The 10 Most Common Technical SEO Myths & Misconceptions
In the fast-paced and ever-changing world of digital marketing, there are numerous myths and misconceptions surrounding search engine optimization (SEO), especially when it comes to technical SEO. Following unproven practices when promoting a website can lead to negative consequences, such as wasted resources, time, and effort and missed opportunities.
To avoid falling into this trap, it is necessary to learn how technical SEO myths arise, the most widespread misconceptions, and, most importantly, how to avoid them. All of this is covered in-depth in the article. So stay tuned!
How Do SEO Myths Arise?
Let’s start by taking a quick look at how SEO myths and misconceptions emerge:
- Misinterpretation of guidelines. Search engines like Google provide guidelines and best practices for SEO, but these can sometimes be misunderstood or taken out of context, leading to the spread of myths.
- Outdated information. The SEO industry is extremely dynamic, which means that what worked a few years ago or even a few months ago may no longer work as effectively. Unfortunately, many sources on the web do not update the information on their pages in a timely manner. And some of them only change the date of publication/update of the article to a more recent one to attract more visitors, which greatly contributes to the spread of outdated information.
- Correlation vs. causation. Some SEO specialists might observe a correlation between certain factors and good or improved search rankings but mistakenly assume a causal relationship, thus creating a myth. If this specialist is also a well-known and reputable one, such a myth can spread very quickly. In reality, causation in SEO is a rare occurrence due to the huge number of different parameters and variables.
- Lack of understanding. The complex and ever-changing algorithms of search engines are difficult to fully understand, especially given the fact that certain aspects are carefully kept secret. The lack of understanding of certain concepts, mechanisms, and processes can lead to the creation of myths to fill the knowledge gaps.
- Oversimplification. Trying to explain complex SEO concepts in an accessible way can sometimes lead to a failure to convey the information in full. In turn, this can distort the information and contribute to the spread of myths.
- Clickbait. Some content creators deliberately spread SEO myths to attract an audience to their websites, as sensational or controversial information tends to spread far more strongly and quickly. Unfortunately, there are many such websites these days, and it is important to be aware of this.
Myth 1. Technical SEO Is a One-time Thing
One common misconception is that it is enough to do technical SEO at the stage of website development, or if technical SEO is for an existing website, it is enough to do it only once. How nice would that be, right?
Technical SEO is an ongoing process.
At least it should be to ensure its maximum effectiveness and return. This is because search engines are constantly improving their algorithms in an effort to give their users the best search results possible so that they come back again.
A prime example of this is INP (Interaction to Next Paint), a new Core Web Vitals metric that replaced FID (First Input Delay) in March 2024. This metric allows for a better and more comprehensive measurement of page responsiveness, reflecting how users actually experience a page.
Those who have already optimized their website around the new metric, especially if they had started preparing in advance, have improved their SEO performance and gained a significant advantage. This is confirmed by the case study of the e-commerce platform Trendyol, which reduced its INP by 50% and improved CTR by 1%.
Another reason SEO is not a one-time event is that technical issues can arise after new changes are implemented on the website. For example, adding new website features, improving existing ones, redesigning the user interface, switching to a new CMS, updating third-party integrations, etc.
When making changes to a website, certain problems may occur that can hinder SEO efforts.
Even if you have an exceptionally experienced and skillful developer, technical problems may still arise due to the specifics of the CMS, third-party resources used, and numerous other factors. This is especially true for large websites: it is more challenging to properly maintain them and much easier to make a severe mistake.
This is where having an SEO specialist or, ideally, a dedicated team involved throughout the process becomes invaluable. By collaborating closely with developers, they can provide guidance on how to implement changes with SEO best practices in mind. Then, once the work is complete, they can check if everything was implemented correctly and if any new issues were inadvertently introduced.
Dive into our glossary for key SEO definitions to boost your expertise!
Myth 2. Technical SEO Is Only for Search Engines
Here is another common SEO myth that needs to be debunked: technical SEO is only needed for search engines to rank website pages better and for nothing else. This is untrue. Although tech SEO does affect rankings, it is also important for both users and the business itself.
Technical SEO has a positive effect on user experience – the faster the site loads initially, the less likely the user wants to leave it right away. Not only that, sites that are responsive to interaction and visually stable are likely to load subsequent pages more quickly. All of these will encourage the user to:
- stay on such a website
- perform a certain targeted action
- return to it in the future
- recommend it to friends or their audience (an opportunity to earn a backlink).
Myth 3. Robots.txt Can Block Indexing of a Web Page
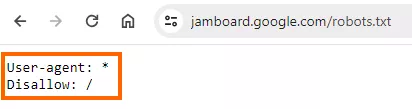
In fact, this file is used only to control the crawling of the website, namely to indicate to the crawler which pages it has access to and which pages it is prohibited from accessing. This applies only to “obedient” crawlers such as Googlebot, since some malicious crawlers may not follow the directives placed in the file.
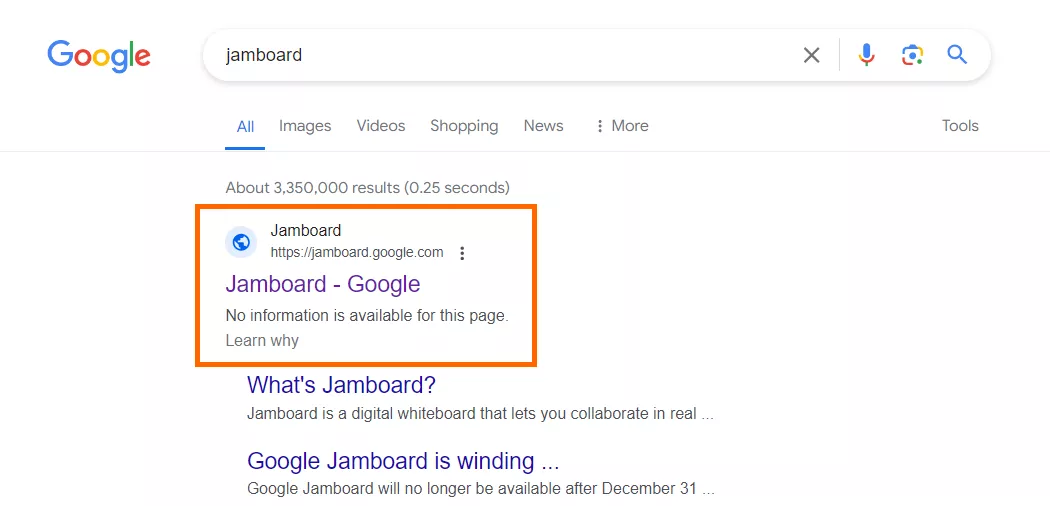
If you decide to disallow a page from being indexed using the robots.txt file, you might still find it in search results. Yes, a search engine crawler will not be able to crawl such a page as it has been disallowed, but a search engine may still add it to its index if it is linked to by some other webpage.
This often happens when the search engine believes that the page was blocked in robots.txt by mistake. To understand its content and display it in search results, a search engine will use the link’s anchor text. See the screenshot below for an example:
The following screenshot shows that the website is indeed blocked from crawling:
Google is explicitly clear about this and mentions in its documentation that the robots.txt file is not a mechanism for keeping a web page out of Google.
In order to truly block a webpage from being indexed, it is necessary to either implement password access to it or add the noindex meta tag to its <head> block, for example, as follows:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">Myth 4. Pagination Attributes rel="next" & rel="prev" Are Ranking Signals
Pagination attributes rel="next" and rel="prev" are HTML tags that are used to help Google understand the relationship between paginated pages of a website. Some people believe that this is still the case, but in fact, since 2019, these attributes have ceased to be indexing signals:
Spring cleaning!
– Google Search Central (@googlesearchc) March 21, 2019
As we evaluated our indexing signals, we decided to retire rel=prev/next.
Studies show that users love single-page content, aim for that when possible, but multi-part is also fine for Google Search. Know and do what's best for your users! #springiscoming pic.twitter.com/hCODPoKgKp
If your website has the rel="next" and rel="prev" attributes implemented, there is no need to remove them – they do not cause any harm and can still be used by the Bing search engine. However, if you are not purposefully promoting your site for Bing or other search engines that still use these pagination attributes, adding them is a waste of time and effort.
Myth 5. HTML Lang Attribute Helps with Website Localization
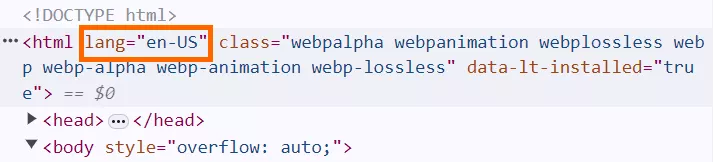
The HTML lang attribute is one of the attributes of the <html> tag that allows you to specify the language of the page. Most webpages on the Internet have it, including the ones on this website:
Note that “US” in this case is not the target country of the page but a language dialect. It means that the text of the page is written in US English (as opposed to British or Australian English).
The technical SEO misconception associated with this attribute is that it is supposedly necessary for website localization and contributes to a better ranking of localized pages. However, the truth is that Google simply ignores this attribute because it has found that the language specified in it is often incorrect and also because it has its own algorithms for determining a page’s language.
This was confirmed by John Mueller, a Search Advocate at Google, in a video response.
Therefore, if someone tells you that using the lang attribute alone is sufficient or somehow helps to optimize localized versions of web pages, they are wrong. For this purpose, it is necessary to use either the hreflang HTML attribute/HTTP header, or the xhtml:link XML Sitemap attribute.
However, you do not have to remove this attribute, since it is still useful, e.g., for browsers, translation, or accessibility tools such as screen readers.
Myth 6. Outbound Links are Bad for SEO
According to the concept of link equity or “link juice” as it is colloquially called, inbound links give us value from an external resource and outbound links transfer out this value. Therefore, it may seem best to have as many inbound links as possible and no outbound links at all. However, this is not always the case.
Indeed, adding too many links, especially links to not topically relevant resources, may appear weird to the search engine and may even cause some harm. However, adding a reasonable number of links when they are appropriate and useful for a user can, on the contrary, contribute to strengthening E-E-A-T and, as a result, help the site gain better rankings, especially in YMYL niches.
YMYL niches refer to types of content that can significantly impact a person’s financial stability, health, safety, or overall well-being. Google holds websites in these niches to higher content quality, accuracy, and trustworthiness standards.
This was confirmed in the following statement made by John Mueller in the first episode of “Ask Google Webmasters”:
Linking to other websites is a great way to provide value to your users. Often, links help users to find out more, to check out your sources and to better understand how your content is relevant to the questions that they have.
Tip: To further enhance the effect, link to topically related, authoritative resources that are truly interesting and useful to users. Focus on adding value, not just inserting a link to some reputable website for the sake of it.
For example, if you are promoting a page of a cooking recipe, instead of linking to Wikipedia, link to a related article by Gordon Ramsay. In most cases, this will be more interesting to your visitors and send a clearer signal to a search engine.
Additional tips include using the appropriate rel attributes for links (rel="nofollow" or rel="ugc") to prevent the transfer of link equity to external resources. Use the target="_blank" attribute to open external links in a new tab and the rel="noopener noreferrer" to avoid security issues otherwise associated with this approach.
Myth 7. HTTPS Is Not Important
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), which is basically HTTP with TLS (Transport Layer Security) extension, is a way to ensure encrypted and secure communication between a user and a website.
One of the biggest technical SEO mistakes is to assume that HTTPS is not important nowadays. In reality, implementing this protocol is essential for several key reasons.
- HTTPS is a ranking signal. In August 2014, HTTPS was announced as a ranking signal in a post on the Google Search Central Blog:
… over the past few months we’ve been running tests taking into account whether sites use secure, encrypted connections as a signal in our search ranking algorithms. We’ve seen positive results, so we’re starting to use HTTPS as a ranking signal.
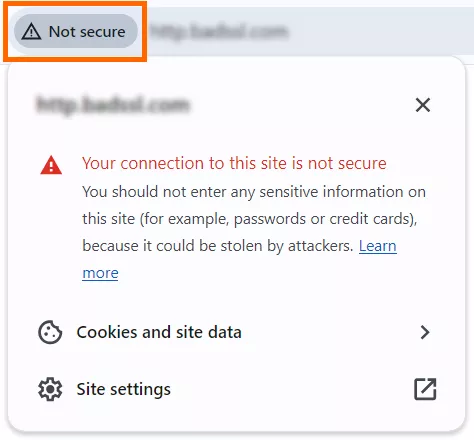
- It increases trust from users. HTTPS provides secure data transmission for website visitors and is now an established standard. The majority of Internet users are already aware of this, thanks to the following message:
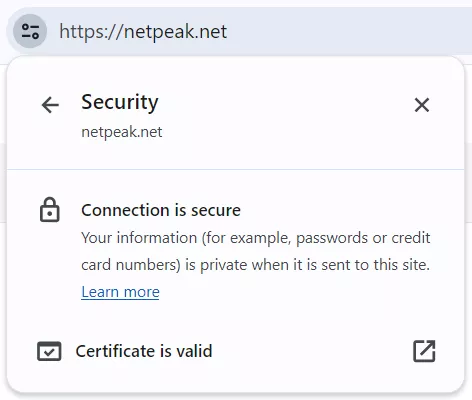
Accordingly, if HTTPS is properly implemented on a website, there will be no such message:
Users may be wary of sites that still use the HTTP protocol and often leave them even before a website loads.
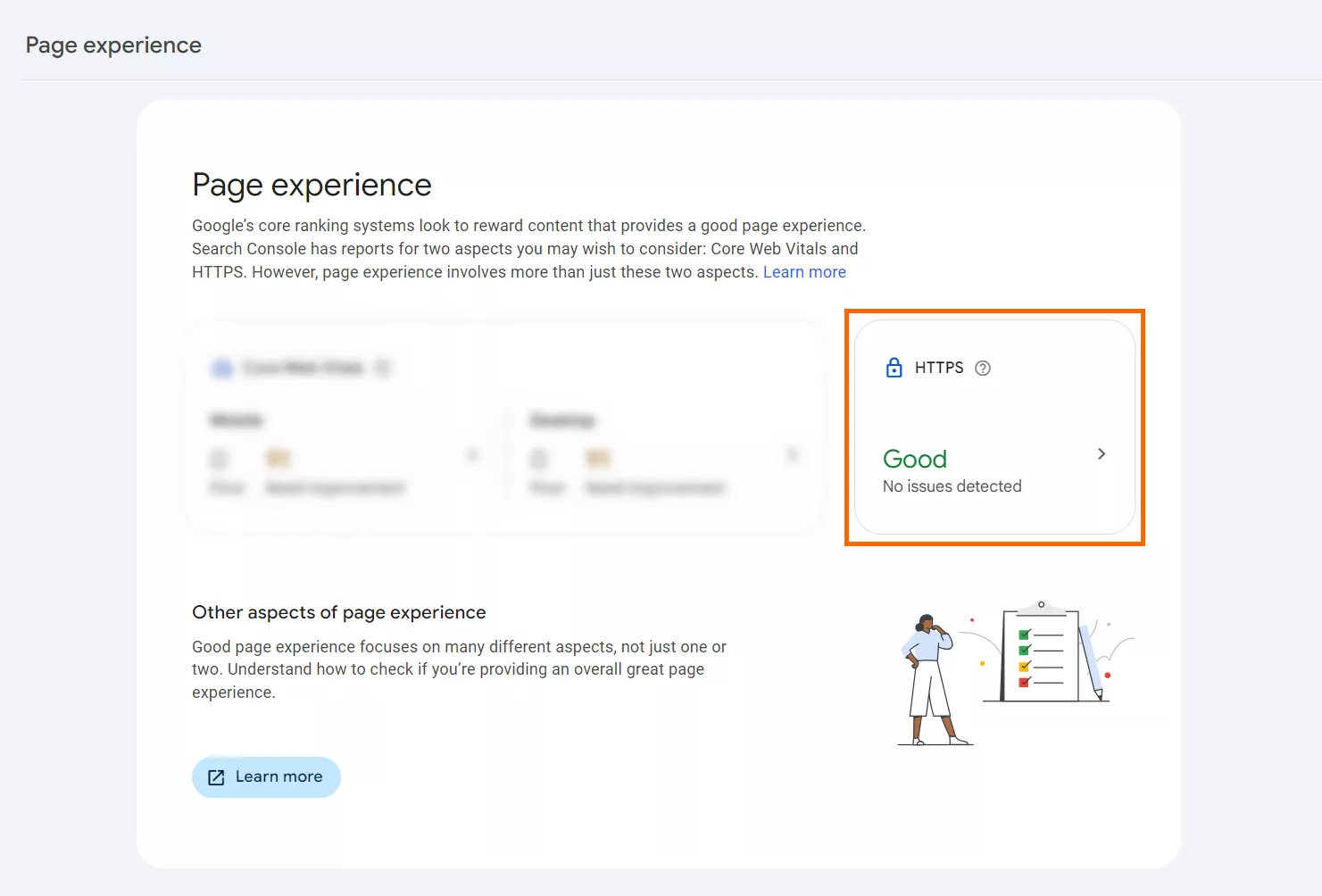
- The presence of HTTPS implementation is one of the criteria for Google when assessing Page Experience and the corresponding report in the Search Console:
More details about this assessment and the report can be found in Google’s documentation.
Myth 8. Page Speed Does Not Affect Ranking
Optimizing page loading performance is not an easy task, as it requires technical knowledge, effort, and time. However, it is definitely worth it. There are several reasons for this:
- Page speed has been a ranking factor for desktop devices for almost a decade and a half. This was confirmed in the following statement from Google in April 2010:
Like us, our users place a lot of value in speed – that’s why we’ve decided to take site speed into account in our search rankings.
- For a while now, since July 2018, page speed on mobile devices has also become one of the ranking factors in Googles’ search algorithm. This can be confirmed by the following quote from the respective post on the Google Search Central Blog:
People want to be able to find answers to their questions as fast as possible – studies show that people really care about the speed of a page. Although speed has been used in ranking for some time, that signal was focused on desktop searches. Today we’re announcing that starting in July 2018, page speed will be a ranking factor for mobile searches.
- Optimizing your website’s loading speed not only helps you rank better in SERPs but also improves business metrics, including conversion rate. An example of this is the crowd-sourced review platform Yelp, which increased conversions by 15% by optimizing FCP from 3.25 seconds to 1.8 seconds.
Myth 9. Mobile Friendliness Isn’t Important
This couldn’t be further from the truth, especially in today’s digital landscape where the number of mobile searches is growing rapidly. In fact, having a mobile-friendly website is absolutely essential for any business or organization that wants to reach its audience effectively. Let’s take a look at why mobile friendliness matters so much.
- People are increasingly reliant on their mobile devices to solve certain tasks, search for necessary information, and make purchases. At the same time, mobile users expect the websites they use to do these things to be fast, responsive, and easy to navigate. Websites that perform well on mobile devices can significantly enhance user satisfaction and reduce bounce rates. Features such as large, tappable buttons, text that is readable without zooming, and streamlined content help a lot with this.
- Besides providing a good experience for users, mobile friendliness is a ranking factor in Google’s search algorithms. The following excerpt from a Google Search Central blog post confirms this:
Starting April 21, we will expand our use of mobile-friendliness as a ranking signal. This change will affect mobile searches in all languages worldwide and will have a significant impact in our search results. Consequently, users will find it easier to get relevant, high quality search results that are optimized for their devices.
So, websites that are not optimized for mobile devices are lowered in mobile search results.
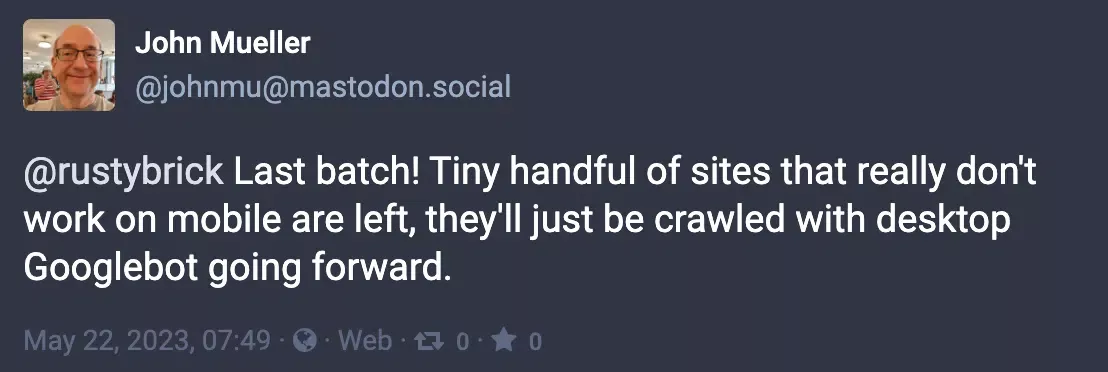
- Even if your website has an insignificant number of mobile users, this is not a reason to neglect mobile friendliness, since your website pages are crawled and indexed based on their mobile versions. The mobile-first indexing approach was announced in November 2016 and began to be tested on some websites. Two years later, in March 2018, a larger-scale rollout of this approach was launched. In May 2023, all sites (except for those that do not work on mobile devices) were switched to mobile-first indexing:
Myth 10. XML Sitemaps Are Only Useful for Large Websites
An XML sitemap is a file containing a list of links to pages that we consider important and would like to be crawled by search engines in the first place. These are definitely not limited to only large websites. XML sitemaps can be useful for medium and small websites as well, and here’s how:
- XML sitemaps help search engines find and index all pages on a website, ensuring that no pages are missed, even on smaller sites. This is especially true for websites that do not have proper internal linking implemented. An XML sitemap can also be helpful for a website that does not have many external links pointing to it.
- XML sitemaps can be used to inform search engines about newly added or updated pages, allowing for faster crawling and indexing. For this purpose, it is necessary to use the lastmod attribute. The ability to notify a search engine about the appearance of a new page on a website can be especially useful for news sites. There is a separate type of sitemap for them called a news sitemap.
- Creating and submitting an XML sitemap is a relatively simple process, even for smaller websites or those with limited technical resources. There are CMS plugins and technical SEO tools that can automatically generate sitemaps. For example, Netpeak Spider has a built-in tool for this called Sitemap Generator. It also provides a feature for validating an already existing XML Sitemap.
How to Avoid SEO Myths and Misconceptions?
Search engine algorithms are constantly evolving, and practices that may have worked in the past may become outdated and sometimes even harmful. Therefore, it is extremely important to stay up to date with the latest algorithm changes and SEO best practices. Stick to reputable sources, such as the following ones:
These resources are constantly updated with the most up-to-date information and best practices from technical SEO experts. In fact, they are excellent sources of knowledge for anyone interested in SEO, even beginners.
When using other resources, be sure to double-check facts that seem even slightly questionable or controversial. This is especially important if you are going to put acquired knowledge into practice. Check whether this information matches what is presented in other technical SEO articles. Additionally, verify the recency of information, as articles even from a year or two ago may contain outdated and irrelevant content.
Conclusion
- Technical SEO is an important pillar of a successful online presence. Accordingly, understanding and therefore avoiding common myths and misconceptions is crucial to effective SEO optimization.
- SEO myths can arise for a wide variety of reasons, including outdated information, misinterpretation of search engine guidelines, and oversimplification of complex concepts.
- Since search engines are constantly updating their algorithms and best practices, it’s important to stay informed and rely only on reputable resources. This will help you separate facts from fiction and avoid common misconceptions.
For those who want to build a solid foundation from the start, it’s worth exploring SEO at the website development stage — a proactive approach that helps avoid many mistakes before they happen.
FAQ
Is technical SEO worth it?
Yes, technical SEO is absolutely worth the investment. Not only does it improve a website’s visibility in search engines, but it also improves the overall user experience, which can lead to more traffic, better engagement, and potentially higher conversion rates.
How long does technical SEO take?
The time required for technical optimization can vary depending on the website’s size and complexity, as well as the number of technical SEO issues that need to be addressed. Some technical SEO changes can be implemented relatively quickly, while others may require more substantial effort. Overall, it tends to be an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and adjustments.
How much does technical SEO cost?
The cost of technical SEO can vary greatly depending on factors such as the size of a website, the amount of work required, the CMS used, and whether you engage an agency, freelancer, or handle it in-house. Some CMS, especially custom ones, have certain features and limitations that can hinder SEO; these require additional effort and time to fix.
Related Articles
Display Advertising Effectiveness Analysis: A Comprehensive Approach to Measuring Its Impact
In this article, I will explain why you shouldn’t underestimate display advertising and how to analyze its impact using Google Analytics 4
Generative Engine Optimization: What Businesses Get From Ranking in SearchGPT
Companies that master SearchGPT SEO and generative engine optimization will capture high-intent traffic from users seeking direct, authoritative answers
From Generic to Iconic: 100 Statistics on Amazon Marketing for Fashion Brands
While traditional fashion retailers were still figuring out e-commerce, one company quietly revolutionized how U.S. consumers shop for everything from workout gear to wedding dresses