How to Write an SEO Article to Get into the Top 10 Search Results
For an article to be worthy of the top ten rankings in search results, it must be optimized for the Google search engine. This process requires certain skills and knowledge, but the basic algorithm can be boiled down to several understandable points.
This article may take a little longer to read than usual, but it contains extensive practical advice on optimizing articles, such as optimizing keyword frequency and achieving the right mix of short and long sentences. There is also a bonus checklist for those who read it to the end.
About SEO text in simple words
SEO text is detailed, structured content optimized for the needs of search algorithms. It must contain keywords and phrases matching users’ intentions and headings that make it easier for search engines to crawl pages.
Such text is needed on your website to attract the target audience, increase the position of the resource in search results, and the level of authority of your content.
To create high-quality, optimized SEO content, you must create text that:
- Engages the target audience and answers their questions.
- Generates steady traffic from search engines (organic traffic).
- Provides users with relevant information that encourages them to buy on your website, attracts more targeted subscribers to your blog, etc.
Dive into our glossary for key SEO definitions to boost your expertise!
The difference between an SEO article and a regular article
|
SEO article |
Regular article |
|
It uses specific keywords and phrases at a high frequency to clearly show the search bot what your content is about. |
It does not necessarily contain keywords and phrases. |
|
It is intended not only for readers but also for search robots. |
It focuses primarily on the reader instead of search engine algorithms. |
|
It provides helpful information to the reader with a goal of improving your site’s search rankings and increasing the number of potential customers. |
It provides interesting and/or useful information, just so the reader can learn something useful for themselves. |
An SEO article is created to achieve several goals:
- Provide readers with the information they are looking for and give them the answers they need.
- Provide the best possible answer to a given search query.
- Help the site rank higher in search results.
- Increase the site’s visibility.
- Increase organic traffic from search engines (to attract a new audience for your blog or as many potential customers as possible for your business, etc.).
- Make your services more popular and your business more profitable.
How to start optimizing text for SEO?
Choose a topic
According to Google’s algorithms, content should be primarily created to fulfill the needs of people. To get a new audience, you need to catch their attention, so choosing a topic is important.
Here are a few ways to find a relevant topic:
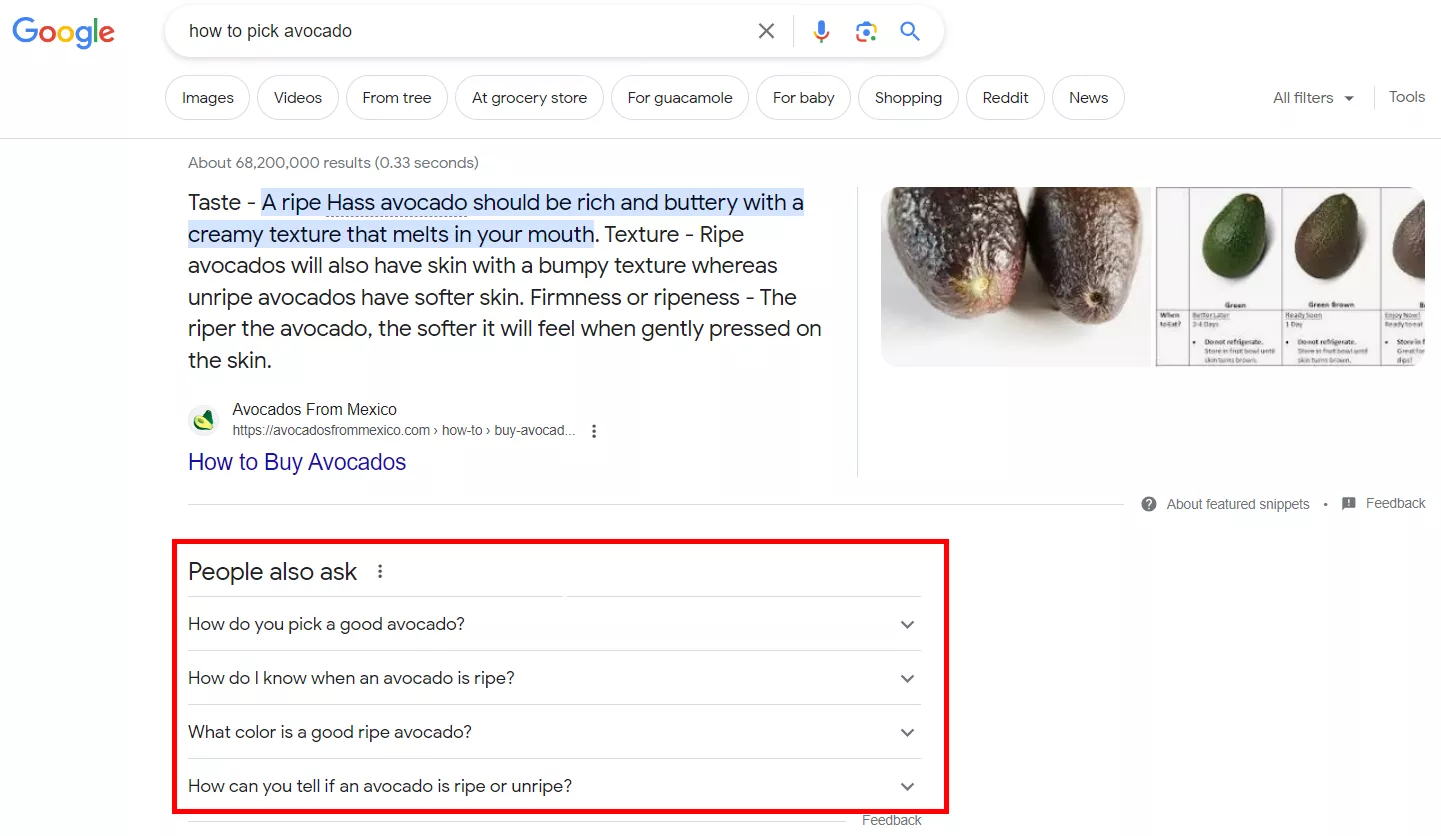
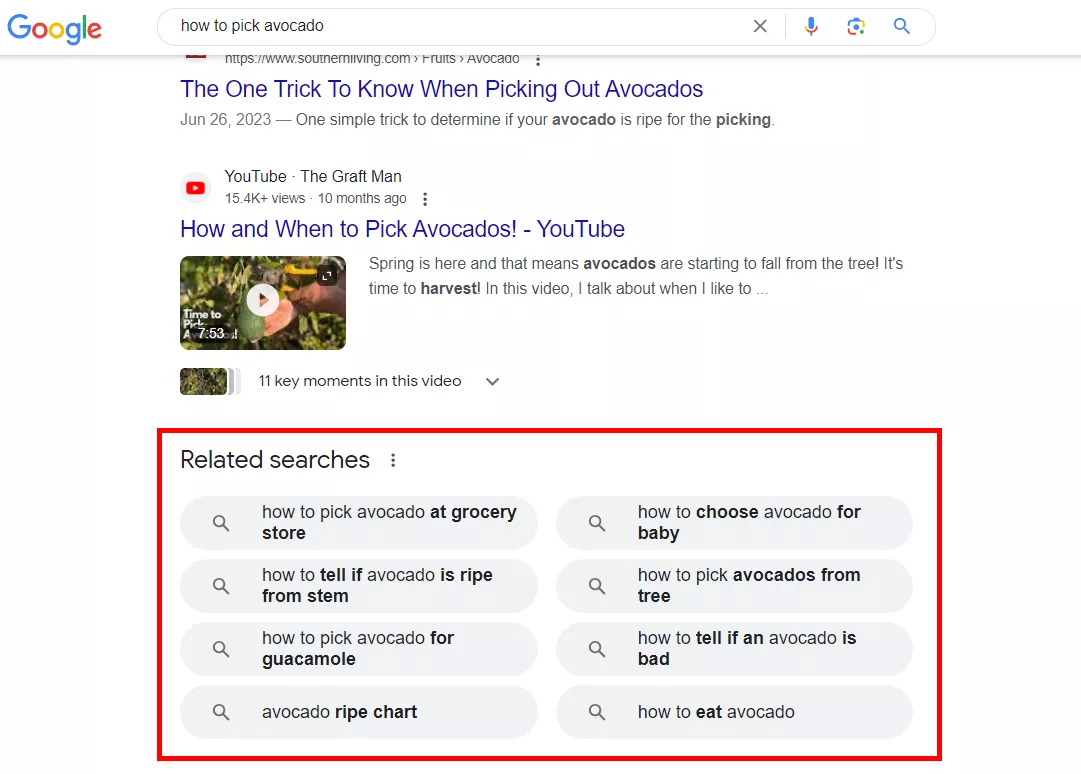
- Enter a search query related to the topic of your site, and go to the “People also ask” and “Related searches” blocks in the results.
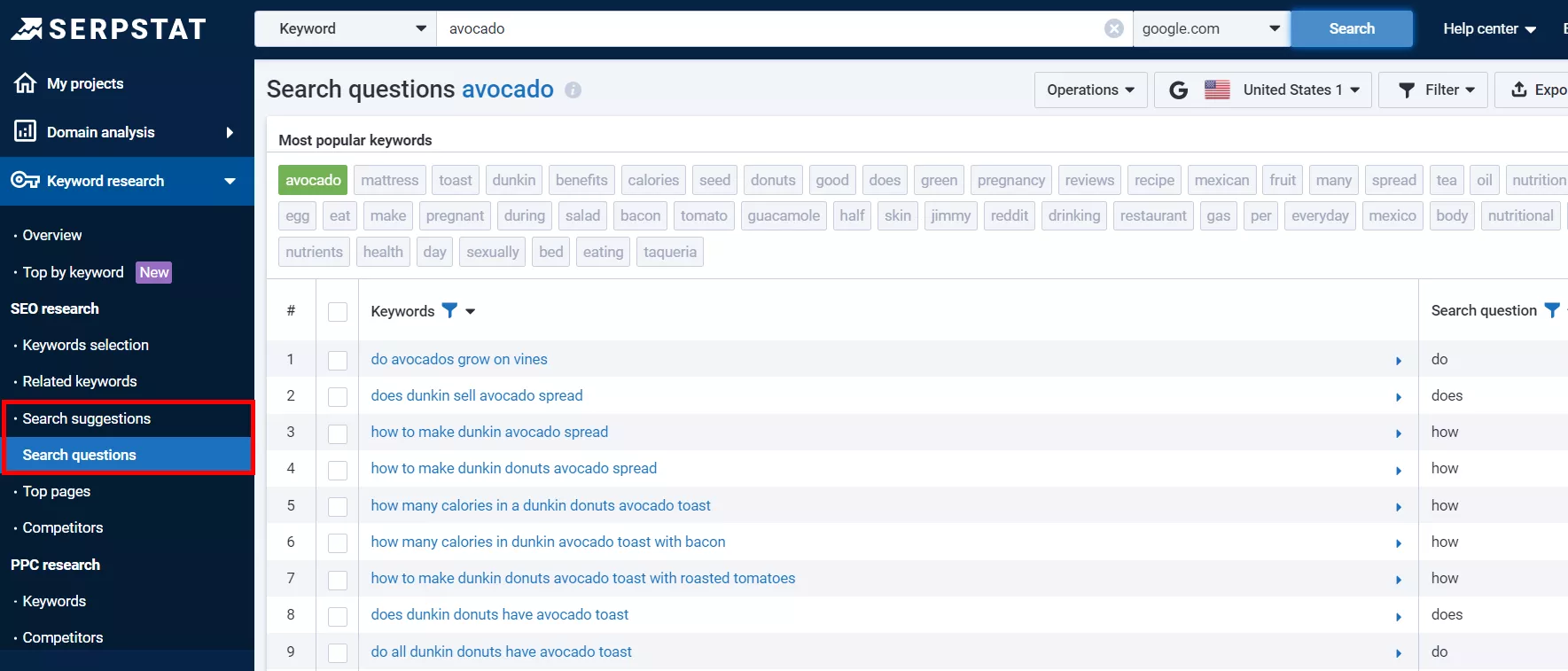
- You can also select a topic in Serpstat. See the “Search suggestions” and “Search questions” to find the questions most frequently googled by users.
- Review your competitors’ articles and identify topics that you have not covered or only partially covered on your site. To save time, you can use services like Netpeak Spider to compile the titles of your competitors’ blog posts.
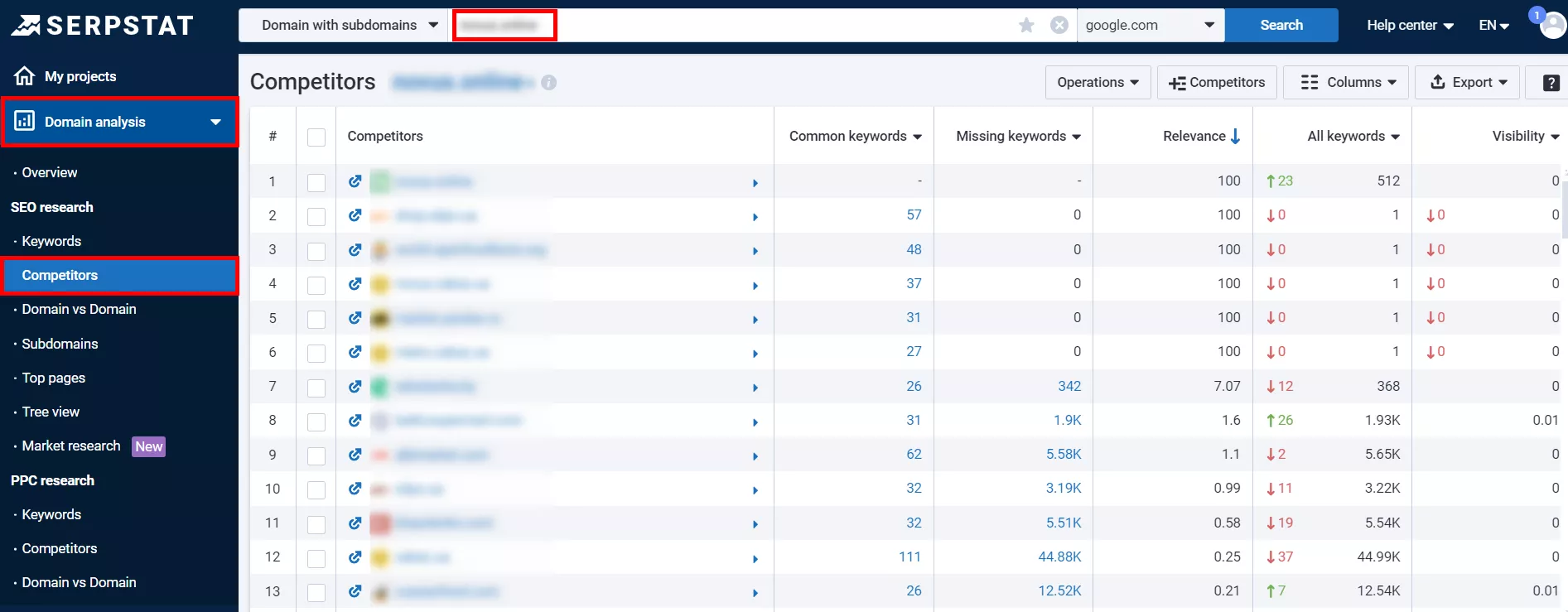
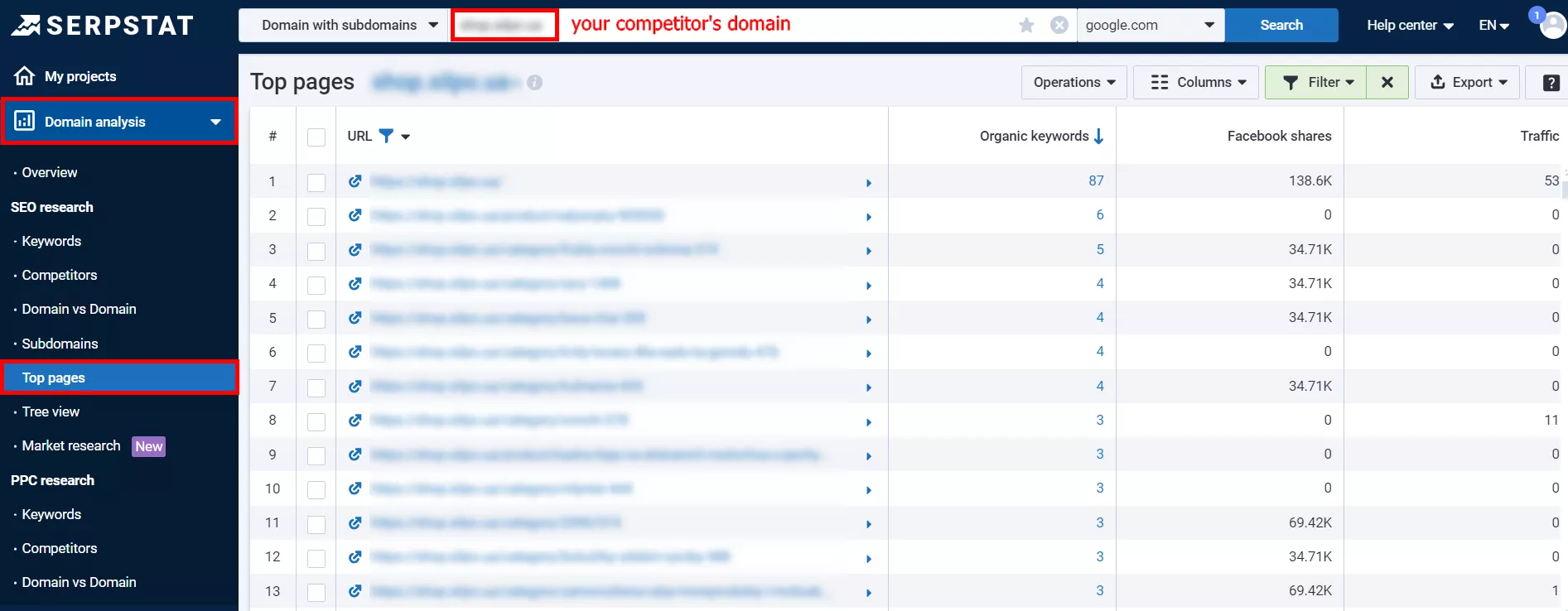
To find out which articles drive the most traffic to your competitors, look at the data in Serpstat’s “Domain Analysis” section → “Competitors”.
Then click on the competitor’s domain and go to Top pages where you can see the most visited pages of the competitor’s website or blog.
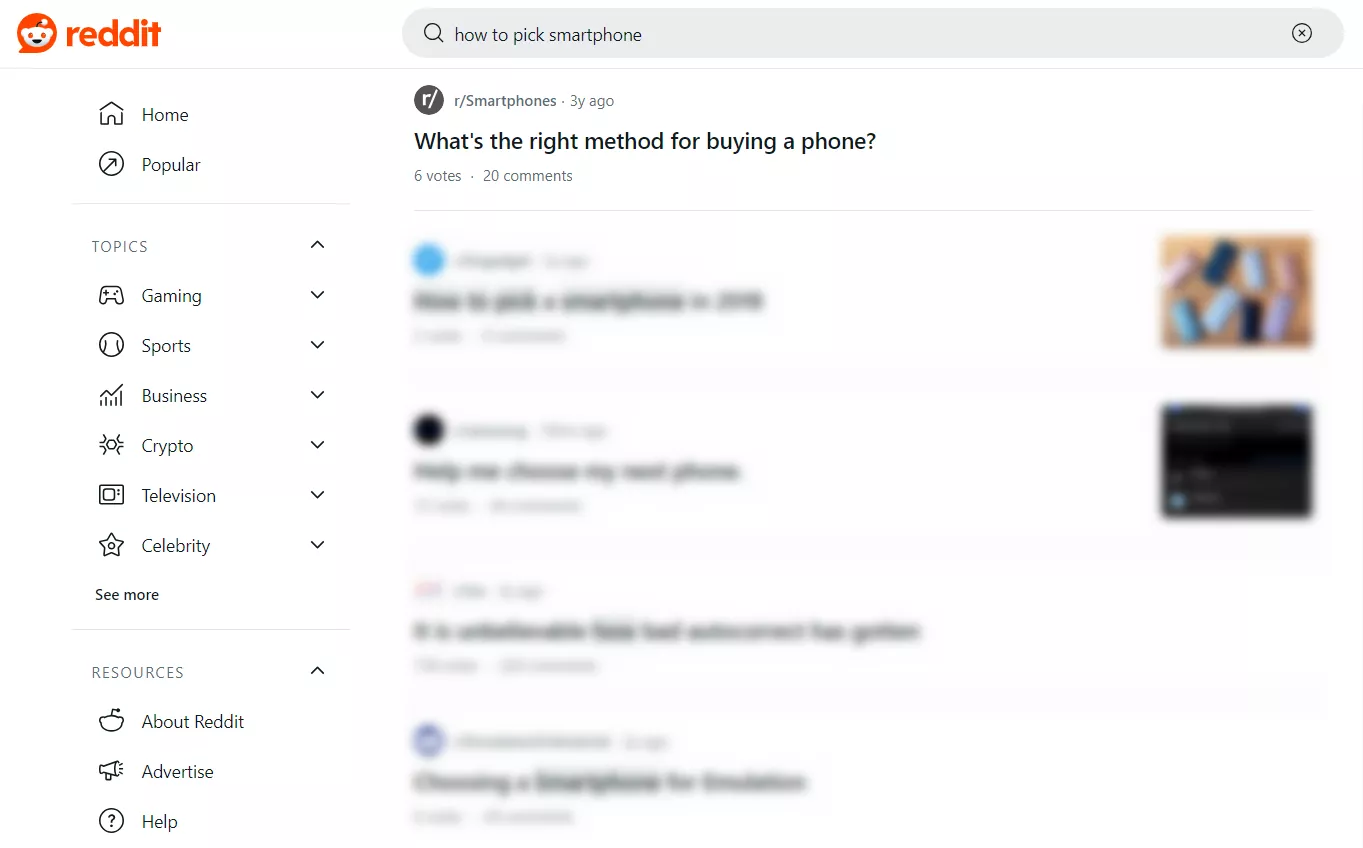
- Visit Reddit to find the most popular and engaging topics.
If your business is seasonal, take this into account in your content plan. You don’t want to publish an article in winter about what to wear with a crop top.
Analyze your competitors and make some hypotheses
For most niches, it is very likely that your competitors have similar articles. Once you have decided on a topic, enter the relevant query in the search engine and check the first 10 results.
You then need to make an SEO analysis of the text on the competitors’ pages, i.e. analyze their articles and the features of their writing: the structure and length of the article, keywords and LSI words, images, the way they present information, etc.
Keep in mind that the articles may have different content. For example, let’s say you have found three good articles about millet porridge from competitors. The first article may have a section about the benefits for the body, while the second tells who should eat it and the third has the quickest recipe.
If you combine these three points, your article will automatically become more useful and attractive to both readers and search robots.
Identify additional elements to structure your article
I advise you to identify repetitive elements and pay attention to the specific features of your competitors that make their content different. This will help you understand the additional elements you need to boost the structure of your article.
For example, if all of your competitors have images on their pages, you may want to add them as well. If some articles have a Q&A section or a comparison chart, you should do the same.
After analyzing your competitors’ articles, you will know what elements to include in your SEO-optimized article.
Build a keyword list
A search engine needs to understand the focus of the content, and keywords help it do this. With the help of keywords, Google will be able to display that content to readers.
While there are several tools to build a keyword list, I use Serpstat the most.
Create a list of LSI words
In addition to keywords, Google analyzes the page as a whole. From an SEO point of view, it is useful to add words related to the content topic (LSI) to your page.
For example, if you have an article about summer dresses, the LSI words would be style, cut, color, print, length, short, light, image, bow, combine, etc.
LSI can be found using Serpstat in the “Related keywords” section, Google autocomplete, or the Istio service.
Write an SEO article plan
The article plan should include the following points:
- Different variations of the title;
- The purpose of writing the article;
- Keywords in descending order of frequency;
- A list of LSI words;
- Length (number of characters or words);
- Subheadings or hypotheses);
- Other content structuring elements (lists, images, infographics, tables, etc.);
- Anchors (the text on which the link is placed) and links for linking;
- Ideas to improve the text and make it stand out.
How to write a search-optimized article
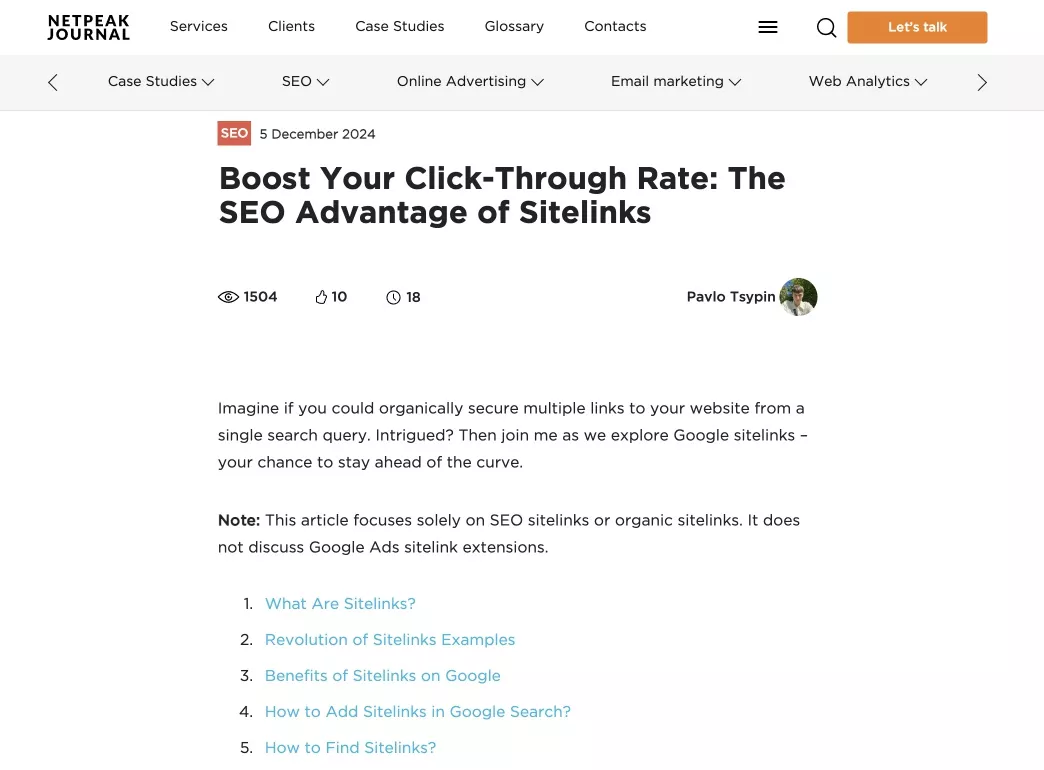
Create an anchor menu of contents
SEO articles can vary in length: if the article is long, a clickable block with the article content at the top of the page will help the reader.
Here is an example of an anchor menu:
Highlight headings and subheadings
It is worth highlighting headings and subheadings in the text, i.e. tags H1-H6. In practice, the most commonly used subheadings are H1-H4.
As H1 is the title, it is strongly recommended to use the keyword with the highest frequency in H1. In the lower level subheadings (H2-H6), you can use average frequency keywords.
The heading and subheading tags help the search engine crawler to define the topic more precisely. The search engine then shows the article in the search results to users with relevant queries.
Include lists in your content
Lists make text more visually appealing:
- Bulleted lists (like this one) are implemented in HTML markup using the <ul> tag.
- Bulleted lists start with a capital letter and (sometimes) end with a period.
- Numbered lists are implemented in HTML markup using the <ol> tag.
- Numbered lists start with a capital letter after the number and end with a period.
If your article contains any kind of sequential information, it is advisable to present it as a list.
Compare the text with and without a list. Which looks better to you?
Don’t forget the images
It is recommended to enhance the information on the page with relevant images and photos.
Once you have added images, be sure to optimize them with the alt tag.
The alt attribute is a short alternative text that describes to the reader what exactly is depicted in the image or photo. This attribute, especially if you include a keyword or phrase in it, confirms to the search engine that the image is relevant to the article. A well-written alt attribute will therefore help with ranking.
Add a video
A useful, relevant video attracts attention and enhances the content. To improve the ranking of a page with video content, you can use Schema.org video markup.
Create a table
Tables help readers better perceive and remember information.
In a table, you can compare product features, describe the pros and cons of a product, share tips or hacks, what to do and what to avoid, and so on.
Use the <table> tag to add a table to a page.
Add quotes to your text
Adding appropriate quotes from experts will make your article look more knowledgeable and trustworthy.
Check content for errors
Be sure to check for spelling, grammar, lexical, syntactical, punctuation, and other errors in the article.
- Language errors reduce confidence in the author’s expertise.
- Search bots also notice content errors. Too many errors will prevent the bot from correctly identifying the topic, which can lead to lower rankings and lower page positions. According to Google Search representative John Mueller, for most web pages, spelling and grammar errors are more damaging than incorrectly implemented HTML markup.
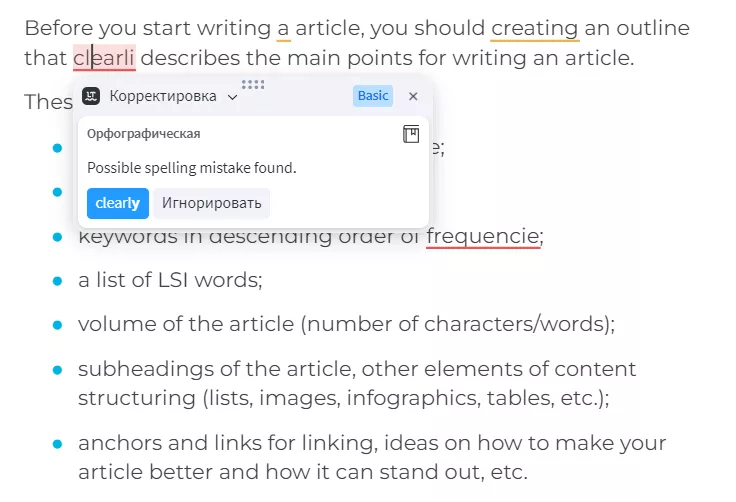
To check the text, I like the Language Tool extension, which highlights different types of language errors with different colors.
Check content for uniqueness
This is one of the most important factors influencing a page’s ranking in search results. Search engine algorithms analyze the content and determine whether it is duplicated or too similar to another web page.
John Mueller emphasizes that the text should be unique, especially in the part of the page that the reader sees before scrolling.
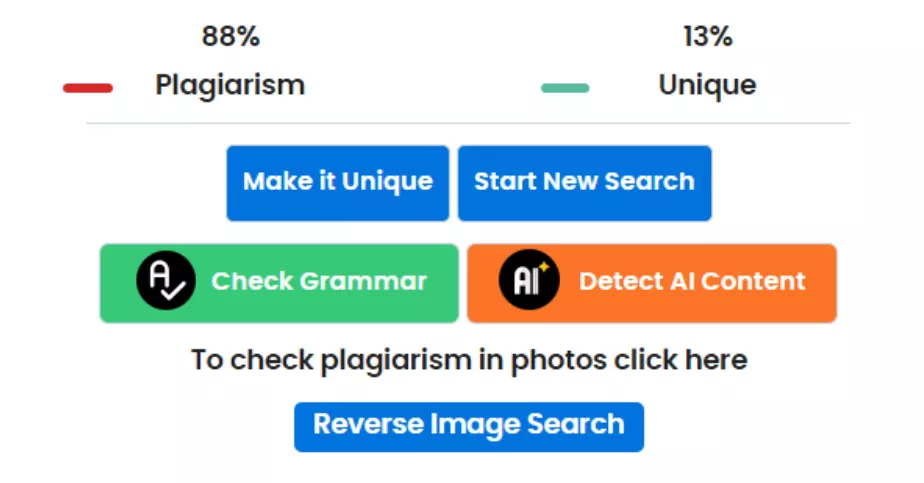
You can check an article for plagiarism using the Duplichecker tool. I advise you to focus on achieving a uniqueness score of at least 95%. In topics where it is too difficult to create unique content (medication instructions, recipes, etc.), the minimum threshold for uniqueness can be lowered to 80%.
Create schema markup
User markup to help the search engine determine the kind of page content: a recipe for a delicious snack, a FAQ, a video, etc.
Schema markup allows Google to better understand the content on the page and generate a better snippet (the text that represents a website in search engine results). To do this, you can use Schema.org schema markup and its tags, which are added to the HTML code of the page.
Another type of markup, micro-markup, is a special technology for marking up web pages to make them easier for search engines to understand.
Here are instructions on how to mark up structured data that is supported in Google Search. You can use the Schema Markup testing tool to check for errors when entering data in schema markup.
Set up interlinking
To get higher rankings in Google, you should include links to other pages on your site in your article. Known as internal links, these contribute to a better distribution of backlinks. This means that other pages on your site can also be ranked higher.
Not only that, internal links also help the audience discover more content and understand that you are a reliable source of information. However, you should only use internal links where it naturally fits the context.
For instance, when you publish a new article, you should add internal links from other pages on your site to the new article to encourage search engines and users to find it.
Create manual meta tags
Meta tags are HTML code elements that contain information about the content of a page. They provide important information to search engines for proper indexing, title, keywords, description, etc.
The title and description meta tags display a brief description of the content. These are seen by the user, so they should be written with an aim of attracting and encouraging users to visit your site.
Meta tags also affect search engine rankings, so don’t forget to use keywords in them.
Learn more about creating manual meta tags.
Allow indexing and crawling
The page should be open for indexing and crawling by search robots. This requires the robots meta tag:
<meta name=«robots» content=«index, follow» />
You will also need to add the URL of the article to the XML sitemap.
The most common mistakes in SEO texts
Plain text
If you go to a page and see plain text with no subheadings, lists, or paragraphs, you’ll probably leave without reading anything.
Remember, the visual aspect of search-optimized articles is really important. It’s the first thing a reader pays attention to and influences whether or not they stay on the page.
Too much padding
Text with a lot of “empty words” and little meaningful content will rank lower. The padding rate in the text is the percentage of empty words out of the total number of words on the page.
It’s important to balance “concise” and “clear” so that the reader gets the most out of the content.
Highlighted keywords
If you have highlighted keywords in the draft, you must remove them before publishing. Highlighting looks unnatural to users, and the search engine will likely penalize you.
I advise you to highlight only the sentences that are truly important to readers.
Language errors
As mentioned earlier, language errors indicate low-quality content and may diminish the reader’s trust in both the information presented and the company publishing the content.
In his video, Mat Cutts, an American software engineer at US Digital Service, explains why errors (primarily spelling errors) negatively affect the ranking of an article in search results. The more errors in the content, the lower it will be ranked.
Nausea
Nausea is a parameter that determines the degree of saturation of the text with keywords and phrases. It is important because if certain words are used too often, the search engine may view the content as spam. This will decrease your site’s rankings.
Use alternative synonyms or corresponding pronouns in the text. As an added bonus, such text will be more natural and easier to read for users.
Keyword stuffing
Using too many keywords can lead to search engine penalties. Keyword stuffing degrades the quality of the content and makes the text less readable and useful.
From my experience, I recommend using about one keyword phrase per 500 characters to avoid over-stuffing the text.
Too complex or wordy writing
Text with long, complex sentences is difficult to read. I recommend alternating long and short sentences according to the following pattern: one long sentence followed by two medium or short sentences.
AI-generated text
Google does allow AI-generated content when the quality of that content is appropriate, useful, truthful, and relevant. But more often than not, AI generates text that contains outdated and incorrect information. Such low-quality content has a bad effect on page ranking by Google algorithms.
Therefore, I do not recommend using AI to generate text if you are working on optimizing your website for search engines.
How to analyze the effectiveness of your SEO text
After implementing changes to optimize your text, you’ll need to analyze the effectiveness of your SEO copy to see if you’ve achieved your traffic goals.
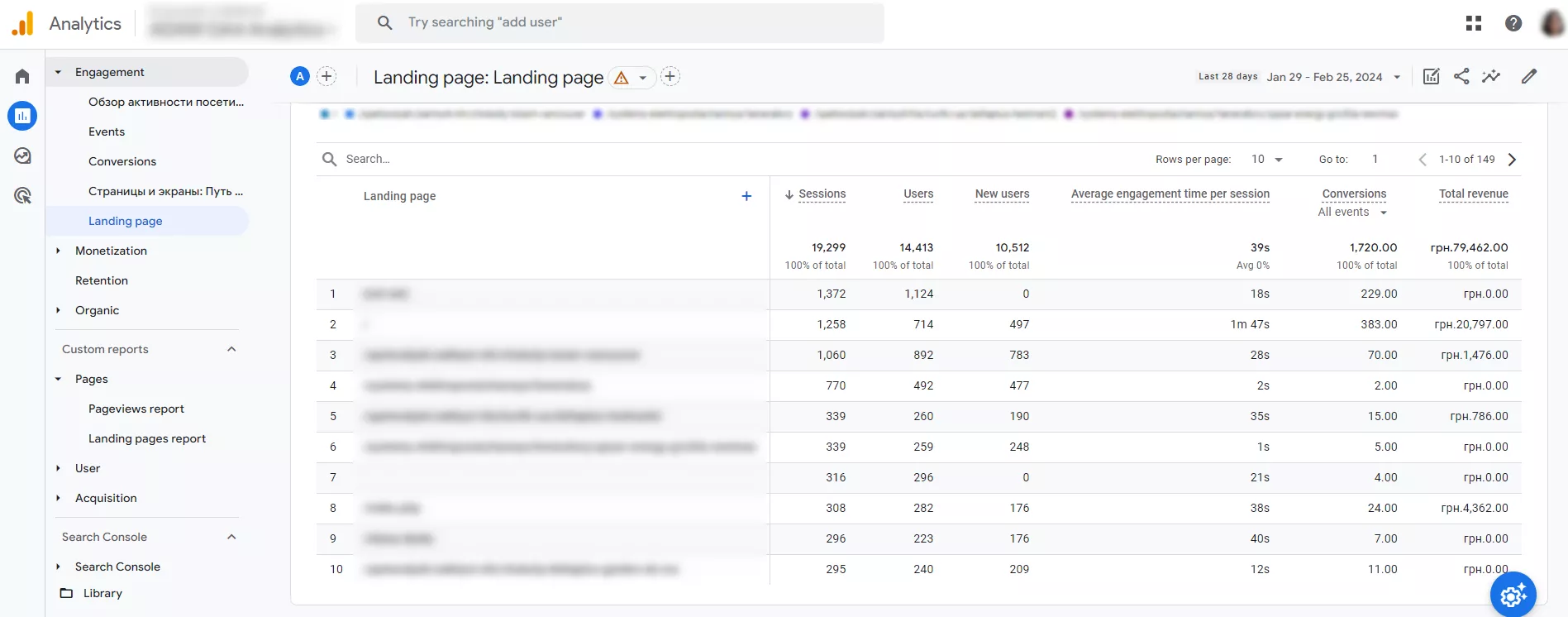
This is where Google Analytics comes in. Go to your website account, click Engagement > Landing page, and get a report.
Google Analytics also allows you to create custom reports where you can select the indicators you are most interested in when analyzing a page, such as bounce rates, exit rates, and average time of user interaction during a session.
It is also worth checking in Google Search Console to see if the site is ranking for new keywords. If it is already ranked, track the change in positions. Check the CTR and position two months after publishing and then after a while to see the trend.
Text optimization with Serpstat
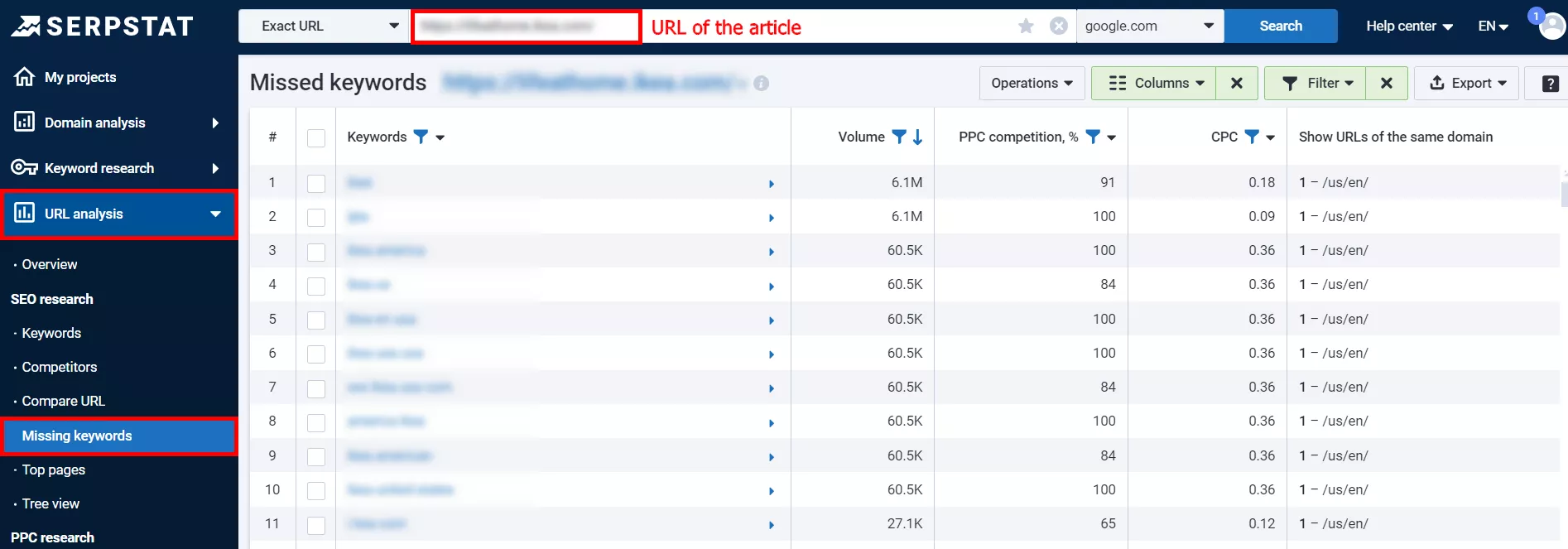
Even the best article loses relevance over time. Use the Missing keywords report in Serpstat to check for this.
What additional text elements are included in search-optimized articles?
You can add additional elements to the article:
- Content author and a brief bio
- Subscription form
- Product and service blocks
Author of the content
It’s a good idea to provide brief information about the author and their accomplishments, as this will make the content appear to be expertly written and increase the credibility of the company.
Subscription form
To increase traffic, you can invite readers to fill out a subscription form so they can receive notifications of new articles.
Products and services block
At the bottom of the article page, you can add a block of products and services. It is best to add products and services that are relevant to the context.
Tips on distinguishing a good SEO article from a bad one
|
High-quality SEO text |
Low-quality SEO text |
|
High-frequency and medium-frequency queries are evenly distributed throughout the text. |
Keywords are clustered in one part of the text, or only low-frequency queries are used. |
|
The table of contents is outlined at the top of the article, and each item is clickable. |
There is no table of contents at the top of the article. |
|
The structure of the article is clearly visible. Headings H2, H3, etc. are highlighted and contain keywords. |
The article is a solid block of text without clear subheadings. |
|
The article contains at least one bulleted or numbered list. |
The article contains no lists. |
|
The text is divided into paragraphs. |
Text is not divided into paragraphs. |
|
The text includes relevant images, optimized using the alt attribute. When suitable, videos and tables are included. |
Images are of poor quality, not optimized with the alt attribute, or not present at all. |
|
The trustworthiness of the information is confirmed by citations. |
The accuracy of the information is not confirmed by reliable sources. |
|
The text is more than 95% unique. |
The text is not unique. |
|
The article has schema markup using Schema.org (Google recommends using JSON-LD schema markup). |
The article has no schema markup. |
|
The article contains internal links to related articles or services. |
There is no internal linking. |
|
Manual meta tags have been added according to the recommendations and content of the article. |
The page either does not have meta tags, or they do not meet the requirements. |
|
Content is written concisely without padding. |
A significant amount of text is padded. |
|
Keywords fit in naturally and are not bolded. |
Keywords are out of context or in bold. |
|
The number of keywords is optimal (approximately one keyword per 500 characters). |
There are either too many or too few keywords. |
|
The text is written competently and in accordance with the standards of the language in which it is written. |
The text contains language errors. |
|
Information is presented in a clear, accessible manner. Long sentences alternate with short ones. |
The information is hard to read. Sentences are too long, and the reader has to reread them to understand the meaning. |
|
The topic of the article is fully covered. The article has answers to all the questions it raises. |
The topic is not fully covered, and the article is not comprehensive. |
|
The information in the article is presented in a logical and consistent manner. |
The content of the article is chaotic and disorganized. |
|
Written by a human author. |
Generated by AI. |
FAQ
What tools are available to help optimize articles?
- Use the Language Tool or Grammarly to check the text before publishing.
- Use Duplichecker to check for uniqueness and plagiarism.
- To make working with text easier, you can use bookmarklets, which are small applications that can be saved as browser bookmarks. They make it easier to optimize text by allowing you to:
- Determine the amount of text in words and symbols.
- Highlight headings and subheadings.
- Highlight the title, description, and keyword tag information.
- Underline links in the text.
- Perform automatic translation of a fragment, etc.
- Serpstat and Ahrefs are useful tools to perform a comprehensive content audit, get SEO recommendations, and analyze your own site and competitors’ sites.
Can SEO copy be “creative”?
Sometimes you just want to be creative and impress the reader with your style and language skills. But in addition to humans, SEO articles are also intended for search robots.
In his interview for Teal Talk, John Mueller noted that Google does not understand sarcasm, among other things. Content written in that style may be misconstrued by the search engine. Mueller advises to avoid using sarcasm in content.
“I would say that we are very likely to misunderstand something like that or not recognize sarcasm when we see it on the page. I would make sure the content is as clear as possible, especially when it is critical to communicate relevant content to Google and all users.”
Writing an article that is excessively creative can cause Google to misinterpret it and lower its rankings.
Bonus for those who read to the end
If you’ve read this far, well done! Here is a bonus for you: a checklist with an algorithm for writing an SEO article. Use it to quickly check if your article meets the requirements of search engines.
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses