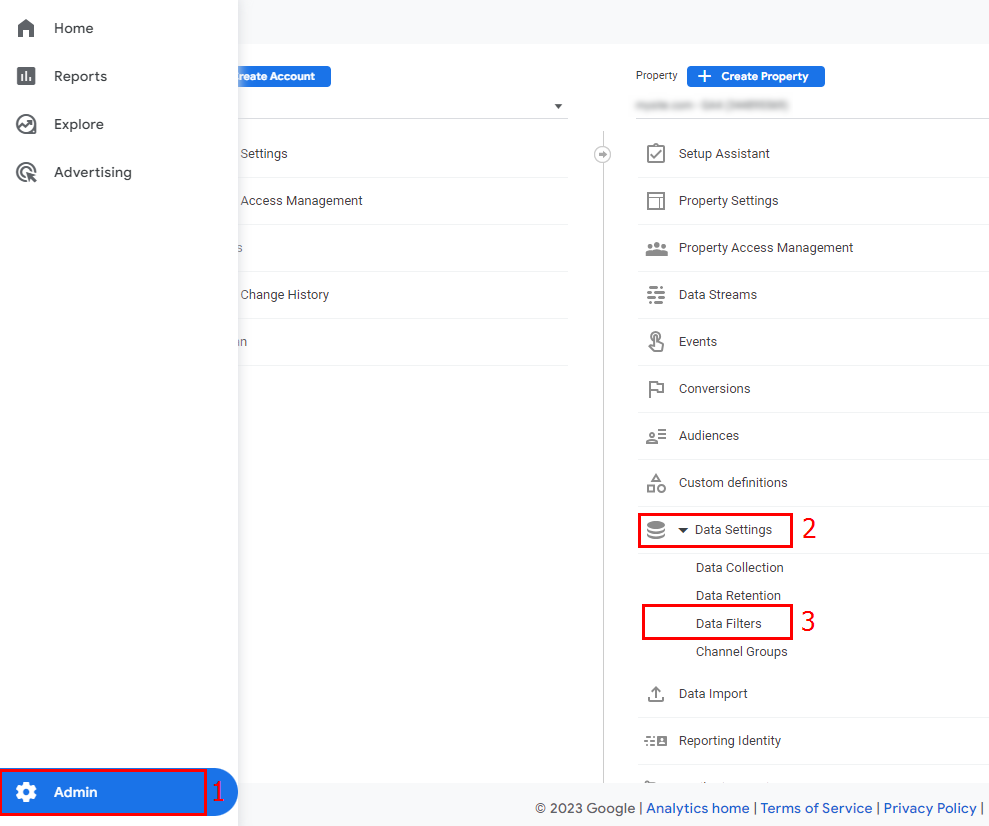
- Open the administration section (1). Click Property > Data Settings (2) > Data Filters (3).
Note: The internal traffic filter in each GA4 meter is automatically added in testing mode.
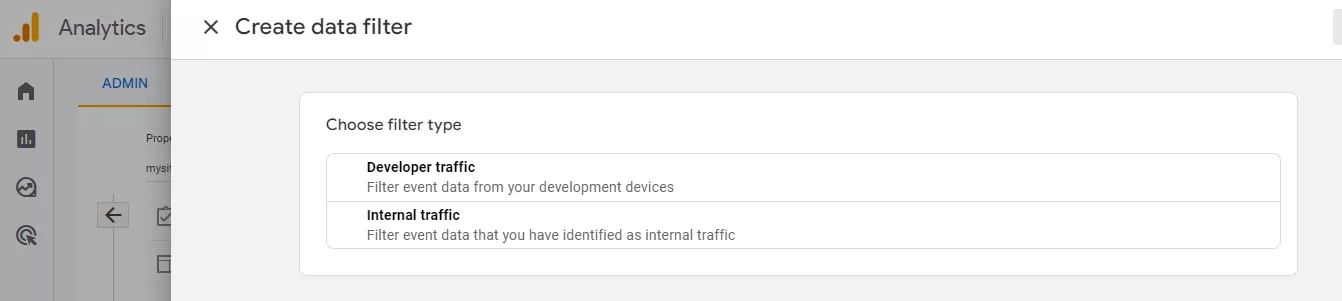
- To create a new filter, click Create filter.
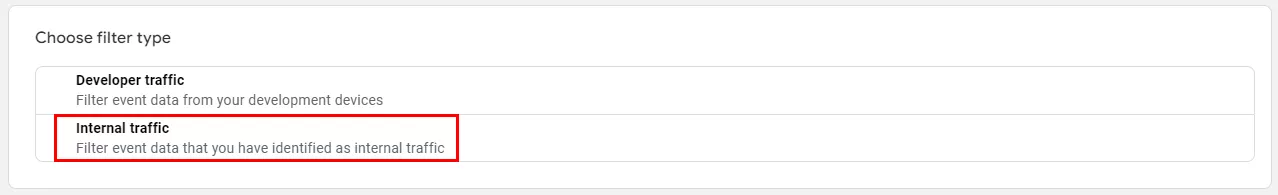
- In a new field, click Internal traffic.
- In the filter settings, type a name for the filter (1).
- In the Filter operation field, select Exclude (2) so the system does not process data from a specific filter. If you want to analyze data only from the filter, select Include only.
- In traffic_type (3), specify the name entered during the internal traffic definition.
- When you are done, click Create (4).
How to filter out developer traffic?
- Go to the admin section (1), select your property, and open the Data Settings drop-down list (2). Click Data Filter (3).
- Click Create filter.
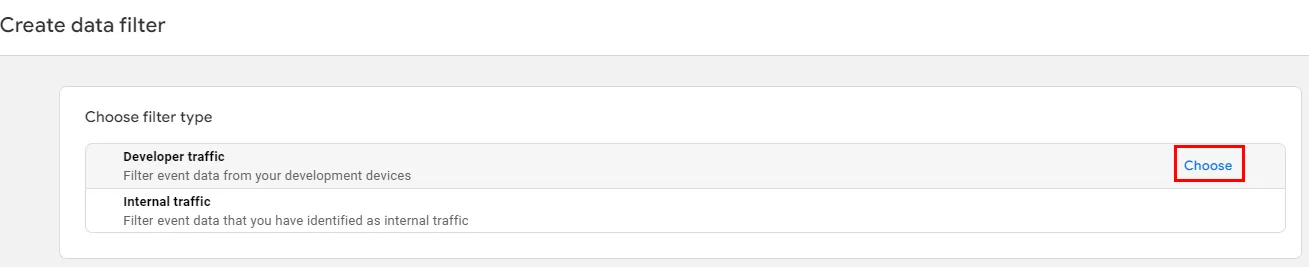
- In a new window, select the desired filter type.
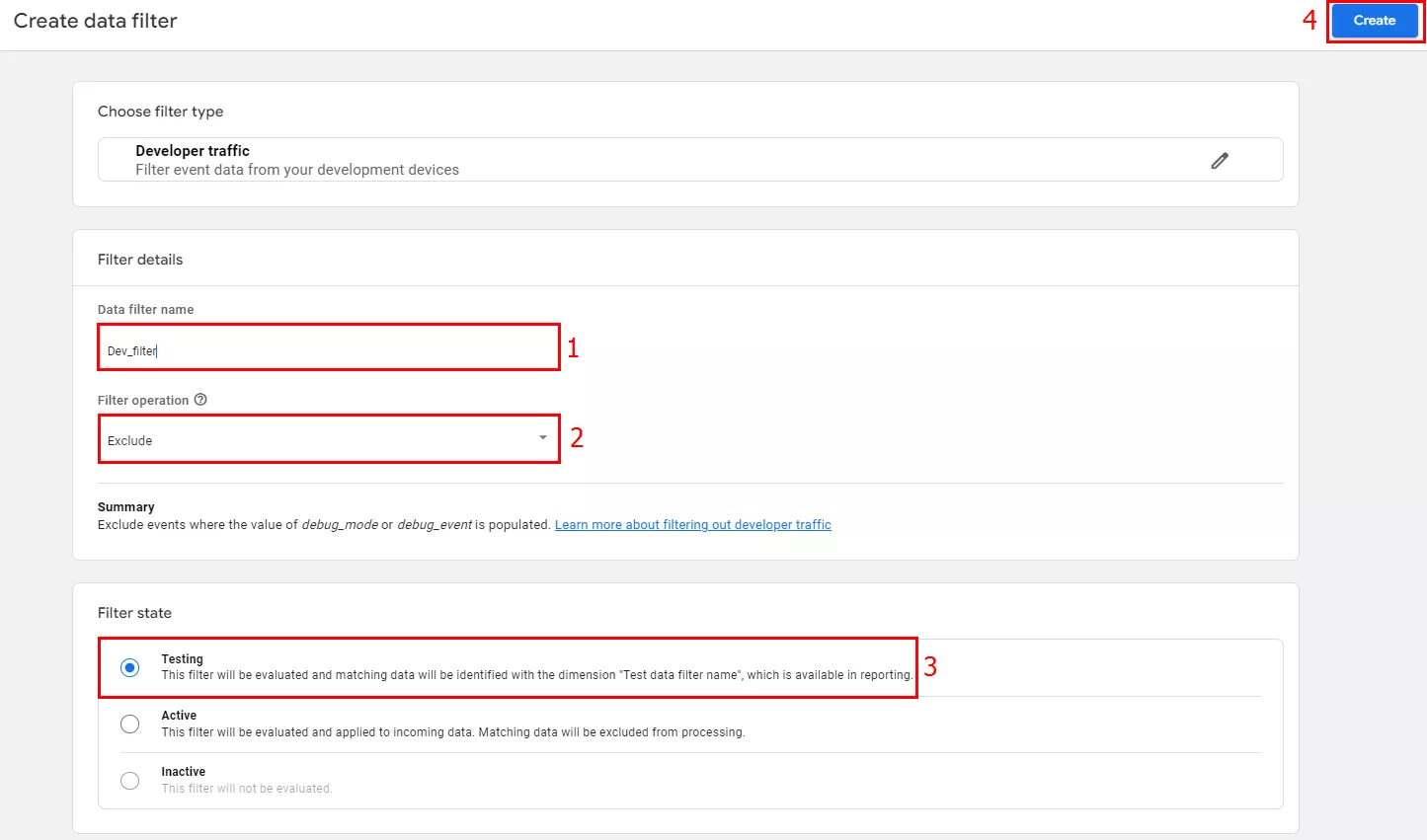
- In a new window, enter a unique and easy-to-understand name for the filter (1).
- In the Google Analytics 4 Filter operation window, select Exclude (2) from the drop-down list to prevent Analytics from processing the filter information. Click Include only (2) if you want to analyze data that is only from this filter.
- Select the Testing mode (3).
- Once configured, click Create (4).
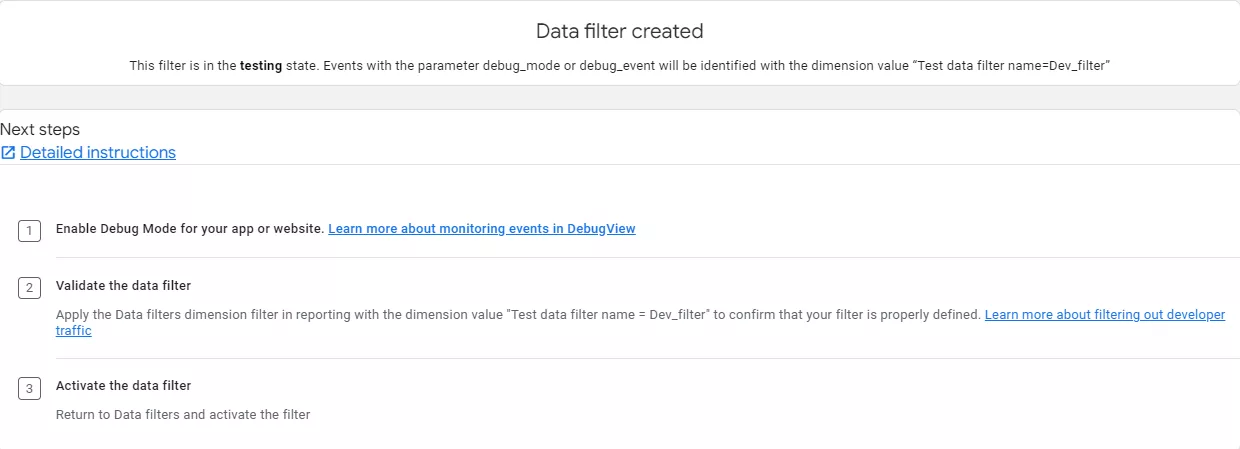
And you’re done! The filter is created, and you will see the following notification on your screen.
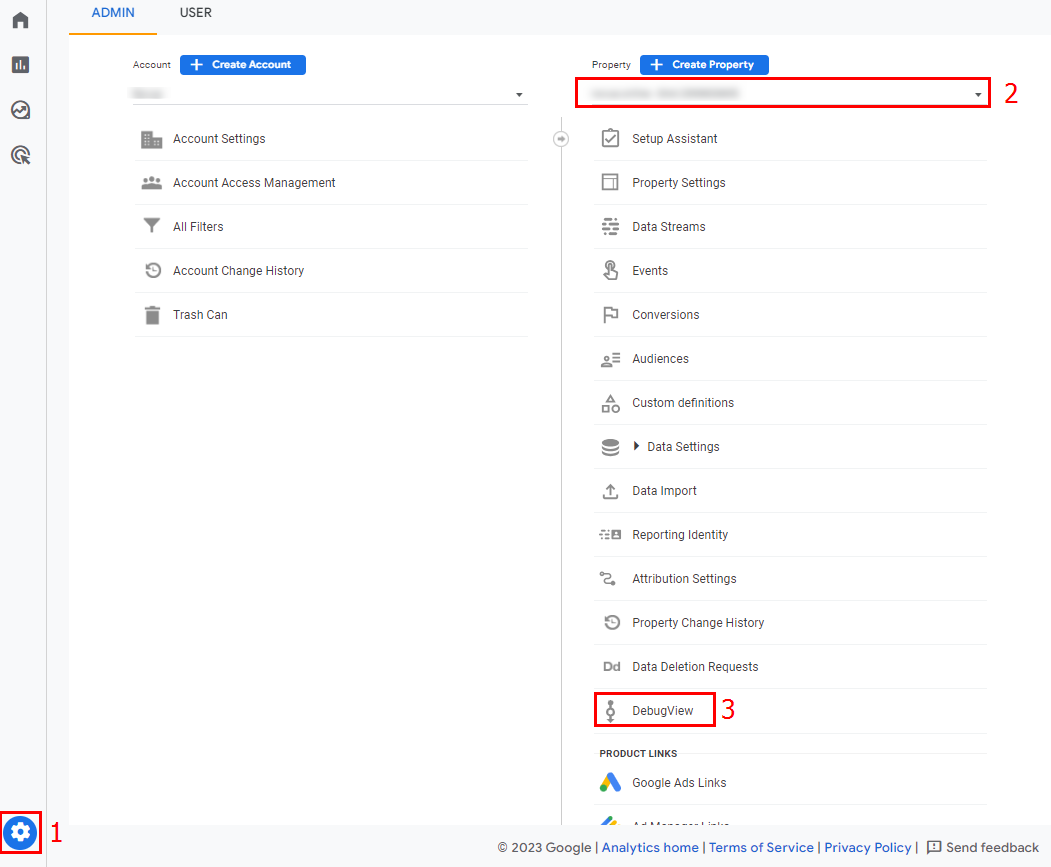
After that, actions in debug mode will not appear in reports and will not affect the data. But if you need to see them, go to Admin (1), select your property (2), and click DebugView (3).
To enable debug mode on your gadget, use the preview mode in Google Tag Manager and the GA Debugger extension for the Chrome browser.
Filter limit in GA4
- One resource can have a maximum of 10 filters.
- The time between setting up and applying data filters can range from one day to one and a half days.
- The maximum length of filter names is 40 characters. They must be unique for a site. The first character must be a letter, and you can use underscores, spaces, Unicode letters, and numbers for subsequent characters.
- You need the site editor’s permission to create, modify, or delete a filter.
- Once activated, GA4 data filters are irreversible; even after the filter is deactivated, you cannot see the filtered information.
- The applied filters do not change the historical data: the information before the filter was set remains the same.
Conclusions
- GA4 currently offers two types of data filters: internal traffic filters and developer traffic filters. Internal traffic is the traffic generated when copywriters, suppliers, managers, SEO specialists, etc., visit the site. Developer traffic is generated by users who customize the resource or monitor it in debugging mode. Both these types of traffic affect the indicators in reports, so they should be filtered.
- To create a filter, you need to have site editor permissions. Filters can be in one of three modes: testing, active, or inactive.
- To create an internal traffic filter, you must define internal traffic by IP address. However, you don't need to define traffic to create a developer filter.
- You can check the filter operation in the DebugView report.
- You can create up to 10 filters for a resource. While the effects of filters are irreversible, historical data is not affected.
FAQ
What data filtering options does Google Analytics offer?
Google Analytics filters fall into two categories:
- Internal traffic filters that exclude the actions of your employees.
- Developer traffic filters that exclude developer actions from all reports except DebugView debugging.
What is the difference between the internal and developer traffic filters?
The internal traffic filter blocks all internal traffic in GA4 in all reports. Therefore, developers will be unable to debug implementations before they go live.
The developer traffic filter filters data generated by specialists but allows you to view events in the DebugView report. If you are editing a site or adding new tags and want to test them, be sure to enable this filter first.
How many filters can I set up in GA4?
Up to ten filters can be created for one resource.
Recommended theme posts
Related Articles
A Netpeak Case Study: How to Generate Leads Through LinkedIn and Get Results in Six Months
We show our approaches step by step
Importing Data into Google Analytics 4: A Complete Guide to End-to-End Analysis
In this article, we will explain the types of data you can import, the analytics benefits of importing data, and how to implement importing
What Is the CPV Model, and What Are Its Advantages?
How is the viewing fee calculated, and how does it differ from the screening fee?