Tagging Plans: Why They Matter and How to Make One
Have you ever tried to make sense of the marketing tags on a website — whether it is your own, a client’s site, or one you help manage — and found yourself lost in a tangle of unclear tracking codes? You may have wondered why certain tags exist, why some parts of the website are not tagged, or what each tag is doing. Or perhaps you were unsure who implemented them and if they were still relevant. A tagging plan is the solution to this.
In this article, I will explore what a tagging plan is, why it is important, and how to create one. I will also break down each step of the process, from defining objectives to implementing the plan and maintaining it.
What is a tagging plan?
A marketing tagging plan is a detailed, strategic document that maps out exactly how data will be collected on a website or app to measure user actions, engagement, and overall site performance.
It’s essentially a blueprint for organizing tracking tags, which are snippets of code that capture user interactions, such as clicks, form submissions, or page views, and send this data to analytics platforms like Google Analytics.
By clearly defining what needs to be tracked and how, a tagging plan aligns your business objectives with measurable data.
Creating a tagging plan involves working closely with business owners to:
- Understand key business goals
- Identify specific actions that need to be measured
- Assign tags to track these actions accurately
Typically organized in a spreadsheet or table, a tagging plan may contain multiple tabs or sections that outline different tracking components, such as event triggers, user actions, and data layers. This document also serves as a valuable resource for analytics teams, as it helps them validate and troubleshoot tags to maintain accurate data collection.
Why is a tagging plan important?
Keeps the focus on business objectives
A tagging plan is crucial for ensuring that your website’s data collection is both efficient and purposeful. By having a well-structured tagging plan, you can maintain focus on your business objectives and ensure that your tracking strategy aligns with these goals. This clarity allows for a more intentional approach to tagging instead of just adding random tracking codes across your site.
With this thoughtful method, you can prioritize the metrics that are truly essential to your success.
Acts as a centralized resource for teams
A tagging plan serves as a centralized reference for all stakeholders involved in your digital marketing and analytics efforts. It allows teams — whether they are working on marketing, product development, or data analysis — to collaborate more seamlessly by relying on a single authoritative source.
This shared document becomes invaluable for updating and refining your tracking methods, making it easy to adapt as your website evolves or new business goals emerge.
Improves data governance
The tagging plan also enhances data governance by standardizing naming conventions and event definitions. Consistency in tagging has several benefits:
- The collected data is clean and reliable.
- A lower risk of errors that could compromise data integrity (e.g., duplicate event tracking, misattributed conversions).
- Data is more easily interpreted for informed decision-making.
When everyone follows the same tracking guidelines, data becomes more transparent, accurate, and actionable.
Transforms data into insights
The goal is to transform data into information and information into insight.
— Carly Fiorina, former CEO of Hewlett-Packard, the first woman to lead a Fortune TOP-20 company
In today’s data-driven world, a tagging plan helps extract meaningful insights from your analytics. By translating business objectives into measurable data points, it allows you to better assess the performance of your marketing campaigns and optimize strategies for higher ROI. Without a proper tagging plan, you could miss valuable opportunities and make misinformed decisions, limiting your potential for growth.
As an example, imagine a SaaS company experiencing significant growth in organic traffic but seeing no corresponding increase in trial sign-ups or account registrations. Without a proper tagging plan in place, it might seem like the marketing strategy is on track simply because the traffic is increasing. However, thoughtful and detailed event tracking would reveal that the organic traffic isn't actually converting because it doesn't align with the target audience. This insight will prompt the business to reassess its content strategy and make adjustments to attract more qualified leads, ensuring business goals are better achieved.
How to create a tagging plan?
Creating a tagging plan might seem complex, but it follows a simple five-step framework. Let’s break down each step in detail.
Step 1: Define key objectives and KPIs.
Before diving into technical details, think about what you aim to achieve with your website and which key performance indicators (KPIs) you will use to measure its performance. Consider specific business goals: do you want to increase conversions, improve customer lifetime value, or improve overall customer retention?
For each goal, select relevant KPIs, such as:
- Conversion rate. Measure the percentage of users who complete desired actions, like purchases or sign-ups.
- Customer lifetime value (LTV). Monitor the projected revenue from a customer over their entire relationship with your business.
- Retention rate. Measure the percentage of customers who return over a given period, indicating long-term engagement.
Aligning KPIs with business goals creates a focused tracking approach and ensures that data collection directly supports decision-making.
Step 2: Identify the tools to be used.
Selecting the right tracking tools is crucial for effective data collection and analysis. Many platforms offer tracking features tailored to specific metrics, so evaluate which platforms best align with your objectives. Key tools may include:
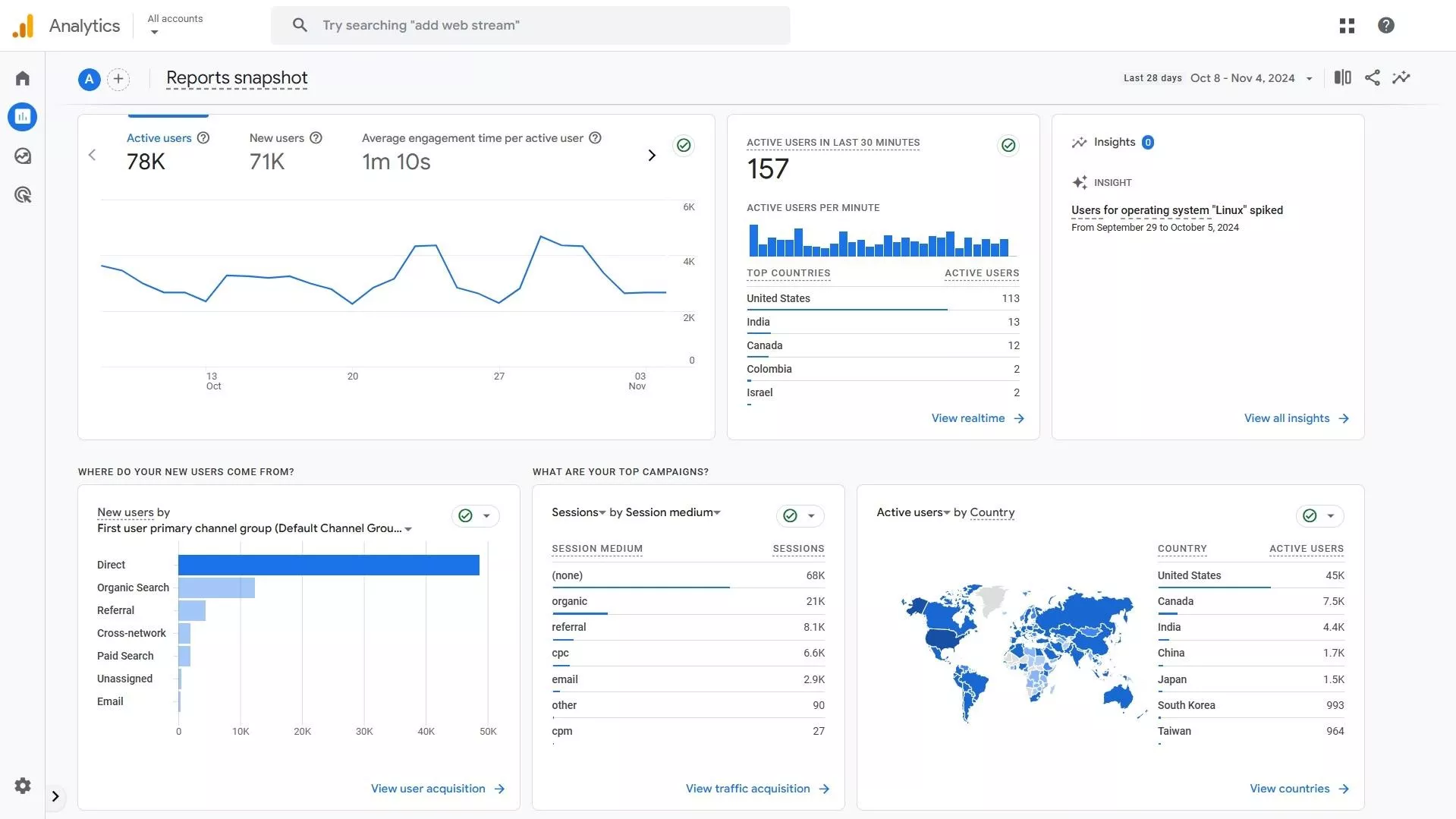
- Google Analytics 4. A robust solution for tracking user behavior, popular pages, and traffic patterns.
Google Analytics 4: Reports snapshot example
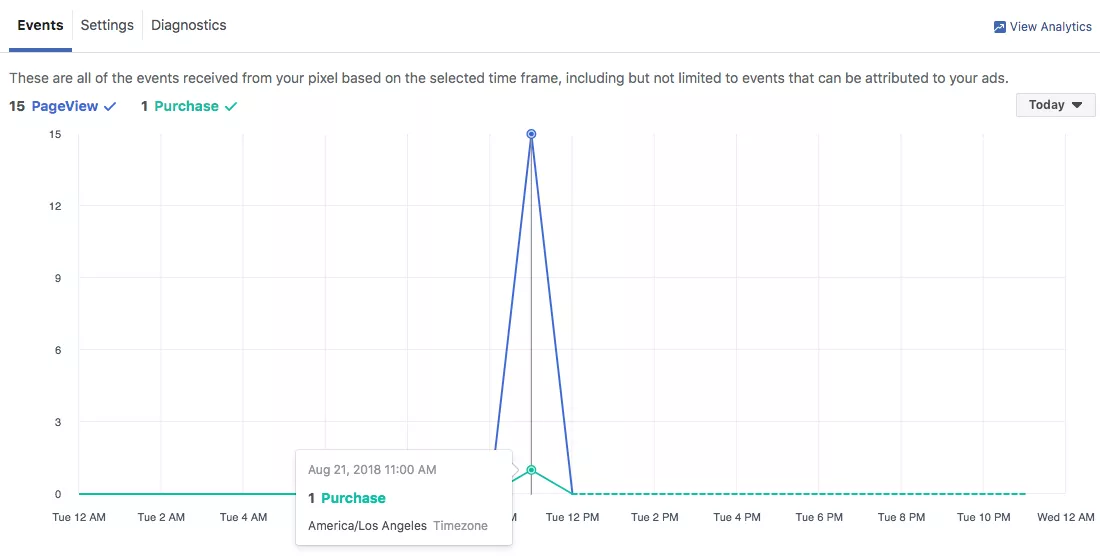
- Meta Pixel. Ideal for retargeting visitors on Facebook and Instagram by collecting data on user actions.
Meta Pixel: Events report example
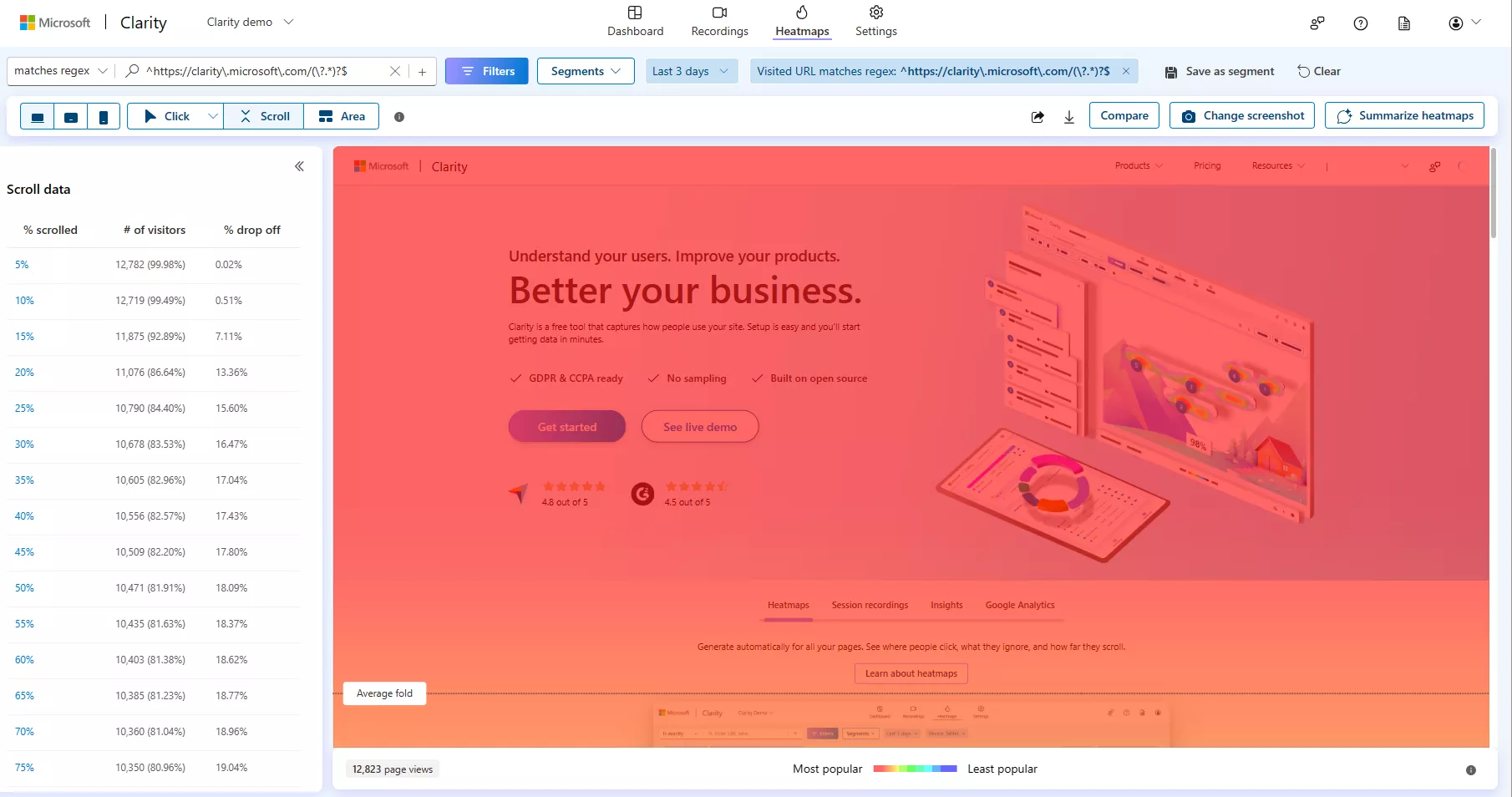
- Heatmap tools (e.g., Hotjar, MS Clarity). Visualize user interactions through heatmaps and session recordings.
Hotjar: Click map example
Clarity: Scroll map example
- Advertising platforms (e.g., Google Ads). Each ad network has unique tracking pixels that help optimize ad performance.
Google Ads: Ad group example
- Google Tag Manager (GTM). This platform simplifies tag management, allowing you to add and edit tags without changing the website code directly.
Google Tag Manager: Overview example
Using a combination of these tools provides a well-rounded view of user activity, from behavioral insights to conversion tracking.
Step 3: Build the tagging plan.
Now that you have goals, KPIs, and tools selected, the next step is to create a tagging plan document. This serves as a blueprint for tracking user interactions and should include the following components:
- Objective/KPI. Link each tag to a business objective and KPI.
- Tracking tool. Indicate which platform (e.g., Google Analytics directly, GTM) will handle the event.
- Event name and description. Assign a clear name and description to each tracked interaction. If you plan to use Google Analytics, ensure event names follow its naming conventions and avoid reserved prefixes or event names to prevent conflicts. Read about event naming rules in detail.
- Type of the page and URL. Specify the section and page where the event takes place.
- Tag details. Specify tag, trigger, and variable names to facilitate consistent management.
- Responsibility and status. Assign team members responsible for each tag and update the tag status (e.g., testing, active).
This structured approach not only improves tracking accuracy but also makes it easier to scale or adjust tags as business needs evolve.
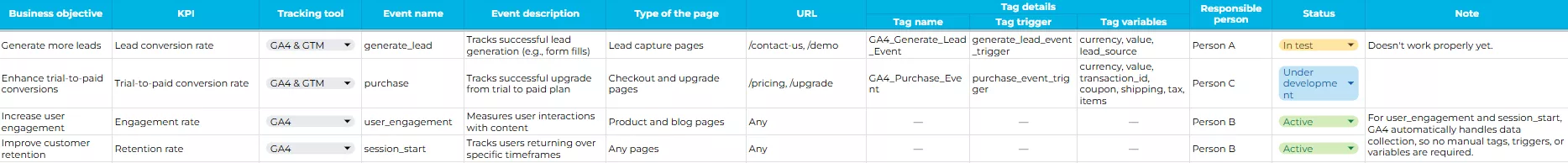
Example. In the screenshot below, you can see an example of a tagging plan that can be used by a SaaS company. It organizes essential information, including objectives, KPIs, tracking tools, event names, and tag configuration details.
Example of a Tagging Plan
This marketing measurement ready-to-use plan template is available for free and could serve as a helpful starting point. You can access it here. However, your tagging plan may differ based on your specific goals. You may want to include additional elements important to your website tagging strategy or exclude any irrelevant ones.
Step 4: Implement the tagging plan.
With your tagging plan in place, proceed to implement tags using a tag management tool like Google Tag Manager. GTM is especially beneficial as it centralizes all tags in a single interface, eliminating the need for direct code updates on the website. Follow these steps:
- Add tags. Create tags for each defined event in GTM.
- Set triggers. Assign the appropriate triggers that define when each tag fires (e.g., on a page load, button click).
- Test tags. Use GTM’s built-in preview mode to verify that tags fire correctly in real time. For more details, refer to the article on how to check if Google Tag Manager is working.
- Publish tags. After testing, publish the changes to activate the tags on your live site.
Tip: Use GTM’s version control features to document each update. This will help you maintain a clear record of changes and ensure consistency.
Note: When implementing tags through Google Tag Manager, it is essential to comply with GDPR, CCPA, and other regulatory policies by obtaining user consent for processing their personal data, particularly for the use of cookies. Tags that process personal data should only fire after the user has provided consent. Additionally, be sure to update your privacy policy in accordance with these regulations to ensure transparency in data collection and processing.
Step 5: Test and maintain the tagging plan.
After implementing the plan, regularly monitor and test the tags to maintain data accuracy. Frequent testing, especially after website updates, is essential as new features or changes might impact tag performance.
Here are some best practices for tag maintenance:
- Schedule regular audits. Review all tags periodically to ensure they still align with business goals.
- Test important tags. Use tools like Google Tag Assistant to verify that the tags fire as expected.
- Fix broken tags. Identify tags that are inactive or misfiring and fix them.
- Update tags as needed. Adjust tags to accommodate changes in business objectives or KPIs.
Consistent maintenance not only ensures reliable data but also allows different teams to adapt to changing needs effectively. A well-maintained tagging plan is a valuable long-term asset for your digital strategy.
Conclusion
A tagging plan is a strategic framework for systematically tracking and organizing data across digital platforms. It is essential for any organization that wants to harness the power of data-driven insights.
By providing clear objectives to work towards, aligning data analytics with business goals, and establishing standardized tracking methods, a tagging plan enhances both the accuracy and effectiveness of data collection. It provides both clarity and organization, making it easier for teams to collaborate, adapt to changes, and maintain data integrity across digital platforms.
To create an effective tagging plan, follow these streamlined steps:
- Set clear objectives and KPIs. Define what you want to track and measure.
- Choose the right tools. Identify the platforms and tools for tagging.
- Develop the tagging strategy. Design a structured, consistent tagging plan.
- Execute the implementation. Apply the tags across your website.
- Test and optimize. Regularly test and maintain the tags, and refine your tagging plan for optimal performance.
When implemented thoughtfully, a tagging plan transforms raw data into actionable insights that drive meaningful results. As digital landscapes grow increasingly complex, having this blueprint is crucial: it will enable your organization to track key metrics, optimize performance, and make informed, strategic decisions.
FAQ
Is a tagging plan mandatory?
While a tagging plan is not mandatory, it is highly recommended for any organization that relies on data for decision-making. Without a tagging plan, tracking efforts can become chaotic and inefficient, leading to inconsistencies in data collection and analysis. A tagging plan serves as a roadmap and ensures that all data is collected systematically and aligns with your business objectives.
Who can benefit from a tagging plan?
A tagging plan is beneficial for a variety of stakeholders, including marketers, web developers, data analysts, and project managers. It provides these teams with a clear understanding of the data that needs to be tracked and how to track it, facilitating collaboration and ensuring that everyone is on the same page. Ultimately, anyone involved in digital marketing or analytics can use a tagging plan to enhance their workflow and data quality.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when creating a tagging plan?
When creating a tagging plan, it’s important to avoid several common pitfalls:
- A lack of clear objectives. Failing to define specific business goals can lead to irrelevant or excessive tagging.
- Inconsistent naming conventions. Not standardizing tag, trigger, and variable names can create confusion and hinder data analysis.
- Overcomplicating the plan. Including too many tags or complex triggers can overwhelm users and complicate implementation.
- Not doing testing and maintenance. Skipping thorough testing or neglecting to perform regular updates can result in inaccurate data and lost insights.
- Not involving all stakeholders. Excluding key team members from the planning process can lead to misaligned objectives and incomplete tracking.
By being aware of these common mistakes and addressing them proactively, you can create a robust tagging plan that makes the most of your data collection efforts.
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses