While surfing the web, you’ve probably come across URLs that contain an unintelligible mix of letters and numbers. These are called dynamic URLs.
What is a dynamic URL? Are dynamic URLs a threat to SEO? Do search engines crawl and index them? Let’s dig deeper to find out.
Dynamic URL: what is it
A dynamic URL is a non-static web page address. The address and the content of a dynamic web page don’t exist in a permanent form in an HTML document on the server. They are displayed in response to a specific request.
A dynamic web page can contain a database or a script. When the database receives a request, the server’s programming language generates a dynamic URL with a specific set of filters and parameters.
This technology allows us to use filters on the web page and immediately see the page with the required content. For example, when users select search filters in an online store, they receive a page created for their query.
Dynamic URLs can look complicated with symbols like “?”, “&”, and “=”.
An example of a dynamic URL: https://example.com/microwaves?brand=lg&finishcolour=black&depthmmmin=400&depthmmmax=500.
Where are dynamic URLs used?
Dynamic URLs can be found on webpages with search filters and websites with a lot of information. Those include:
- Online stores. When applying filters or sorting products in an online store, you end up on a page with a dynamic URL showing you a selection of products you seek.
- E-media. You might want to choose a date or a topic in search of a specific piece of news on the Internet. This is when you get a page with a dynamic URL created for your preferences.
- Search engines. After typing your query in the search bar and pressing the search button, you get a page with relevant results. This page also has a dynamic URL.
- Bookings. Booking tickets or choosing appropriate accommodation in a certain country are usually based on your preferred criteria. So, this gets you to the page with a dynamic URL.
- User profiles on social nets. Visiting different social media profiles is accompanied by dynamic URLs that are created depending on each user ID.
- Ads and specific links. There might be separate dynamic URL pages with definite content for visitors who reach it by clicking on the specific link or ad.
Dynamic URL parameters
In dynamic URL https://www.example.com/drumsticks.php?size=5a&material=hickory&sort=price:
- The first part, http://www.example.com/drumsticks, is a static webpage URL.
- The second part, ?size=5a&material=hickory&sort=price, contains variables.
Dynamic URL parameters are typically presented in the form of “key=value” and contain a few separation symbols by which they could be easily identified. They include:
- question mark (?);
- equals sign (=);
- ampersand (&).
The variable parameters of a dynamic URL include material, price, size, color, length, width, and other dimensions, as well as language.
Examples of dynamic URLs
To illustrate the aforementioned, I will show you a few examples of dynamic URLs.
Example 1. Parameters are labeled with the words
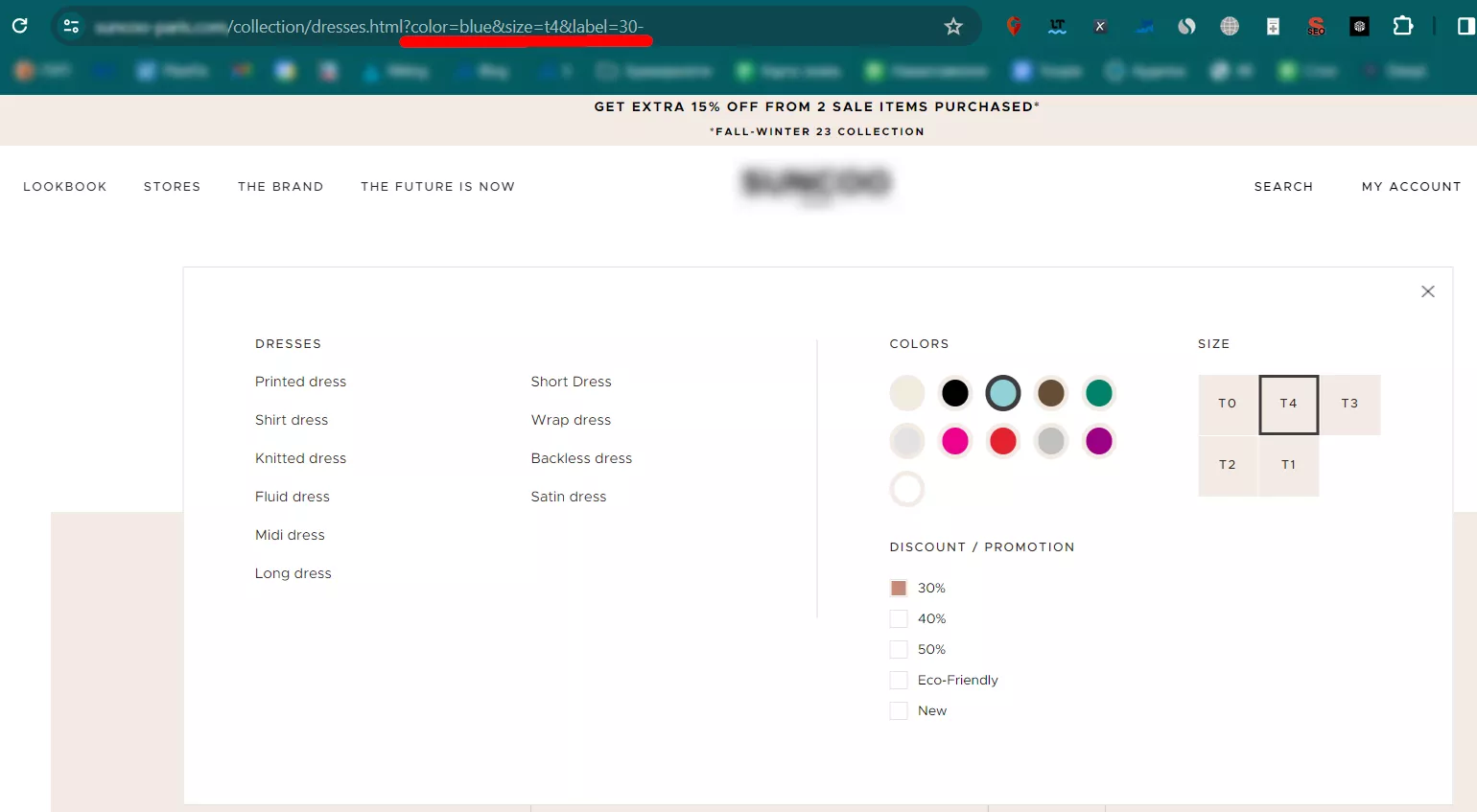
Imagine you are looking for a blue dress, size 14, and you go to the website where this dress is sold.
A dynamic URL from this site looks like this: https://storename.com/collection/dresses.html?color=blue&size=t4&label=30-
Right after the “?” you can see the parameters of this dynamic URL that refer to different filter values. In this case, three pairs of “key=value” are separated by “&.”
- color=blue – the first “key=value” corresponds to the chosen dress color
- size=t4 – describes the dress size
- label=30- – indicates the user is interested in the dress with a 30%-discount
This dynamic URL is easily understood. There are, however, those that are not so clear.
Example 2. Parameters are labeled with the numbers
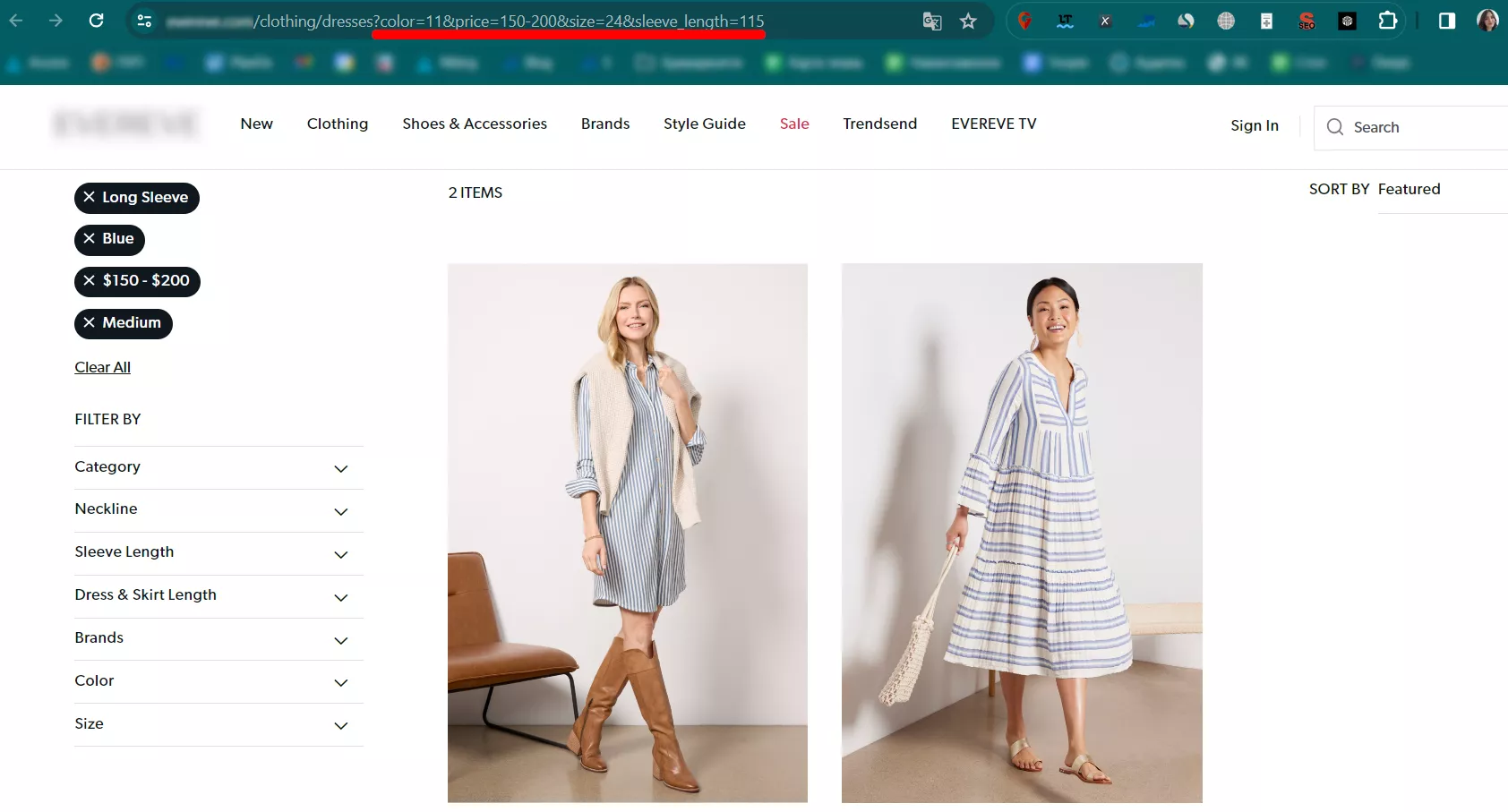
Imagine you’re searching for a blue dress with long sleeves in size M within the price range of $150-200 at an online clothing store.
This is how the page URL will look like: https://storename.com/clothing/dresses?color=11&price=150-200&size=24&sleeve_length=115
It consists of a few parameters:
- color=11 – apparently, the blue color refers to the number “11” in the database
- price=150-200 – describes the dress price
- size=24 – the M size corresponds to the number “24” in the database
- sleeve_length=115 – “long” is transformed into the value “115”
Example 3. Parameters that show the depth of the product
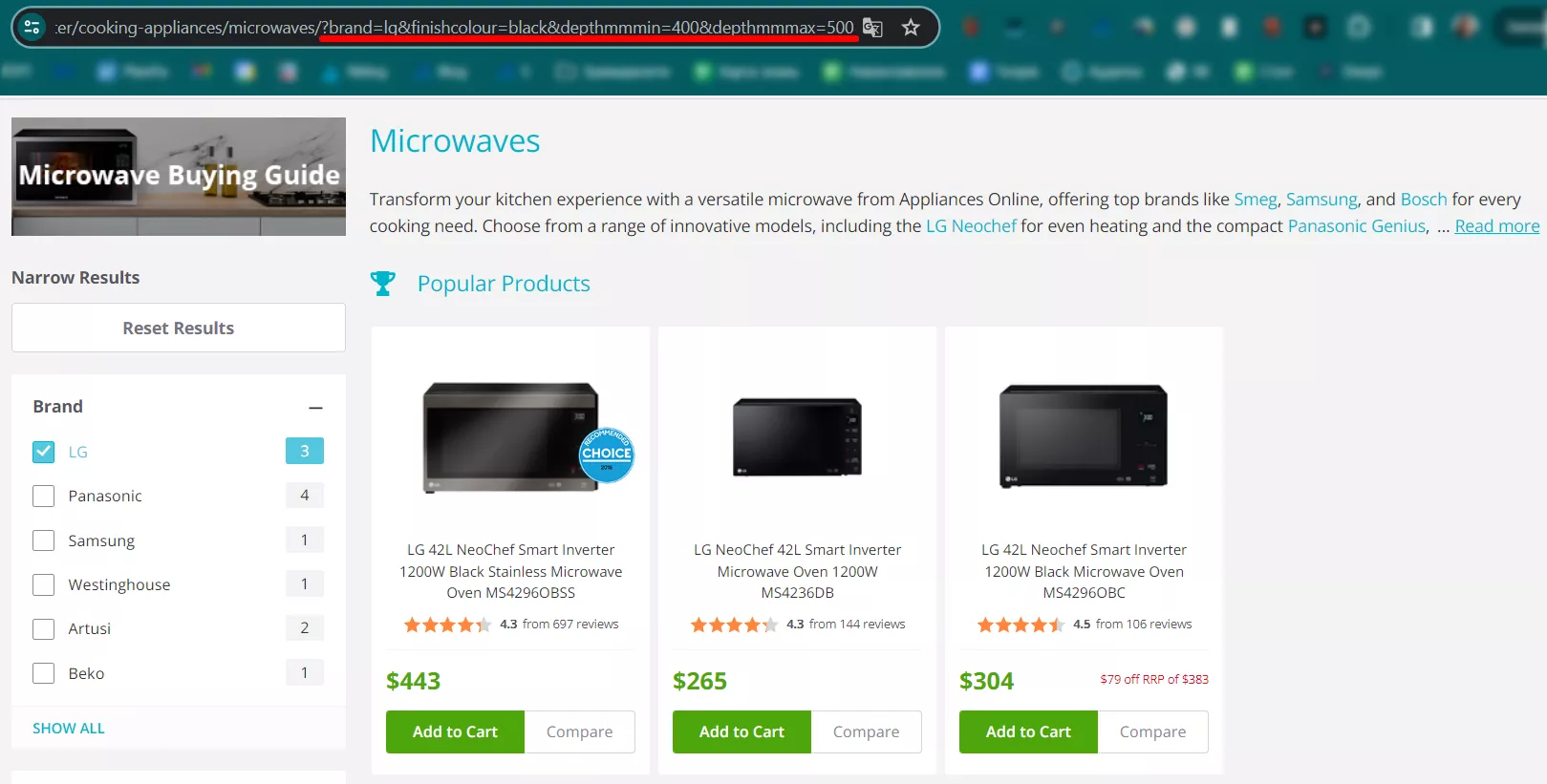
Let’s say you’d like to buy a black LG brand microwave with a depth between 400 and 500 mm. This query created a page with database content corresponding to your parameters.
This is how the page URL will look like: https://www.storename.com/filter/cooking-appliances/microwaves/?brand=lg&finishcolour=black&depthmmmin=400&depthmmmax=500
- brand=lg – the first “key=value” corresponds to the chosen brand
- finishcolour=black – describes the color of a microwave
- depthmmmin=400 – indicates that the user is interested in the microwave with a depth of 400 mm at the least
- depthmmmax=500 – indicates that the user is interested in the microwave with a depth of up to 500 mm
Example 4. Parameters that show the country and language
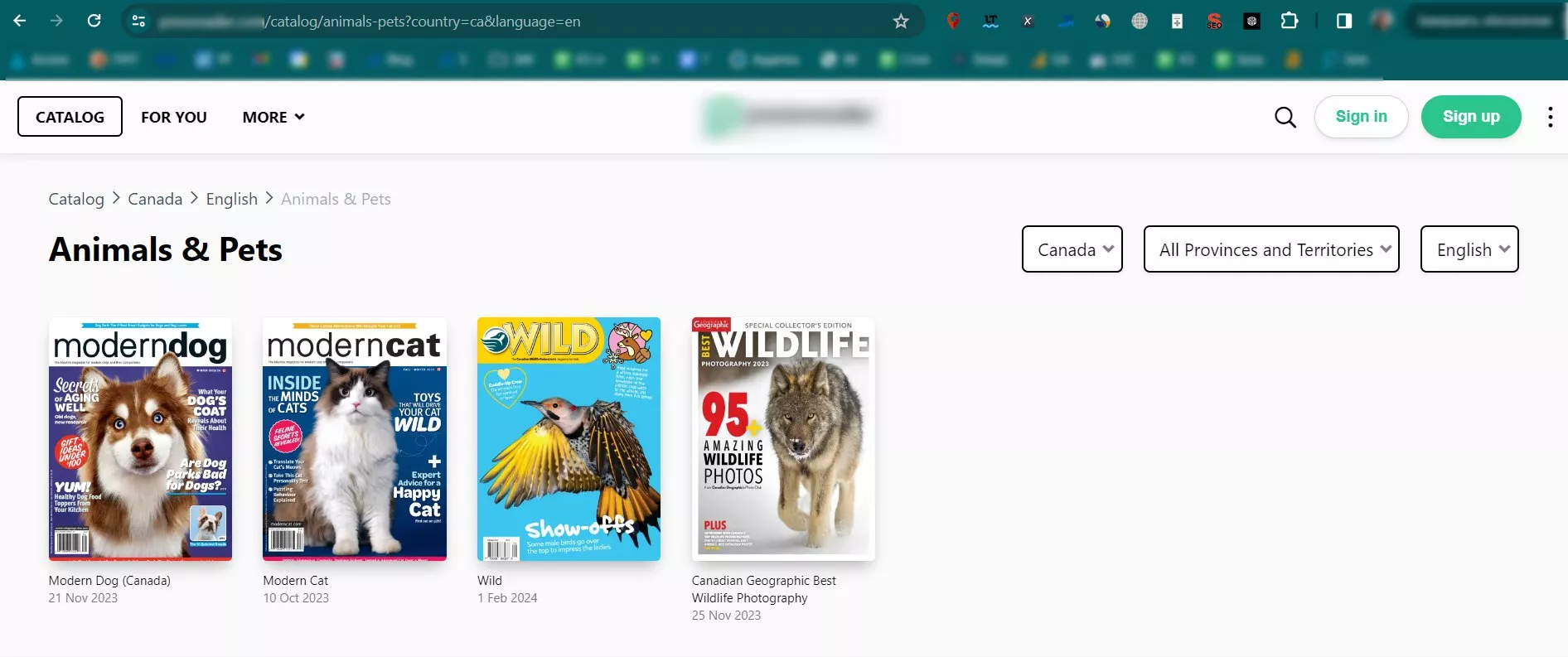
Here’s an example of an online magazine where you can choose the preferred country and language you’d like to read.
This is how the page URL will look like: https://www.storename.com/catalog/animals-pets?country=ca&language=en
- country=ca – indicates that the user wants to shop in Canada
- language=en – refers to the English language
Example 5. A dynamic URL of a paid social
An example illustrates a dynamic URL of a page, which you get when you follow an ad on Facebook, Instagram, etc.:
https://example.com/sip/justanswer-1?r=ppc|ga|13|US-Tech-Topic-Content-All-Devices||&JPKW=&JPDC=C&JPST=example.com&JPAD=661088317166&JPMT=&JPNW=d&JPAF=img&JPRC=1&JPCD=&JPOP=&cmpid=20242939104&agid=158436578388&fiid=&tgtid=&ntw=d&dvc=c&gclid=EAIaIQobChMImI2MmJqkhAMVVA2iAx1kNwRGEAEYASAAEgLEefD_BwE
In this case, the URL is much longer than in the previous examples. It has lots of incomprehensible parameters. What you can understand just by looking at them is that:
- This dynamic URL tells us about the website you followed the ad from (example.com)
- The ad can be followed on all devices (US-Tech-Topic-Content-All-Devices)
- Other sets of letters and numbers are mostly about the information about the user's ID and features of the ad itself
What are the pros of a dynamic URL?
Using dynamic URLs has proved to have a few significant advantages.
- Dynamic URLs facilitate the webpage-fixing process. There’s no need to open the HTML file while fixing something on the page. Instead, you can make the changes with the help of the website’s admin panel, which will be applied to all dynamic pages.
- Dynamic URLs allow you to work faster with multi-page websites with a large database. They come in handy when you need to update or fix content because you can do it without having to manually manage hundreds or thousands of dynamic pages.
- Users get absolutely personalized pages. When looking for products that meet their tastes, users can select each item’s preferred qualities, types, and other criteria. Besides, there’s usually an option to sort the results ascending or descending by price, etc.
- Users get up-to-date content on a dynamic page because it’s just been retrieved from the database according to their needs.
- Dynamic URLs prove efficient for temporary content such as discounts and promotions, user-specific content, etc. In this case, you don’t necessarily need search engines to index that type of web page.
The downsides of dynamic URLs
Dynamic URLs have some downsides you shouldn’t lose sight of.
- Dynamic URLs are long enough. Sometimes they are too long. This makes it difficult to remember and almost impossible to manually type that mix of characters.
- A dynamic URL is an unordered combination of symbols and characters instead of words. That means this type of URL doesn’t contain keywords that are a part of search engine optimization. Thus, a lack of relevant keywords can have a negative impact on Page Rank.
- Users cannot understand what the page is about just by looking at its dynamic URL, which doesn’t provide important descriptive information about the page’s content.
- Users don’t tend to trust dynamic URLs much, as they might look suspicious. This leads to a lower CTR (click-through rate) because users might think twice about clicking on such a link.
- There is a possibility of a 404 error when copying and pasting a dynamic URL. This is because the last part of the link may be cut off, making it impossible for users to go to the corresponding page.
- Dynamic URLs can cause duplicate content because you can get the same page via different links. For example, the page showing silk blue dresses on offer can be reached by two URLs: https://www.example.com/dresses.php?color=blue&material=silk and https://www.example.com/dresses.php?material=silk&color=blue.
Google can lower the site’s ranking for duplicate content if its algorithms think that repeated information on the site is placed with the intent to have some impact on search results.
- The crawl budget can be wasted on crawling different versions of the same content instead of spending it on the pages that present more value to SEO.
- Dynamic content generation is inconvenient, as search robots might have difficulties finding them, so there is a probability that the content will be considered uninteresting for search results.
The difference between dynamic and static URL
|
Static URL |
Dynamic URL |
|
Example: https://storename.com/lg-microwaves-black |
Example: https://storename.com/microwaves?brand=lg&finishcolour=black&depthmmmin=400&depthmmmax=500 |
|
They are shorter and easier to read and understand. |
They are longer and harder to read and understand. |
|
They often consist of relevant keywords, which makes them more SEO-friendly. |
They may include keywords but have a bunch of parameters. |
|
The URL of the page required is constant. |
The URL of the required page is generated while the request is processed. |
|
They tend to appeal more to users, increasing the click-through rate. |
They can deter users from clicking on them, which brings about a lower click-through rate. |
|
They are easier to copy, paste, and share. |
There might be some difficulties with sharing the dynamic link. |
|
Managing static pages (e.g., fixing, updating, etc.) requires lots of time, as the process is manual. |
They prove useful for websites with an advanced filtering system and a large catalog of products because managing dynamic pages saves time and effort. |
|
Implementing static URLs limits the diversity of pages that could be created based on the users’ preferences. |
Dynamic URLs make it possible to create personalized pages according to users’ needs. |
Can dynamic URLs be crawled and indexed by Google?
According to Google, search robots crawl and index dynamic URLs. Yet, keep in mind that static URLs have an advantage over dynamic URLs when it comes to crawling. Since dynamic URLs are created immediately after the user’s query, search engines might have issues determining the content on the page and evaluating its relevance.
Should I implement static or dynamic URLs on my website?
The best option is to follow an integrated approach, adding static and dynamic URLs. Static URLs work better for high-quality content, while dynamic URLs are more suitable for pages with numerous scripts to filter content, etc.
Key Takeaways
- Dynamic URLs are generated on the fly upon a certain user’s request.
- Dynamic URL use cases include online stores, e-media, search engines, bookings, and user profiles on social networks.
- Dynamic URL parameters are typically presented in the form of “key=value.” Dynamic URLs contain a few separation symbols by which they could be easily identified: a question mark (?), equals sign (=), and ampersand (&).
- The positive points about dynamic URLs are as follows:
- Facilitate the webpage-fixing process
- Enable to work with multipage websites faster
- Users get absolutely personalized pages
- The content retrieved from the database is up-to-date
- Better for temporary content
- The disadvantages of dynamic URLs are that they are:
- Long, difficult to remember, and almost impossible to type manually
- Don’t contain relevant keywords and are not SEO-friendly
- Hard to understand
- Difficult to share
- Can cause duplicate content
- Can lead to waste of the crawl budget
- Don’t always crawl well
- In general, search robots crawl and index dynamic URLs. Yet, sometimes, dynamic pages experience poor crawling, which negatively impacts their PageRank.
- The best option is to follow an integrated approach, which means adding static and dynamic ones.
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses